Abstract
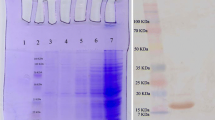
Expression of carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX) significantly increases under hypoxic conditions in tumor cells. CAIX activity is executed by the catalytic domain (CA) located on the extracellular part of the enzyme. Neutralization of CAIX enzymatic activity reduces malignancy and survival of tumor cells. To inhibit the enzymatic activity, a VHH nanobody was developed against the CA domain of CAIX using phage display technology. Following immunization of a camel with the recombinant CAIX, VHH fragments were isolated by nested PCR on lymphocyte cDNA. Binding affinity of isolated nanobodies was tested by ELISA. A clone (K24) with the highest binding affinity was expressed in a soluble form. Affinity of K24 nanobody was determined to be approx. 2.3 × 10−5. K24 nanobody recognized the expressed CAIX in the HeLa cell lines with high selectivity and specificity. These findings thus have usefulness for the diagnosis and treatment of cancers.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlskog J, Schliemann C, Marlind J, Qureshi U, Ammar A, Pedley R, Neri D (2009) Human monoclonal antibodies targeting carbonic anhydrase IX for the molecular imaging of hypoxic regions in solid tumours. Brit J Cancer 101:645–657
Atkins M, mcdermott D, Regan M, Stanbridge E, Upton M, Youmans A, Febbo P, Lechpammer M, Signoretti S (2004) Carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX) expression predicts for renal cell cancer (RCC) patient response and survival to IL-2 therapy. In: Proceeding American Society of Clinical Oncology, vol 14S. p 4512
Brekke O, Loset G (2003) New technologies in therapeutic antibody development. Curr Opin Pharmacol 3:544–550
Brennan DJ, Jirstrom K, Kronblad A, Millikan RC, Landberg G, Duffy MJ, Ryden L, Gallagher WM, O’Brien SL (2006) CA IX is an independent prognostic marker in premenopausal breast cancer patients with one to three positive lymph nodes and a putative marker of radiation resistance. Clin Cancer Res 12:6421–6431
Dubois L, Douma K, Supuran CT, Chiu RK, van Zandvoort MA, Pastoreková S, Scozzafava A, Wouters BG, Lambin P (2007) Imaging the hypoxia surrogate marker CA IX requires expression and catalytic activity for binding fluorescent sulfonamide inhibitors. Radiother Oncol 83:367–373
Dubois L, Lieuwes NG, Maresca A, Thiry A, Supuran CT, Scozzafava A, Wouters BG, Lambin P (2009) Imaging of CA IX with fluorescent labelled sulfonamides distinguishes hypoxic and (re)-oxygenated cells in a xenograft tumour model. Radiother Oncol 92:423–428
Ebrahimizadeh W, Mousavi Gargari S, Rajabibazl M, Safaee Ardekani L, Zare H, Bakherad H (2013) Isolation and characterization of protective anti-LPS nanobody against V. Cholerae O1 recognizing Inaba and Ogawa serotypes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:4457–4466
Fu Y, Lee AS (2006) Glucose regulated proteins in cancer progression, drug resistance and immunotherapy. Cancer Biol Ther 5:741–744
Gieling RG, Williams KJ (2012) Carbonic anhydrase IX as a target for metastatic disease. Bioorg Med Chem 21:1470
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Simopoulos K, Pastorek J, Wykoff CC, Gatter KC, Harris AL (2001) Hypoxia-regulated carbonic anhydrase-9 (CA9) relates to poor vascularization and resistance of squamous cell head and neck cancer to chemoradiotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 7:3399–3403
Nishimori I, Onishi S (2001) Carbonic anhydrase isozymes in the human pancreas. Dig Liver Dis 33:68–74
Shvarts O, Janzen N, Lam JS, Leppert JT, Caliliw R, Figlin RA, Belldegrun AS, Zeng G (2006) RENCA/carbonic anhydrase-IX: a murine model of a carbonic anhydrase-IX-expressing renal cell carcinoma. Urology 68:1132–1138
Svastova E, Hulíkova A, Rafajova M, Zatovicova M, Gibadulinova A, Casini A, Cecchi A, Scozzafava A, Supuran CT, Pastorek J (2004) Hypoxia activates the capacity of tumor-associated carbonic anhydrase IX to acidify extracellular pH. FEBS Lett 577:439–445
Trail PA (2013) Antibody directed delivery for treatment of cancer: antibody drug conjugates and immunotoxins. In: Antibody-drug conjugates and immunotoxins. Springer, New York, pp 3–22
Zatovicova M, Jelenska L, Hulikova A, Csaderova L, Ditte Z, Ditte P, Goliasova T, Pastorek J, Pastorekova S (2010) Carbonic anhydrase IX as an anticancer therapy target: preclinical evaluation of internalizing monoclonal antibody directed to catalytic domain. Curr Pharm Des 16:3255–3263
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Shahed University and Biotechnology Development Council of I. R. Iran for their financial support. We also extend our sincere thanks to Prof. Heather MA Cavanagh of Charles Sturt University, Australia for her kind assistance in English editing and polishing of the final version of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Araste, F., Ebrahimizadeh, W., Rasooli, I. et al. A novel VHH nanobody against the active site (the CA domain) of tumor-associated, carbonic anhydrase isoform IX and its usefulness for cancer diagnosis. Biotechnol Lett 36, 21–28 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1340-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1340-1