Abstract
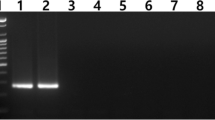
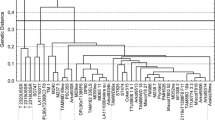
Chloroplast molecular markers can provide useful information for high-resolution analysis of inter- and intra-specific variation in Brassicaceae and for differentiation between its species. Combining data generated from nuclear and chloroplast markers enables the study of seed and pollen movement, and assists in the assessment of gene-flow from genetically modified (GM) plants through hybridization studies. To develop chloroplast DNA markers for monitoring of transgene introgression in Brassica napus L., we searched for sequence variations in the chloroplast (cp) genome, and developed a simple cpDNA marker that is reliable, time-saving, and easily discriminates among 4 species (B. napus, B. rapa, Raphanus sativus, and Sinapis alba) based on PCR-product length polymorphism. This marker will be useful to identify maternal lineages and to estimate transgene movement of GM canola.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allender CJ, King GJ (2010) Origins of the amphiploid species Brassica napus L. investigated by chloroplast and nuclear molecular markers. BMC Plant Biol 10:54–62
Aono M, Wakiyama S, Nagatsu M, Nakajima N, Tamaoki M et al (2006) Detection of feral transgenic oilseed rape with multiple-herbicide resistance in Japan. Environ Biosafety Res 5:77–87
Beckie HJ, Warwick SI, Nair H, Seguin-Swartz G (2003) Gene flow in commercial fields of herbicide-resistant canola (Brassica napus). Ecol Appl 13:1276–1294
Chen X, Li M, Shi J, Fu D, Qian W, Zou J, Zhang C, Meng J (2008) Gene expression profiles associated with intersubgenomic heterosis in Brassica napus. Theor Appl Genet 117:1031–1040
Crawley MJ, Brown SL (1995) Seed limitation and the dynamics of feral oilseed rape on the M25 motorway. Proc R Soc B 256:49–54
Dass H, Nybom H (1967) The relationships between Brassica nigra, B. campestris, B. oleracea, and their amphidiploids hybrids studied by means of numerical chemotaxonomy. Can J Genet Cytol 9:880–890
Flannery ML, Mitchell FJG, Coyne S, Kavanagh TA, Burke JI, Salamin N, Dowding P, Hodkinson TR (2006) Plastid genome characterisation in Brassica and Brassicaseae using a new set of nine SSRs. Theor Appl Genet 113:1221–1231
Hasterok R, Wolny E, Hosiawa M, Kowalczyk M, Kulak-Ksiazczyk S, Ksiazczyk T, Heneen WK, Maluszynska J (2006) Comparative analysis of rDNA distribution in chromosomes of various species of Brassicaceae. Ann Bot 97:205–216
Hu ZY, Hua W, Huang SM, Wang HZ (2011) Complete chloroplast genome sequence of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) and its evolutionary implications. Genet Resour Crop Evol 58:875–887
James C (2011) Global status of commercialized biotech/GM crops. ISAAA brief no 43. ISAAA, Ithaca
Jorgensen RB, Andersen B, Landbo L, Mikkelsen TR (1996) Spontaneous hybridization between oilseed rape (Brassica napus) and weedy relatives. Acta Hortic 407:193–200
Knispel AL, McLachlan SM (2010) Landscape-scale distribution and persistence of genetically modified oilseed rape (Brassica napus) in Manitoba, Canada. Environ Sci Pollut Res 17:13–25
Knispel AL, McLachlan SM, Van Acker RC, Friesen LF (2008) Gene flow and multiple herbicide resistance in escaped canola populations. Weed Sci 56:72–80
Lazaro A, Aguinagalde I (1996) Phylogenetic relationships between the wild taxa of the Brassica oleracea L. group (2n = 18) using the random amplified polymorphic DNA assay. Scientia Hortic 65:219–227
Negi MS, Devic M, Delseny M, Lakshmikumaran M (2000) Identification of AFLP fragments linked to seed coat color in Brassica juncea and conversion to a SCAR marker for rapid selection. Theor Appl Genet 101:146–152
Panda S, Martin JP, Aguinagalde I (2003) Chloroplast and nuclear DNA studies in a few members of the Brassica oleracea L. group using PCR-RFLP and ISSR-PCR markers: a population genetic analysis. Theor Appl Genet 106:1122–1128
Pessel FD, Lecomte J, Emeriau V, Krouti M, Messean A, Gouyon PH (2001) Persistence of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) outside of cultivated fields. Theor Appl Genet 102:841–846
Plieske J, Struss D (2001) Microsatellite markers for genome analysis in Brassica. I. development in Brassica napus and abundance in Brassicaceae species. Theor Appl Genet 102:689–694
Quinn MP (2010) Potential impacts of canola (Brassica napus L.) on Brassica vegetable seed production in the Willametle Valley of Oregon. Ph.D. thesis, Oregon State University, USA
Quirós CF (2001) DNA-based marker Brassica maps. In: Phillips RL, Vasil IK (eds) Advances in cellular and molecular biology of plants. DNA based marker in plants, vol I. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 201–238
Quirós CF, Paterson AH (2004) Genome mapping and analysis. In: Pua EC, Douglas CJ (eds) Biotechnology in agriculture and forestry. Brassica, vol 54. Springer, Berlin, pp 31–42
Rieger MA, Lamond M, Preston C, Powles SB, Roush RT (2002) Pollenmediated movement of herbicide resistance between commercial canola fields. Science 296:2386–2388
Rodriguez JM, Berke T, Engle L, Nienhuis J (1999) Variation among and within Capsicum species revealed by RAPD marker. Theor Appl Genet 99:147–156
Saski C, Lee S, Fjellheim S, Guda C, Jansen RK, Luo H, Tomkins J, Rognli OA, Daniell H, Clarke JL (2007) Complete chloroplast genome sequences of Hordeum vulgare, Sorghum bicolor and Agrostis stolonifera, and comparative analyses with other grass genomes. Theor Appl Genet 115:571–590
Semagn K, Bjørnstad Å, Ndjiondjop MN (2006) An overview of molecular marker methods for plants. Afr J Biotechnol 5:2540–2568
Shaw J, Lickey EB, Schilling EE, Small RL (2007) Comparison of whole chloroplast genome sequences to choose noncoding regions for phylogenetic studies in angiosperms: the tortoise and the hare III. Am J Bot 94:275–288
Song KM, Osborn TC (1992) Polyphyletic origins of Brassica napus: new evidence based on nuclear and RFLP organelle analysis. Genome 35:992–1001
Song KM, Osborn TC, Williams PH (1988) Brassica taxonomy based on nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs). Theor Appl Genet 75:784–794
Suwabe K, Iketani H, Nunome T, Kage T, Hirai M (2002) Isolation and characterization of microsatellites in Brassica rapa L. Theor Appl Genet 104:1092–1098
Wang YP, Zhao XX, Sonntag K, Wehling P, Snowdon RJ (2005) Behaviour of Sinapis alba chromosomes in a Brassica napus background revealed by genomic in situ hybridization. Chromosome Res 13:819–826
Warwick SI, Sauder C (2005) Phylogeny of tribe Brassiceae (Brassicaceae) based on chloroplast restriction site polymorphism and nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer (ITS) and chloroplast trnL intron sequences. Can J Bot 83:467–483
Warwick SI, Simard M-J, Légère A, Beckie HJ, Braun L, Zhu B, Mason P, Séguin-Swartz G, Stewart CN Jr (2003) Hybridization between transgenic Brassica napus L. and its wild relatives: B. rapa L., Raphanus raphanistrum L., Sinapis arvensis L., and Erucastrum gallicum (Willd.) O. E. Schulz. Theor Appl Genet 107:528–539
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from Research Program for Agricultural Science & Technology Development (Project No. PJ008545), National Academy of Agricultural Science and the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (Plant Molecular Breeding Center No. PJ008021), Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woo, HJ., Lim, MH., Shin, KS. et al. Development of a chloroplast DNA marker for monitoring of transgene introgression in Brassica napus L.. Biotechnol Lett 35, 1533–1539 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1236-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1236-0