Abstract
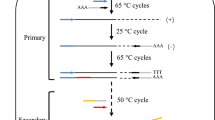
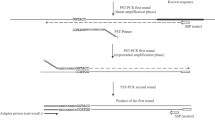
To identify the transposon insertion sites in a soil actinomycete, Saccharopolyspora spinosa, a genome walking approach, termed SPTA-PCR, was developed. In SPTA-PCR, a simple procedure consisting of TA cloning and a high stringency PCR, following the single primer-mediated, randomly-primed PCR, can eliminate non-target DNA fragments and obtain target fragments specifically. Using SPTA-PCR, the DNA sequence adjacent to the highly conserved region of lectin coding gene in onion plant, Allium chinense, was also cloned.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fu J, Teucher M, Anastassiadis K, Skarnes W, Stewart AF (2010) A recombineering pipeline to make conditional targeting constructs. Methods Enzymol 477:125–144
Hermann SR, Miller JA, O’Neill S, Tsao TT, Harding RM, Dale JL (2000) Single-primer amplification of flanking sequences. Biotechniques 29(6):1176–1180
Horn C, Hansen J, Schnutgen F, Seisenberger C, Floss T, Irgang M, De-Zolt S, Wurst W, von Melchner H, Noppinger PR (2007) Splinkerette PCR for more efficient characterization of gene trap events. Nat Genet 39(8):933–934
Ji J, Braam J (2010) Restriction site extension PCR: a novel method for high-throughput characterization of tagged DNA fragments and genome walking. Plos One 5(5):e10577
Karlyshev AV, Pallen MJ, Wren BW (2000) Single-primer PCR procedure for rapid identification of transposon insertion sites. Biotechniques 28(6):1078–1082
Liu YG, Chen Y (2007) High-efficiency thermal asymmetric interlaced PCR for amplification of unknown flanking sequences. Biotechniques 43(5):649–656
Mishra R, Singla-Pareek S, Nair S, Sopory S, Reddy M (2002) Directional genome walking using PCR. Biotechniques 33(4):830–834
Pilhofer M, Bauer AP, Schrallhammer M, Richter L, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH, Petroni G (2007) Characterization of bacterial operons consisting of two tubulins and a kinesin-like gene by the novel Two-Step Gene Walking method. Nucleic Acids Res 35(20):e135
Tan G, Gao Y, Shi M, Zhang X, He S, Chen Z, An C (2005) SiteFinding-PCR: a simple and efficient PCR method for chromosome walking. Nucleic Acids Res 33(13):e122
Tsaftaris A, Pasentzis K, Argiriou A (2010) Rolling circle amplification of genomic templates for inverse PCR (RCA-GIP): a method for 5′- and 3′-genome walking without anchoring. Biotechnol Lett 32(1):157–161
Waldron C, Matsushima P, Rosteck PR Jr, Broughton MC, Turner J, Madduri K, Crawford KP, Merlo DJ, Baltz RH (2001) Cloning and analysis of the spinosad biosynthetic gene cluster of Saccharopolyspora spinosa. Chem Biol 8(5):487–499
Yuanxin Y, Chengcai A, Li L, Jiayu G, Guihong T, Zhangliang C (2003) T-linker-specific ligation PCR (T-linker PCR): an advanced PCR technique for chromosome walking or for isolation of tagged DNA ends. Nucleic Acids Res 31(12):e68
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31070006), the National Basic Research Program (973) of China (2012CB722300), "973" special preliminary study program (2011CB311800), and the National High Technology Research and Development program (863) of China (2011AA10A203).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Yao, T., Cai, M. et al. A genome walking strategy for the identification of nucleotide sequences adjacent to known regions. Biotechnol Lett 35, 279–284 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-1076-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-1076-3