Abstract
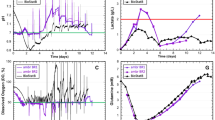
The proliferation and differentiation characteristics of umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells were examined in a non-rotational suspension bioreactor with a fishtail mixer. The system consisted of a glass vessel, a mixer that moved vertically, a data acquisition and control system to continuously monitor pH, temperature and dissolved O2. The bioreactor provided superior expansion of total HSCs and not total cell number, as well as expression of stemness-related genes which followed with increasing in number of colony-forming cells during 14 days of culture compared to T -lask culture. Vertical agitation thus reduces the total cell number, which may be related to increased shear stress, but has no effect on HSC function.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrade-Zaldívar H, Santos L, De León Rodríguez A (2008) Expansion of human hematopoietic stem cells for transplantation: trends and perspectives. Cytotechnology 56(3):151–160
Astori G, Adami V, Mambrini G, Bigi L (2005) Evaluation of ex vivo expansion and engraftment in NOD-SCID mice of umbilical cord blood CD34+ cells using the DIDECO “Pluricell System”. Bone Marrow Transplant 35(11):1101–1106
Bárcena A, Muench MO, Kapidzic M, Gormley M, Goldfien GA, Fisher SJ (2011) Human placenta and chorion: potential additional sources of hematopoietic stem cells for transplantation. Transfusion 51(Suppl 4):94S–105S
Beiki B, Ebrahimi M (2009) Characterization of expanded cord blood cells in medium supplemented with different cytokines. Sci J Blood Transfuse Organ 6(2):95–105
Cabrita GJ, Ferreira BS, da Silva CL et al. (2003) Hematopoietic stem cells: from the bone to the bioreactor. Trend Biotechnol 21(5):233–239
Cho CH, Eliason JF, Matthew HW (2008) Application of porous glycosaminoglycan-based scaffolds for expansion of human cord blood stem cells in perfusion culture. J Biomed Mater Res A 86(1):98–107
Dennis JE, Esterly K, Awadallah A et al. (2007) Clinical-scale expansion of a mixed population of bone-marrow-derived stem and progenitor cells for potential use in bone-tissue regeneration. Stem Cells 25(10):2575–2582
Kimura Y, Ding B, Imai N, Nolan DJ, Butler JM, Rafii S (2011) c-Kit-mediated functional positioning of stem cells to their niches is essential for maintenance and regeneration of adult hematopoiesis. PLoS ONE 6(10):e26918–e26924
Koller MR, Emerson SG, Palsson BO (1993) Large-scale expansion of human stem and progenitor cells from bone marrow mononuclear cells in continuous perfusion cultures. Blood 82(2):378–384
Kwon J, Kim BS, Kim MJ, Park HW (2003) Suspension culture of hematopoietic stem cells in stirred bioreactors. Biotechnol Lett 25(2):179–182
Liu Y, Liu T, Fan X, Ma X, Cui Z (2006) Ex vivo expansion of hematopoietic stem cells derived from umbilical cord blood in rotating wall vessel. J Biotechnol 124(3):592–601
Perdomo-Arciniegas AM, Vernot JP (2012) Optimized cord blood sample selection for small–scale CD34 + cell immunomagnetic isolation. Mol Med Report 5(3):749–752
Petropoulou AD, Rocha V (2011) Risk factors and options to improve engraftment in unrelated cord blood transplantation. Stem Cells Int: 1–8
Rubinstein P, Dobrila L, Rosenfield RE et al. (1995) Processing and cryopreservation of placental/umbilical cord blood for unrelated bone marrow reconstitution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(22):10119–10122
Sideri A, Neokleous N, De La Grange PB et al. (2011) An overview of the progress on double umbilical cord blood transplantation. Haematologica 96(8):1213–1220
Tang L, Bergevoet SM, Gilissen C, de Witte T, Jansen JH, van der Reijden BA, Raymakers RA (2010) Hematopoietic stem cells exhibit a specific ABC transporter gene expression profile clearly distinct from other stem cells. BMC Pharmacol 10:12
Yao CL, Feng YH, Lin XZ et al. (2006) Characterization of serum-free ex vivo-expanded hematopoietic stem cells derived from human umbilical cord blood CD133 (+) cells. Stem Cells Dev 15(1):70–78
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to Dr. Vousogh taghi Dizaj A. and Dr. Shahverdi A.H. for valuable supporting for this project. The research was supported by the Royan Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shayan, N., Ebrahimi, M., Beiki, B. et al. A non-rotational, computer-controlled suspension bioreactor for expansion of umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells. Biotechnol Lett 34, 2125–2131 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-0993-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-0993-5