Abstract
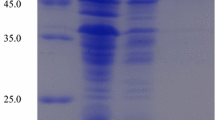
To investigate novel extremozymes encoded by sequenced metagenes from a microbial community in an extreme environment, we have characterized a recombinant glycosyl hydrolase (rGH) from an uncultured bacterium within the order Chloroflexi. rGH formed insoluble bodies in an Escherichia coli protein expression system. The protein was partially dissolved by a surfactant and was enzymatically characterized. The MW of the monomeric peptide was ~62 kDa, and it formed a homodimers in buffer. It was optimally active at 65 °C and from pH 4 to 8. rGH showed hydrolytic activity for α-1,1, α-1,2 and α-1,6 linkages, including isomaltose, but not α-1,4 and β-linkages.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Costantino HR, Brown SH, Kelly RM (1990) Purification and characterization of an alpha-glucosidase from a hyperthermophilic archaebacterium, Pyrococcus furiosus, exhibiting a temperature optimum of 105 to 115 °C. J Bacteriol 172:3654–3660
Crount DHC, Critchley P, Muller D, Scigelova M, Singh S, Vic G (1991) Application of glycosylases in the synthesis of complex carbohydrates. In: Gilbelt HJ, Davies GJ, Henrissat B, Svensson B (eds) Recent advances in carbohydrate bioengineering. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp 15–23
Davies G, Henrissat B (1995) Structures and mechanisms of glycosyl hydrolases. Structure 3:853–859
Frandesen TP, Svensson B (1998) Plant α-glucosidases of glycoside hydrolase family 31. Molecular properties, substrate specificity, reaction mechanism, and comparison with family members of different origin. Plant Mol Biol 37:1–13
Henrissat B, Bairoch A (1996) Updating the sequence-based classification of glycosyl hydrolases. Biochem J 316:695–696
Henrissat B, Callebaut I, Fabrega S, Lehn P, Mornon JP, Davies G (1995) Conserved catalytic machinery and the prediction of a common fold for several families of glycosyl hydrolases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(15):7090–7094
Hirayama H, Takai K, Inagaki F, Yamato Y, Suzuki M, Nealson KH, Horikoshi K (2007) Culture-dependent and -independent characterization of microbial community in a Japanese epithermal gold mine. Extremophiles 7:307–317
Hirayama H, Suzuki Y, Abe M, Miyazaki M, Makita H, Inagaki F, Uematsu K, Takai K (2010) Methylothermus subterraneus sp. nov., a moderately thermophilic methanotroph isolated from a terrestrial subsurface hot aquifer. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2646–2653
Hung VS, Hatada Y, Goda S, Lu J, Hidaka Y, Li Z, Akita M, Ohta Y, Watanabe K, Matsui H, Ito S, Horikoshi K (2005) α-Glucosidase from a strain of deep-sea Geobacillus: a potential enzyme for the biosynthesis of complex carbohydrates. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68:757–765
Kato N, Suyama S, Shirokane M, Kato M, Kobayashi T, Tsukagoshi N (2002) Novel α-glucosidase from Asperillus nidurans with strong transglycosylation activity. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1250–1256
Konishi M, Fukuoka T, Shimane Y, Mori K, Nagano Y, Ohta Y, Kitamoto D, Hatada Y (2011) Biochemical synthesis of self-assembling glycolipid from ricinoleic acid by α-glucosidase of Geobacillus. Biotechnol Lett 33:139–145
Lorenz P, Eck J (2005) Metagenomics and industrial applications. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:510–516
Nunoura T, Hirayama H, Takami H, Oida H, Nishi S, Simamura S, Suzuki Y, Inagaki F, Takai K, Nelson KH, Horikoshi K (2005) Genetic and functional properties of uncultivated thermophilic crenarchaeotes from a subsurface gold mine as revealed by analysis of genome fragments. Environ Microbiol 7:1967–1984
Sekiguchi Y, Yamada T, Hanada S, Ohashi A, Harada H, Kamagata Y (2003) Anaerolinea thermophila gen. nov. and Caldilinea aerophila gen. nov. sp., novel filamentous thermophilies that represent a previously uncultured lineage of the domain Bacteria at the subphylum level. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1843–1851
Shirai T, Hung VS, Akita M, Hatada Y, Ito S, Horikoshi K (2003) Crystallization and preliminary X-ray study of alpha-glucosidase from Geobacillus sp strain HTA-462, one deepest sea bacteria. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 59:1278–1279
Sunna A, Moracci M, Rossi M, Antranikian G (1997) Glycosyl hydrolases from hyperthermophiles. Extremophiles 1:2–13
Takai K, Kobayashi H, Nealson KH, Horikoshi K (2003) Sulfurihydrogenibium subterraneum gen. nov., sp. nov., from a subsurface hot aquifer. Int Syst Evol Microbiol 53:823–827
Takami H, Noguchi H, Takaki Y, Uchiyama I, Toyoda A, Nishi S, Chee G-J, Arai W, Nunoura T, Itoh T, Hattori M, Takai K (2012) A deeply branching thermophilic bacterium with an ancient acetyl-CoA pathway dominates a subsurface ecosystem. PLoS ONE 7:e30559
Teste MA, François JM, Parrou JL (2010) Characterization of a new multigene family encoding isomaltases in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae the IMA family. J Biol Chem 285:26814–26815
Vihinen M, Mäntsälä V (1989) Microbial amylolytic enzymes. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 24(3):29–418
Zhang D, Li N, Lok S-M, Zhang L-H, Swaminathan K (2003) Isomaltulose synthase (PalI) of Klebsiella sp. LX3. J Biol Chem 278:35428–35434
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konishi, M., Nishi, S., Takami, H. et al. Unique substrate specificity of a thermostable glycosyl hydrolase from an uncultured Anaerolinea, derived from bacterial mat on a subsurface geothermal water stream. Biotechnol Lett 34, 1887–1893 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-0983-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-0983-7