Abstract
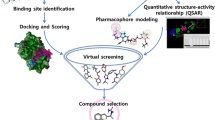
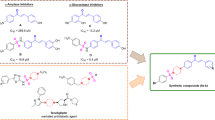
Human intestinal maltase (HMA) is an α-glucosidase that hydrolyses α-1,4-linkages from the non-reducing end of malto-oligosaccharides. HMA is an important target to discover of new drugs for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. In this study, 308,307 compounds were virtually screened with HMA using Autodock 3.0.5 in a WISDOM production environment to discover novel inhibitors. The 42 top-scoring free binding energy compounds, representing 17 groups containing potential hydrogen bonding with key residues in the active site pocket of HMA, were tested in vitro for their inhibitory activities against recombinant HMA expressed from Pichia pastoris. Compounds 17 and 18 were competitive inhibitors exclusively for HMA without any in vitro inhibition for human pancreatic α-amylase. The K i values were 20 μM for both compound 17 and 18.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asano N (2003) Glycosidase inhibitors: update and perspectives on practical use. Glycobiology 13:93r–104r
Brayer GD, Luo YG, Withers SG (1995) The structure of human pancreatic alpha-amylase at 1.8 angstrom resolution and comparisons with related enzymes. Protein Sci 4:1730–1742
Brayer GD, Sidhu G, Maurus R, Rydberg EH, Braun C, Wang Y, Nguyen NT, Overall CM, Withers SG (2000) Subsite mapping of the human pancreatic alpha-amylase active site through structural, kinetic, and mutagenesis techniques. Biochemistry 39:4778–4791
Chan JC, Malik V, Jia W, Kadowaki T, Yajnik CS, Yoon KH, Hu FB (2009) Diabetes in Asia: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. JAMA 301:2129–2140
Guido RVC, Oliva G, Andricopulo AD (2008) Virtual screening and its integration with modern drug design technologies. Curr Med Chem 15:37–46
Hanh Nguyen TT, Ryu HJ, Lee SH, Hwang S, Breton V, Rhee JH, Kim D (2011) Virtual screening identification of novel severe acute respiratory syndrome 3C-like protease inhibitors and in vitro confirmation. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21:3088–3091
Hou TJ, Xu XJ (2004) Recent development and application of virtual screening in drug discovery: an overview. Curr Pharm Design 10:1011–1033
Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Halliday RS, Huey R, Hart WE, Belew RK, Olson AJ (1998) Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J Comput Chem 19:1639–1662
Park H, Hwang KY, Oh KH, Kim YH, Lee JY, Kim K (2008) Discovery of novel alpha-glucosidase inhibitors based on the virtual screening with the homology-modeled protein structure. Bioorg Med Chem 16:284–292
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25:1605–1612
Rossi EJ, Sim L, Kuntz DA, Hahn D, Johnston BD, Ghavami A, Szczepina MG, Kumar NS, Sterchi EE, Nichols BL, Pinto BM, Rose DR (2006) Inhibition of recombinant human maltase glucoamylase by salacinol and derivatives. FEBS J 273:2673–2683
Sanner MF, Olson AJ, Spehner JC (1996) Reduced surface: an efficient way to compute molecular surfaces. Biopolymers 38:305–320
Sim L, Quezada-Calvillo R, Sterchi EE, Nichois BL, Rose DR (2008) Human intestinal maltase-glucoamylase: crystal structure of the N-terminal catalytic subunit and basis of inhibition and substrate specificity. J Mol Bio 375:782–792
Suzuki Y, Sano M, Hayashida K, Ohsawa I, Ohta S, Fukuda K (2009) Are the effects of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors on cardiovascular events related to elevated levels of hydrogen gas in the gastrointestinal tract? FEBS Lett 583:2157–2159
Wallace AC, Laskowski RA, Thornton JM (1995) LIGPLOT: a program to generate schematic diagrams of protein-ligand interactions. Protein Eng 8:127–134
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (No. 2010-0021474 and No. 2009-0090025). Authors acknowledge support from FKPPL Internal Associated Laboratory for grid computing resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, T.T.H., Ryu, HJ., Lee, SH. et al. Discovery of novel inhibitors for human intestinal maltase: virtual screening in a WISDOM environment and in vitro evaluation. Biotechnol Lett 33, 2185–2191 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-011-0675-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-011-0675-8