Abstract
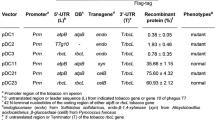
An economical method for the conversion of lignocellulosic biomass is to use plants as bioreactors for cellulases production. Two bacterial thermostable cellulases (E2 and E3) and a E3-E2 fusion form were expressed in tobacco, driven by a double 35S promoter and 5′ TEV-UTL. The enzymes were targeted to the apoplast and cytosol via 5′ signal peptides and 3′ retention signal peptides, respectively, and all showed functional activities. All transgenic plants exhibited normal growth compared to wild type. Transgenic plants that expressed apoplast-localized E2 had the highest average activity, about 1.5 and 3 times higher than those expressed ER-localized and cytosolic E2, respectively. Effect of subcellular compartment localization was due primarily to post-transcriptional modification, since mRNA abundances were similar despite the range of cellulase activities obtained. The recombinant cellulases exhibited good thermostability below 65°C. After storing for 3 days at −20 and 28°C, the enzymes lost nearly 20 and 80% of activity, respectively. The results suggested a potential application for heterologous expression of cellulases in plant for biomass conversion.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 35S:
-
Cauliflower Mosaic Virus 35s
- TEV:
-
Tobacco etch virus
- UTL:
-
Untranslated leader
- CALSP:
-
Tobacco calreticulin signal peptide
- MUC:
-
4-Methylumbelliferyl-β-d-cellobioside
- MU:
-
4-Methylumbelliferone
References
Biswas G, Ransom C, Sticklen M (2006) Expression of biologically active Acidothermus cellulolyticus endoglucanase in transgenic maize plants. Plant Sci 171:617–623
Conrad U, Fiedler U (1998) Compartment-specific accumulation of recombinant immunoglobulins in plant cells: an essential tool for antibody production and immunomodulation of physiological functions and pathogen activity. Plant Mol Biol 38:101–109
Dai Z, Hooker BS, Anderson DB, Thomas SR (2000) Expression of Acidothermus cellulolyticus endoglucanase E1 in transgenic tobacco: biochemical characteristics and physiological effects. Transgenic Res 9:43–54
Dai Z, Hooker BS, Quesenberry RD, Thomas SR (2005) Optimization of Acidothermus cellulolyticus endoglucanase (E1) production in transgenic tobacco plants by transcriptional, post-transcription and post-translational modification. Transgenic Res 14:627–643
Jiang XR, Li WL (2009) Research progress in genetic engineering for cellulosic ethanol. China Biotechnol 29:127–133
Jiang XR, Liu JW, Li WL (2010) The progress in thermophile research and its application prospect in cellulosic ethanol. Life Sci Res 5:449–455
Jung S, Kim S, Bae H, Lim HS, Bae HJ (2010) Expression of thermostable bacterial β-glucosidase (BglB) in transgenic tobacco plants. Bioresour Technol 101:7144–7150
Kozak M (1986) Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell 44:283–292
Pang Z, Dong Z, Liang J, Chen S, Wei P, Huang R (2005) Study on cellulase properties of Thermophilic actinomycete GPL1. Mod Food Sci Technol 22:20–23
Wilson DB (2004) Studies of Thermobifida fusca plant cell wall degrading enzymes. Chem Rec 4:72–82
Youm JW, Kim H, Han JH, Jang CH, Ha HJ, Mook-Jung I, Jeon JH, Choi CY, Kim YH, Kim HS, Joung H (2005) Transgenic potato expressing Aβ reduce Aβ burden in Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. FEBS Lett 579:6737–6744
Ziegelhoffer T, Will J, Austin-Phillips S (1999) Expression of bacterial cellulase genes in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.), potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) and tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Mol Breed 5:309–318
Ziegelhoffer T, Raasch JA, Austin-Phillips S (2001) Dramatic effects of truncation and sub-cellular targeting on the accumulation of recombinant microbial cellulase in tobacco. Mol Breed 8:147–158
Ziegler MT, Thomas SR, Danna KJ (2000) Accumulation of a thermostable endo-1, 4-β-d-glucanase in the apoplast of Arabidopsis thaliana leaves. Mol Breed 6:37–46
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by “the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities” (DUT10JN01) and China Environmental Protection Foundation Liaoning Representative Office. Liaoning environmental scientific research “123” fund project (CEPF2008-123-2-11). We thank Alan K Chang (Dalian University of Technology) for helpful discussion and for revising the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Xr., Zhou, Xy., Jiang, Wy. et al. Expressions of thermostable bacterial cellulases in tobacco plant. Biotechnol Lett 33, 1797–1803 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-011-0642-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-011-0642-4