Abstract
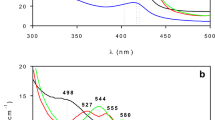
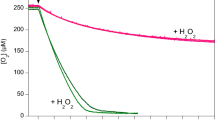
The stability (half-life, t½) of the large catalase (CAT) isolated from Aspergillus terreus was decreased under acidic conditions (maximum t½ ~8.5 months at pH ≤ 6) versus alkaline conditions (t½ ~15 months at pH 8–12). Acidic conditions induce the dissociation of haem from CAT, as revealed from a reduction in the Soret peak intensity at 405 nm and an increase in the peak current at Fe3+/Fe2+ redox potentials. This increase in current is attributed to the facile electron transfer from the free haem generated on the electrode surface as a result of its disintegration from the insulating protein matrix. The haem isolated from CAT at acidic condition was reconstituted with apo-CAT at alkaline denaturing conditions to regenerate the CAT activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calera JA, Sanchez-Weatherby J, Lopez-Medrano R, Leal F (2000) Distinctive properties of the catalase B of Aspergillus nidulans. FEBS Lett 475:117–120
Das A, Hecht MH (2007) Peroxidase activity of de novo heme proteins immobilized on electrodes. J Inorg Biochem 101:1820–1826
Diaz A, Rangel P, De Montes Oca Y, Lledias F, Hansberg W (2001) Molecular and kinetic study of catalase-1, a durable large catalase of Neurospora crassa. Free Radic Bio Med 31:1323–1333
Eriksson CE, Olsson PA, Svensson SG (1971) Denatured hemoproteins as catalysts in lipid oxidation. J Am Oil Chem Soc 48:442–447
Fruk L, Kuo CH, Torres E, Niemeyer CM (2009) Apoenzyme reconstitution as a chemical tool for structural enzymology and biotechnology. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:1550–1574
Gilles-Gonzalez MA, Gonzalez G (2005) Heme-based sensors: defining characteristics, recent developments, and regulatory hypotheses. J Inorg Biochem 99:1–22
Kroliczewski J, Szczepaniak A (2002) In vitro reconstitution of the spinach chloroplast cytochrome b6 protein from a fusion protein expressed in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta 1598:177–184
Liu HH, Tian ZQ, Lu ZX, Zhang ZL, Zhang M, Pang DW (2004) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of heme-proteins entrapped in agarose hydrogel films. Biosens Bioelectron 20:294–304
Samejima T, McCabe WJ, Yang JT (1968) Reconstitution of alkaline-denatured catalase. Arch Biochem Biophys 127:354–360
Spiro TG, Jarzecki AA (2001) Heme-based sensors: theoretical modeling of heme-ligand–protein interactions. Curr Opin Chem Biol 5:715–723
Switala J, Loewen PC (2002) Diversity of properties among catalase. Arch Biochem Biophys 401:145–154
Teale FWJ (1959) Cleavage of the haem-protein link by acid methylethylketone. Biochim Biophys Acta 35:543
Zamocky M, Koller F (1999) Understanding the structure and function of catalases: clues from molecular evolution and in vitro mutagenesis. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 72:19–66
Acknowledgment
We acknowledge the financial support from the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India, to carry out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vatsyayan, P., Goswami, P. Acidic pH conditions induce dissociation of the haem from the protein and destabilise the catalase isolated from Aspergillus terreus . Biotechnol Lett 33, 347–351 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-010-0442-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-010-0442-2