Abstract
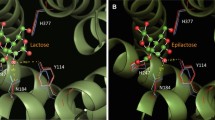
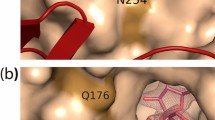
The cellobiose 2-epimerase from Ruminococcus albus (RaCE) catalyzes the epimerization of cellobiose and lactose to 4-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-d-mannose and 4-O-β-d-galactopyranosyl-d-mannose (epilactose). Based on the sequence alignment with N-acetyl-d-glucosamine 2-epimerases of known structure and on a homology-modeled structure of RaCE, we performed site-directed mutagenesis of possible catalytic residues in the enzyme, and the mutants were expressed in Escherichia coli cells. We found that R52, H243, E246, W249, W304, E308, and H374 were absolutely required for the activity of RaCE. F114 and W303 also contributed to catalysis. These residues protruded into the active-site cleft in the model (α/α)6 core barrel structure.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amein M, Leatherwood JM (1969) Mechanism of cellobiose epimerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 36:223–227
Clarke AJ (1987) Essential tryptophan residues in the function of cellulase from Schizophyllum commune. Biochim Biophys Acta 912:424–431
Hagihara H, Hayashi Y, Endo K et al (2001) Deduced amino-acid sequence of a calcium-free α-amylase from a strain of Bacillus. Implications from molecular modeling of high oxidation stability and chelator resistance of the enzyme. Eur J Biochem 268:3974–3982
Hagihara H, Hatada Y, Ozawa T et al (2003) Oxidative stabilization of an alkaliphilic Bacillus α-amylase by replacing a single specific methionine residue by site-directed mutagenesis. J Appl Glycosci 50:367–372
Hopp TP, Woods KR (1981) Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:3824–3828
Hurst PL, Sullivan PA, Shepherd MG (1977) Chemical modification of a cellulase from Aspergillus niger. Biochem J 167:549–556
Ito S, Hamada S, Yamaguchi K et al (2007) Cloning and sequencing of the cellobiose 2-epimerase gene from an obligatory anaerobe, Ruminococcus albus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 360:640–645
Ito S, Taguchi H, Hamada S et al (2008) Enzymatic properties of cellobiose 2-epimerase from Ruminococcus albus and the synthesis of rare oligosaccharides by the enzyme. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:433–441
Itoh T, Mikami B, Maru I et al (2000) Crystal structure of N-acyl-D-glucosamine 2-epimerase from porcine kidney at 2.0 Å resolution. J Mol Biol 303:733–744
Joy M, Amit AG, Alzari PM et al (1992) Three-dimensional structure of a thermostable bacterial cellulase. Nature 357:89–91
Kabsch W, Sander C (1983) Dictionary of protein secondary structure: pattern recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers 22:2577–2637
Kawaminami S, Ozaki K, Sumitomo N (1994) A stable isotope-aided NMR study of the active site of an endoglucanase from a strain of Bacillus. J Biol Chem 269:28752–28756
Lee YC, Wu HM, Chang YN et al (2007) The central cavity from the (alpha/alpha)6 barrel structure of Anabaena sp. CH1 N-acetyl-d-glucosamine 2-epimerase contains two key histidines for reversible conversion. J Mol Biol 367:895–908
Nishimukai M, Watanabe J, Taguchi H et al (2008) Effects of epilactose on calcium adsorption and serum lipid metabolism in rats. J Agric Food Chem 56:10340–10345
Nonaka T, Fujihashi M, Kita A et al (2004) The crystal structure of an oxidatively stable subtilisin-like alkaline serine protease, KP-43, with a C-terminal β-barrel domain. J Biol Chem 279:47344–47351
Ohmiya K, Maeda K, Shimizu S (1987) Purification and properties of endo-(1 → 4)-β-d-glucanase from Ruminococcus albus. Carbohydr Res 166:145–155
Ozaki K, Ito S (1991) Purification and properties of an acid endo-1, 4-β-glucanases from Bacillus sp. KSM-330. J Gen Microbiol 137:41–48
Taguchi H, Senoura T, Hamada S et al (2008) Cloning and sequencing of the gene for cellobiose 2-epimerase from a ruminal strain of Eubacterium cellulosolvens. FEMS Microbiol Lett 287:34–40
Tyler TR, Leatherwood JM (1967) Epimerization of disaccharides by enzyme preparations from Ruminococcus albus. Arch Biochem Biophys 119:363–367
Watanabe J, Nishimukai M, Taguchi H et al (2008) Prebiotic properties of epilactose. J Dairy Sci 91:4518–4526
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by national projects Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology and Knowledge Cluster Initiative (2nd Stage, Sapporo Biocluster Bio-S), The Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, S., Hamada, S., Ito, H. et al. Site-directed mutagenesis of possible catalytic residues of cellobiose 2-epimerase from Ruminococcus albus . Biotechnol Lett 31, 1065–1071 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-9979-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-9979-3