Abstract
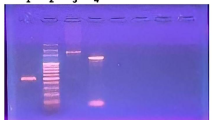
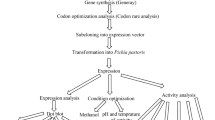
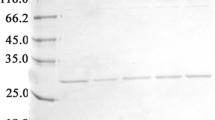
Staphylokinase (SAK) is a promising thrombolytic agent for treating blood-clotting disorders. Recombinant SAK (rSAK) was produced after integration of the gene into Pichia pastoris genome. The recombinant Pichia carrying multiple insertions of the SAK gene yielded high-level (~1 g/l) of extracellular glycosylated rSAK (~18 kDa) with negligible plasminogen activation activity. Addition of tunicamycin during the induction phase resulted in expression of non-glycosylated and highly active rSAK (~15 kDa) from the same clone. Two simple steps of ion-exchange chromatography produced an homogenous rSAK of >95% purity which suitable for future structural and functional studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bayley DP, Kalmokoff ML, Jarrell KF (1993) Effect of bacitracin on flagellar assembly and presumed glycosylation of the flagellins of Methanococcus deltae. Arch Microbiol 160:179–185
Cheng Y, Li Y, Liu B, Guo L (1998) Cloning and secretory expression of staphylokinase in Streptomyces lividans. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 20:428–432
Cregg JM, Vedvick TS, Raschke WC (1993) Recent advances in the expression of foreign genes in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnology 11:905–910
Grella DK, Catsellino FJ (1997) Activation of human plasminogen by Staphylokinase. Direct evidence that preformed plasmin is necessary for activation to occur. Blood 89:1585–1589
Grinna LS, Tschopp JF (1989) Size distribution and general structural features of N-linked oligosaccharides from the methylotropic yeast, Pichia pastoris. Yeast 5:107–115
Hamilton SR, Davidson RC, Sethuraman N, Nett JH, Jiang Y, Rios S, Bobrowicz P, Stadheim TA, Li H, Choi BK, Hopkins D, Wischnewski H, Roser J, Mitchell T, Strawbridge PR, Hoopes J, Wildt S, Gerngross TU (2006) Humanization of yeast to produce complex terminally sialylated glycoproteins. Science 313:1441–1443
Luczak M, Bugajewska A, Wojtaszek P (2008) Inhibitors of protein glycosylation or secretion change the pattern of extracellular proteins in suspension-cultured cells of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:962–969
Maeda H, Chatani E, Koyama T, Sugiura M, Izumi H, Hayashi R (2004) Indiscriminate glycosylation of procarboxypeptidase Y expressed in Pichia pastoris. Carbohyd Res 339:1041–1045
Miele RG, Prorok M, Costa VA, Castellino FJ (1999) Glycosylation of Asparagine-28 of recombinant Staphylokinase with high-mannose-type oligosaccharides results in a protein with highly attenuated plasminogen activator activity. J Biol Chem 274:7769–7776
Nagnath M, Soorapaneni S, Rewanwar S, Kotwal P, Prasad B, Mandal G, Padmanabhan S (2009) High yielding recombinant Staphylokinase in bacterial expression system. Cloning, expression, purification and activity studies. Protein Expr Purif 64:69–75
Rabijns A, De Bondt HL, De Ranter C (1997) Three-dimensional structure of Staphylokinase, a plasminogen activator with therapeutic potential. Nature Struct Biol 4:357–360
Rajamohan G, Dahiya M, Mande SC, Dikshit KL (2002) Function of the 90-loop (Thr90–Glu100) region of staphylokinase in plasminogen activation probed through site-directed mutagenesis and loop deletion. Biochem J 365:379–389
Ren D, Li D, Yang W, Li Y, Gou X, Liang B, Li B, Wu Q (2008) Novel preparation protocol for the expression and purification of recombinant staphylokinase. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 51:9–13
Roland C, Callewaert NLM, Geysens SCJ (2004) Protein glycosylation modification in Pichia pastoris. United States Patent 6803225
Romanos M, Scorer C, Sreekrishna K, Clare J (1998) Methods in molecular biology. In Higgins DR, Cregg JM (eds) Pichia protocols, The generation of multicopy recombinant strains, vol 103. Humana Press Inc, NJ, pp 55–72
Roy N, Padmanabhan S, Smith M, Shi L, Navre M, Das G (1999) Expression of human gelatinase B in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 16:324–330
Sako T (1985) Overproduction of staphylokinase in Escherichia coli and its characterization. Eur J Biochem 149:557–563
Scorer CA, Clare JJ, McCombie WR, Romanos MA, Sreekrishna K (1994) Rapid selection using G418 of high copy number transformants of Pichia pastoris for high level foreign gene expression. Biotechnology 12:181–184
Sebban-Kreuzer C, Deprez-Beauclair P, Berton A, Crenon I (2006) High-level expression of nonglycosylated human pancreatic lipase-related protein 2 in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 49:284–291
Sinnaeve P, Van de Werf F (2001) Thrombolytic therapy. State of the art. Thromb Res 103:71–79
Su H, Zhang Y, He J, Mo W, Zhang Y, Tao X, Song H (2004) Construction and characterization of novel staphylokinase variants with antiplatelet aggregation activity and reduced immunogenicity. Acta Biochimi Biophys Sin 36:336–342
Tsikouris JP, Tsikouris AP (2001) A review of available fibrin-specific thrombolytic agents used in acute myocardial infarction. Pharmacotherapy 21:207–217
Wang XQ, Sun P, O’Gorman M, Tai T, Paller AS (2001) Epidermal growth factor receptor glycosylation is required for ganglioside GM3 binding and GM3-mediated suppression [correction of suppression] of activation. Glycobiology 11:515–522
Wu S, Castellino FJ, Wong S (2003) A fast-acting, modular-structured staphylokinase fusion with kringle-1 from human plasminogen as the fibrin-targeting domain offers improved clot lysis efficacy. J Biol Chem 278:18199–18206
Ye R, Kim JH, Kim B, Szarka S, Sihota E, Wong SL (1999) High-level secretory production of intact, biologically active staphylokinase from Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol Bioeng 62:87–96
Acknowledgment
We sincerely thank Dr. Kamal Sharma, Managing director, Lupin Ltd. for his constant support and encouragement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Apte-Deshpnade, A., Mandal, G., Soorapaneni, S. et al. High-level expression of non-glycosylated and active staphylokinase from Pichia pastoris . Biotechnol Lett 31, 811–817 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-9938-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-9938-z