Abstract
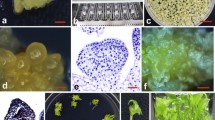
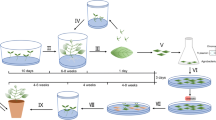
A genetic transformation system has been developed for selected embryogenic cell lines of hybrids Abies alba × A. cephalonica (cell lines AC2, AC78) and Abies alba × A. numidica (cell line AN72) using Agrobacterium tumefaciens. The cell lines were derived from immature or mature zygotic embryos on DCR medium containing BA (1 mg l−1). The T-DNA of plant transformation vector contained the β-glucuronidase reporter gene under the control of double dCaMV 35S promoter and the neomycin phosphotransferase selection marker gene driven by the nos promoter. The regeneration of putative transformed tissues started approximately 1 week after transfer to the selection medium containing 10 mg geneticin l−1. GUS activity was detected in most of the geneticin-resistant sub-lines AN72, AC2 and AC78, and the transgenic nature of embryogenic cell lines was confirmed by PCR approach. Plantlet regeneration from PCR-positive embryogenic tissues has been obtained as well. The presence of both gus and nptII genes was confirmed in 11 out of 36 analysed emblings.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cerda F, Aquea F, Gebauer M, Medina C, Arce-Johnson P (2002) Stable transformation of Pinus radiata embryogenic tissue by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 70:251–257
Clapham D, Ekberg I (1986) Induction of tumors by various strains of Agrobacterium tumefaciens on Abies nordmanniana and Picea abies. Scand J For Res 1:435–437
Covey SN, Al-Kaff NS (2000) Plant DNA viruses and gene silencing. Plant Mol Biol 43:307–322
Ellis D, Roberts D, Sutton B, Lazaroff D, Webb D, Flinn B (1989) Transformation of white spruce and other conifer species by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Cell Rep 8:16–20
Find JI, Charity J, Grace LJ, Kristensen MMM, Krogstrup P, Walter C (2005) Stable genetic transformation of embryogenic cultures of Abies nordmanniana and regeneration of transgenic plants. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 41:725–730
Grant JE, Cooper PA, Dale TM (2004) Transgenic Pinus radiata from Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of cotyledons. Plant Cell Rep 22:894–902
Gupta PK, Durzan DJ (1985) Shoot multiplication from mature trees of Douglas fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii) and sugar pine (Pinus lambertiana). Plant Cell Rep 4:177–179
Häggman H, Aronen T (1998) Transgene expression in regenerating cotyledons and embryogenic cultures of Scots pine. J Exp Bot 49:1147–1156
Jefferson R (1987) Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol Biol Rep 5:387–405
Klimaszewska K, Lachance D, Pelletier G, Lelu MA, Ségiun A (2001) Regeneration of transgenic Picea glauca, P. mariana and P. abies after cocultivation of embryogenic tissue with Agrobacterium tumefaciens. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 37:748–755
Klimaszewska K, Lachance D, Bernier-Cardou M, Rutledge RG (2003) Transgene integration patterns and expression levels in transgenic tissue lines of Picea mariana, P. glauca and P. abies. Plant Cell Rep 21:1080–1087
Le VQ, Belles-Isles J, Dusabenyagasani M, Tremblay F (2001) An improved procedure for production of white spruce (Picea glauca) transgenic plants using Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Exp Bot 52:2089–2095
Levée V, Lelu M-A, Jouanin L, Cornu D, Pilate G (1997) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of hybrid larch (Larix kaempferi × L. decidua) and transgenic plat regeneration. Plant Cell Rep 16:680–685
Levée V, Garin E, Klimaszewska K, Séguin A (1999) Stable transformation of white pine (Pinus strobus L.) after co-cultivation of embryogenic tissues with Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Mol Breed 5:429–440
Loopstra CC, Stomp AM, Sederoff RR (1990) Agrobacterium mediated DNA transfer in sugar pine. Plant Mol Biol 15:1–9
Matzke MA, Mette MF, Matzke AJM (2000) Transgene silencing by the host genome defense: implications for the evolution of epigenetic control mechanisms in plants and vertebrates. Plant Mol Biol 43:401–415
Mihaljević S, Perić M, Jelavska S (2001) The sensitivity of embryogenic tissue of Picea omorika (Panč.) Purk. to antibiotics. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 67:287–293
Morris JW, Castle LA, Morris RO (1989) Efficacy of different Agrobacterium tumefaciens strains in transformation of pinaceous gymnosperms. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 34:451–461
Salajová T, Jásik J, Kormuťák A, Salaj J, Hakman I (1996) Embryogenic culture initiation and somatic embryo development in hybrid firs (Abies alba × Abies cephalonica and Abies alba × Abies numidica). Plant Cell Rep 15:527–530
Tang W (2001) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation and assessment of factors influencing transgene expression in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.). Cell Res 11:237–243
Taniguchi T, Kurita M, Ohmiya Y, Kondo T (2005) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of embryogenic tissue and transgenic plant regeneration in Chamaecyparis obtusa Sieb. et Zucc. Plant Cell Rep 23:769–802
Tereso S, Miguel C, Zoglauer K, Valle-Piquera C, Oliveira MM (2006) Stable Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of embryogenic tissues Pinus pinaster Portuguese genotypes. Plant Growth Regul 50:47–68
Vooková B, Kormuťák A (2002) Some futures of somatic embryo maturation of Algerian fir. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 38:549–561
Wenck AR, Quinn M, Whetten RW, Pullman G, Sederoff R (1999) High-efficiency Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Norway spruce (Picea abies) and loblolly pine (Pinus taeda). Plant Mol Biol 39:407–416
Yu TA, Yeh SD, Yang JS (2003) Comparison of the effects of kanamycin and geneticin on regeneration of papaya from root tissue. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 74:169–178
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Slovak Grant Agency VEGA, projects No. 2-5022-25 and No. 2-0011-08.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salaj, T., Moravčíková, J., Vooková, B. et al. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of embryogenic tissues of hybrid firs (Abies spp.) and regeneration of transgenic emblings. Biotechnol Lett 31, 647–652 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-9923-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-9923-6