Abstract
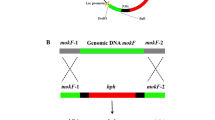
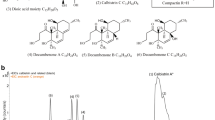
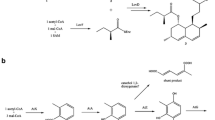
Monacolin K (MK), which is widely used as an antihypercholesterolemia medicine, is produced as a fungal secondary metabolite through the polyketide pathway. The MK biosynthetic gene cluster proposed for Monascus pilosus BCRC38072 was also identified in M. pilosus NBRC4480. The mokB gene, located at the end of the putative gene cluster and possibly encoding polyketide synthase, was disrupted. The mokB disruptant did not produce MK, but accumulated an intermediate that was confirmed to be monacolin J, indicating that mokB encodes the polyketide synthase responsible for the biosynthesis of side-chain diketide moiety.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen YP, Tseng CP, Liaw LL, Wang CL, Chen IC, Wu WJ, Wu MD, Yuan GF (2008) Cloning and characterization of monacolin K biosynthetic gene cluster from Monascus pilosus. J Agric Food Chem 56:5639–5646
Endo A, Hasumim K, Negishi S (1985) Monacolins J and L, new inhibitors of cholesterol biosynthesis produced by Monascus ruber. J Antibiot 38:420–422
Hendrickson L, Davis CR, Roach C, Nguyen DK, Aldrich T, McAda PC, Reeves CD (1999) Lovastatin biosynthesis in Aspergillus terreus: characterization of blocked mutants, enzyme activities and a multifunctional polyketide synthase gene. Chem Biol 6:429–439
Hutchinson CR, Kennedy J, Park C, Kendrew S, Auclair K, Vederas J (2000) Aspects of the biosynthesis of non-aromatic fungal polyketides by iterative polyketide synthases. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 78:287–295
Istvan ES, Deisenhofer J (2001) Structural mechanism for statin inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. Science 292:1160–1164
Kennedy J, Auclair K, Kendrew SG, Park C, Vederas JC, Hutchinson CR (1999) Modulation of polyketide synthase activity by accessory proteins during lovastatin biosynthesis. Science 284:1368–1372
Manzoni M, Rollini M (2002) Biosynthesis and biotechnological production of statins by filamentous fungi and application of these cholesterol-lowering drugs. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58:555–564
Matilde M, Silvia B, Manuela R, Valeria C (1999) Production of statins by filamentous fungi. Biotechnol Lett 21:253–257
Shimizu T, Kinoshita H, Ishihara S, Sakai K, Nagai S, Nihira T (2005) Polyketide synthase gene responsible for citrinin biosynthesis in Monascus purpureus. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:3453–3457
Sorensen JL, Auclair K, Kennedy J, Hutchinson CR, Vederas JC (2003) Transformations of cyclic nonaketides by Aspergillus terreus mutants blocked for lovastatin biosynthesis at the lovA and lovC genes. Org Biomol Chem 1:50–59
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Sports, Culture, Science, and Technology (MEXT) of Japan, and by a grant from the Japan-Thailand program from MEXT, the National Research Council of Thailand, and the National Science and Technology Development Agency of Thailand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakai, K., Kinoshita, H. & Nihira, T. Identification of mokB involved in monacolin K biosynthesis in Monascus pilosus . Biotechnol Lett 31, 1911–1916 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-0093-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-0093-3