Abstract
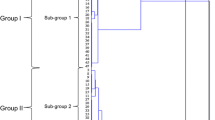
Amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) was used to analyze genomic variability between high pristinamycin-producing recombinants of Streptomyces pristinaespiralis produced by genome shuffling and their ancestral strain. The AFLP fingerprints obtained with two restriction enzyme combinations of ApaI/TaqI and PstI/SacII showed together that there was no major polymorphism (less than 10%) between these high yield recombinants and their ancestor. However, the unique polymorphic bands, which might be related to the yield increasing of pristinamycin, could be distinguished from all the recombinants. Clustering analysis further indicated that the recombinants with similar ability of pristinamycin production had similar genomic variability.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassam BJ, Caetano-Anolles G, Gresshoff PM (1991) Fast and sensitive silver staining of DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 196:80–83
bdel-Hamid ME, Phillips OA (2003) LC-MS/MS determination of synercid injections. J Pharm Biomed Anal 32:1167–1174
Bentley SD, Chater KF, Cerdeno-Tarraga AM et al (2002) Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417:141–147
Cocito C (1979) Antibiotics of the virginiamycin family, inhibitors which contain synergistic components. Microbiol Rev 43:145–192
Hida H, Yamada T, Yamada Y (2007) Genome shuffling of Streptomyces sp. U121 for improved production of hydroxycitric acid. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:1387–1393
Hopwood DA, Bibb MJ, Chater KF et al (1985) Genetic manipulation of Streptomyces: A laboratory manual. The John Innes Foundation, Norwich, UK
Janssen P, Coopman R, Huys G et al (1996) Evaluation of the DNA fingerprinting method AFLP as an new tool in bacterial taxonomy. Microbiology 142(Pt 7):1881–1893
Jia B, Jin ZH, Lei YL et al (2006) Improved production of pristinamycin coupled with an adsorbent resin in fermentation by Streptomyces pristinaespiralis. Biotechnol Lett 28:1811–1815
Jin Z, Lei Y, Lin J et al (2005) Improvement of pristinamycin-producing Streptomyces pristinaespiralis by rational screening. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 22:129–134
Lanoot B, Vancanneyt M, Hoste B et al (2005) Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of mutants of the virginiamycin producing strain 899 and its relatedness to the type strain of Streptomyces virginiae. Syst Appl Microbiol 28:77–84
Rohlf FJ (1998) On applications of geometric morphometrics to studies of ontogeny and phylogeny. Syst Biol 47:147–158
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M et al (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Zhang YX, Perry K, Vinci VA et al (2002) Genome shuffling leads to rapid phenotypic improvement in bacteria. Nature 415:644–646
Acknowledgements
The work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 20576122) and the Department of Science and Technology, Zhejiang Province, China (Grant No. 2004C13007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Q., Jin, Z., Xu, B. et al. Genomic variability among high pristinamycin-producing recombinants of Streptomyces pristinaespiralis revealed by amplified fragment length polymorphism. Biotechnol Lett 30, 1423–1429 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-008-9701-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-008-9701-x