Abstract
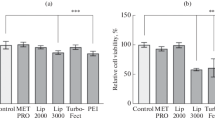
Polyethylenimine (PEI) is one of the most extensively studied non-viral vectors but its cytotoxicity limits its clinical value. PLGA nanospheres are biocompatible and can facilitate sustained release of plasmid DNA. This study compares the cytotoxicity and long-term transgene expression between PLGA nanosphere and PEI. PLGA nanospheres were significantly less cytotoxic than PEI at various concentrations. PLGA nanospheres induced significantly higher transgene expression in vitro for a longer duration (21 days) than PEI. We conclude that PLGA nanospheres have potential as gene delivery vehicles for use in gene therapy for diseases in which a long-term therapeutic gene expression regimen is necessary.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah B, Hassan A, Benoist C, Goula D, Behr JP, Demeneix BA (1996) A powerful nonviral vector for in vivo gene transfer into the adult mammalian brain: polyethylenimine. Hum Gene Ther 7:1947–1954
Benns JM, Maheshwari A, Furgeson DY, Mahato RI, Kim SW (2001) Folate-PEG-folate-graft-polyethylenimine-based gene delivery. J Drug Target 9:123–139
Boussif O, Lezoualc’h F, Zanta MA, Mergny MD, Scherman D, Demeneix B, Behr JP (1995) A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:7297–7301
Cavazzana-Calvo M, Hacein-Bey S, De Saint Basile G, Gross F, Yvon E, Nusbaum P, Selz F, Hue C, Certain S, Casanova JL, Bousso P, Le Deist F, Fischer A (2000) Gene therapy of human severe combined immune deficiency (SCID)-X1 disease. Science 288:669–672
Chonn A, Cullis PR (1998) Recent advances in liposome technologies and their applications for systemic gene delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 30:73–83
Cho SW, Gwak SJ, Kang SW, Bhang SH, Song KW, Yang YS, Choi CY, Kim BS (2006) Enhancement of angiogenic efficacy of human cord blood cell transplantation. Tissue Eng 12:1651–1661
Christiano R (1998) Viral and non-viral vectors for cancer gene therapy. Anticancer Res 18:3142–3246
Cohen H, Levy RJ, Gao J, Fishbein I, Kousaev V, Sosnowski S, Slomkowski S, Golomb G (2000) Sustained delivery and expression of DNA encapsulated in polymeric nanoparticles. Gene Ther 7:1896–1905
Davidson BL, Stein CS, Heth JA, Martins I, Kotin RM, Derksen TA, Zabner J, Ghodsi A, Chiorini JA (2000) Recombinant adeno-associated virus type 2, 4, and 5 vectors: transduction of variant cell types and regions in the mammalian central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3428–3432
Fischer D, Li Y, Ahlemeyer B, Krieglstein J, Kissel T (2003) In vitro cytotoxicity testing of polycations: influence of polymer structure on cell viability and hemolysis. Biomaterials 24:1121–1131
Gao X, Kim KS, Liu D (2007) Nonviral gene delivery: what we know and what is next. AAPS J 9:E92–E104
Gwak SJ, Choi D, Paik SS, Cho SW, Choi CY, Kim BS (2006) A method for the effective formation of hepatocyte spheroids using a biodegradable polymer nanosphere. J Biomed Mater Res 78A:268–275
Jeon O, Lim HW, Lee M, Song SJ, Kim BS (2007) Poly(L-lactide-co-glycolide) nanospheres conjugated with a nuclear localization signal for delivery of plasmid DNA. J Drug Target 15:190–198
Jiang H, Zhang T, Sun X (2005) Vascular endothelial growth factor gene delivery by magnetic DNA nanospheres ameliorates limb ischemia in rabbits. J Surg Res 126:48–54
Kim YH, Park JH, Lee M, Kim YH, Park TG, Kim SW (2005) Polyethylenimine with acid-labile linkages as a biodegradable gene carrier. J Control Release 103:209–219
Kumar MNVR, Bakowsky U, Lehr CM (2004) Preparation and characterization of cationic PLGA nanospheres as DNA carriers. Biomaterials 25:1771–1777
Labhasetwar V, Bonadio J, Goldstein S, Chen W, Levy RJ (1998) A DNA controlled-release coating for gene transfer: transfection in skeletal and cardiac muscle. J Pharm Sci 87:1347–1350
Lemmouchi Y, Schacht E, Kageruka P, De Deken R, Diarra B, Diall O, Geerts S (1998) Biodegradable polyesters for controlled release of trypanocidal drugs: in vitro and in vivo studies. Biomaterials 19:1827–1837
Panyam J, Zhou WZ, Prabha S, Sahoo SK, Labhasetwar V (2002) Rapid endo-lysosomal escape of poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles: implications for drug and gene delivery. FASEB J 16:1217–1226
Shive MS, Anderson JM (1997) Biodegradation and biocompatibility of PLA and PLGA microspheres. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 28:5–24
Zalba G, San Jose G, Beaumont FJ, Fortuno MA, Fortuno A, Diez J (2001) Polymorphisms and promoter overactivity of the p22(phox) gene in vascular smooth muscle cells from spontaneously hypertensive rats. Circ Res 88:217–222
Yi F, Wu H, Jia GL (2006) Formulation and characterization of poly (d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticle containing vascular endothelial growth factor for gene delivery. J Clin Pharm Ther 31:43–48
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a research fund from Seoul R&BD Program, South Korea. The authors thank Prof. Minhyung Lee at Hanyang University for kindly providing pCMV-Luc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gwak, SJ., Kim, BS. Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanosphere as a vehicle for gene delivery to human cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells: comparison with polyethylenimine. Biotechnol Lett 30, 1177–1182 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-008-9676-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-008-9676-7