Abstract
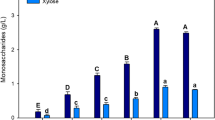
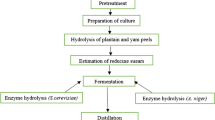
Acid, alkaline and enzymatic hydrolysis of agricultural crop wastes were compared for yields of total reducing sugars with the hydrolysates being evaluated for ethanol production using a mixed culture of Zymomonas mobilis and Candida tropicalis. Acid hydrolysis of fruit and vegetable residues gave 49–84 g reducing sugars l−1 and 29–32 g ethanol l−1 was then obtained. Alkaline hydrolysis did not give significant amount of reducing sugars. Enzymatic hydrolysis of fruit and vegetable residues yielded 36–123 g reducing sugars l−1 and 11–54 g ethanol l−1.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
GM Europe (2002) GM Well-to-wheel analysis of energy use and greenhouse gas emission of advanced fuel/vehicle systems a European study. 27 September 2002. Download at http://www.lbst.de/gm-wtw
Kadam KL (2000) Environmental life cycle implications of using bagasse derived ethanol as a gasoline oxygenaste in Mumbai (Bombay) November 2000
Keating JD, Robinson J, Cotta MA, Saddler JN, Mansfield SD (2004) An ethanologenic yeast exhibiting unusual metabolism in the fermentation of lignocellulosic hexose sugars. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 31:235–244
Reith H, Veenkamp JM, Van Ree R, De Laat WTAM, Niessen JJ, De Jong E, Elbersen HW, Claassen PAM (2001) Coproduction of bioethanol, electricity and heat from biomass wastes: potential and R&D issues. Paper First European Conference on Agriculture & Renewable Energy, 6–8 May 2001, Amsterdam
Ridder DJ (2000) Presentation for the closing meeting of IEA task 26: biotechnology for the conversion of lignocellulosics to ethanol
Sun Y, Cheng J (2002) Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: a review. Biores Technol 83:1–11
Tanaka K, Hilary ZD, Ishizaki A (1999) Investigation of the utility of pineapple juice and pineapple waste material as low-cost substrate for ethanol fermentation by Zymomonas mobilis. J Biosci Bioenergy 87(5):642–646
Wang M, Saricks C, Santini D (1999) Effects of fuel ethanol use on fuel-cycle energy and greenhouse gas emissions. Argonne National Laboratory, Centre for Transportation Research, Energy System Division, ANL/ESD-38
Yu Z, Zhang H (2002) Pretreatment of cellulose pyrolysate for ethanol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Pichia sp. YZ-1 and Zymomonas mobilis. Biomass Bioenergy 24:257–262
Acknowledgement
Authors are thankful to Dr. R. K. Pachauri, DG TERI and Dr. Vibha Dhawan, Vice Chancellor TERI University for providing the infrastructural facilities to execute the present study. Authors are also grateful to Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India for financial support (Grant no. BT/PR2569/AGR/08/183/2001). Authors would like to thank Dr. M.R.V.P. Reddy and Ms. Nitu Sood for their support and technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patle, S., Lal, B. Ethanol production from hydrolysed agricultural wastes using mixed culture of Zymomonas mobilis and Candida tropicalis . Biotechnol Lett 29, 1839–1843 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-007-9493-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-007-9493-4