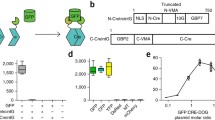
Abstract
A major limitation for the use of Cre recombinase is its toxicity and a lack of temporal control over its activity. We have developed a new recombination system using Cre recombinase α-complementation. Cre recombinase was divided and one fragment (β) was introduced into cells between two loxP sites with a CMV promoter in the upstream. The gene of interest (EGFP) was positioned just downstream of this construct. Cre recombinase activity was recovered by adding the other part of the molecule (α) to cells as a protein fragment, as evidenced by the expression of EGFP under the control of the CMV promoter. The activity of fragmented cre reached 68% of that of the wild type enzyme at 1 μM α-protein.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bothe GW, Haspel JA, Smith CL, Wiener HH, Burden SJ (2000) Selective expression of Cre recombinase in skeletal muscle fibers. Genesis 26:165–166
Casanova E, Lemberger T, Fehsenfeld S, Mantamadiotis T, Schutz G (2003) α complementation in the cre recombinase enzyme. Genesis 37:25–29
Dragatsis I, Zeitlin S (2000) CaMIIalpha–Cre transgene expression and recombination patterns in the mouse brain. Genesis 26:133–135
Feil R, Brocard J, Mascrez B, LeMeur M, Metzger D, Chambon P (1996) Ligand-activated site-specific recombination in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:10887–10890
Gannon M, Shiota C, Postic C, Wright CV, Magnuson M (2000) Analysis of the Cre-mediated recombination driven by rat insulin promoter in embryonic and adult mouse pancreas. Genesis 26:139–142
Garcia EL, Mills A (2002) Getting around lethality with inducible cre-mediated excision. Semin Cell Dev Biol 13:151–158
Huelsken J, Vogel R, Erdmann B, Cotsarelis G, Birchmeier W (2001) Beta-Catenin controls hair follicle morphogenesis and stem cell differentiation in the skin. Cell 105:533–545
Jullien N, Sampieri F, Enjalbert A, Herman JP (2003) Regulation of cre recombinase by ligand-induced complementation of inactive fragments. Nucleic Acids Res 31:e131
Kasim V, Miyagishi M, Taira K (2004) Control of siRNA expression using the cre-loxP recombination system. Nucleic Acids Res 32:e66
Kellendonk C, Tronche F, Monaghan AP, Angrand PO, Stewart F, Schutz G (1996) Regulation of Cre recombinase activity by the synthetic steroid RU 486. Nucleic Acids Res 24:1404–1411
Kuhn R, Schwenk F, Aguet M, Rajewsky K (1995) Inducible gene targeting in mice. Science 269:1427–1429
Le Y, Gagneten S, Tombaccini D, Bethke B, Sauer B (1999) Nuclear targeting determinants of the phage P1 Cre DNA recombinase. Nucleic Acids Res 27:4703–4709
Loonstra A, Vooijs M, Beverloo HB, Al Allak B, Van Drunen E, Kanaar R, Berns A, Jonkers J (2001) Growth inhibition and DNA damage induced by Cre recombinase in mammalian cells. PNAS 98:9209–9214
Mitchell DJ, Kim DT, Steinman L, Fathman CG, Rothbard JB (2000) Polyarginine enters cells more efficiently than other polycationic homopolymers. J Pept Res 56:318–325
Miwa T, Koyama T, Shirai M (2000) Muscle specific expression of Cre recombinase under two actin promoters in transgenic mice. Genesis 26:136–138
Nagy A (2000) Cre recombinase: the universal reagent for genome tailoring. Genesis 26:99–109
Niwa-Kawakita M, Abramowski V, Kalamarides M, Thomas G, Giovannini M (2000) Targeted expression of Cre recombinase to myelinating cells of the central nervous system in transgenic mice. Genesis 26:127–129
Postic C, Magnuson MA (2000) DNA excision in liver by an albumin–Cre transgene occurs progressively with age. Genesis 26:149–150
Sauer B (1998) Inducible gene targeting in mice using the Cre/lox system. Methods 14:381–392
St-Onge L, Furth PA, Gruss P (1996) Temporal control of the Cre recombinase in transgenic mice by a tetracycline responsive promoter. Nucleic Acids Res 24:3875–3877
Utomo AR, Nikitin AY, Lee WH (1999) Temporal, spatial and cell type-specific control of Cre-mediated DNA recombination in transgenic mice. Nature Biotechnol 17:1091–1096
Van den Plas D, Ponsaerts P, Van Tendeloo V, Van Bockstaele DR, Berneman ZN, Merregaert J (2003) Efficien removal of LoxP-Flanked genes by electroporation of Cre-recombinase mRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 305:10–15
Wender PA, Mitchell DJ, Pattabiraman K, Pelkey ET, Steinman L, Rothbard JB (2000) The design, synthesis, and evaluation of molecules that enable or enhance cellular uptake: peptoid molecular transporters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:13003–13008
Will E, Klump H, Heffner N, Schwieger M, Schiedlmeier B, Ostertag W, Baum C, Stocking C (2002) Unmodified cre recombinase crosses the membrane. Nucleic Acids Res 30:e59
Wunderlich FT, Wildner H, Rajewsky K, Edenhofer F (2001) New variants of inducible Cre recombinase: a novel mutant of Cre–PR fusion protein exhibits enhanced sensitivity and an expanded range of inducibility. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e47
Zhang Y, Riesterer C, Ayrall AM, Sablitzky F, Littlewood TD, Reth M (1996) Inducible site-directed recombination in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nucleic Acids Res 24:543–548
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seidi, A., Mie, M. & Kobatake, E. Novel recombination system using Cre recombinase alpha complementation. Biotechnol Lett 29, 1315–1322 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-007-9406-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-007-9406-6