Abstract
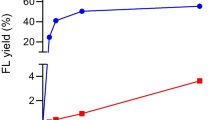
A bioconversion process of producing GM1 (monosialotetrahexosylganglioside) on an industrial scale was developed with a novel sialidase-producing strain Brevibacterium casei. The sialidase hydrolyzed polysialogangliosides to produce GM1 but did not act on GM1. When Brevibacterium casei was cultured in a synthetic medium containing crude pig brain gangliosides (10% w/v) at 30°C for 24 h in a 50 l fermenter, most of the polysialogangliosides were converted to GM1. The content of GM1 was increased from 9% in crude gangliosides to 45% with 70% (w/w) yield.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Z, Lu Y, Zhu C, Zhang G, Jiang J (2002) Neuroprotective effects of ganglioside GM1 on early traumatic brain injury. Acad J Second Mil Med Univ 23:420–422
Fukano Y, Ito M (1997) Preparation of GM1 ganglioside with sialidase-producing marine bacteria as a microbial biocatalyst. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1861–1865
Gandini C, Kitsos M, Massolini G, Delorenzi E, Soldi A, Caccialanza G, Kirschner G (1990) Determination of gangliosides in parenteral dosage form by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Pharm Biomed Anal 8:1063–1066
Ledeen RW, Yu RK (1982) Meth Enzymol 83:139–191
Myers RW, Lee RT, Lee YC, Thomas GH (1985) The synthesis of r-methylumbelliferyl-α-ketoside of N-acetylneuraminic acid and its use in a fluorometric assay for neuraminidase. Anal Biochem 101:166–174
Suzuki K (1965) Pattern of mammalian brain gangliosides. II Evaluation of the extraction procedure, postmortems changes and the effect of formalin preservation. J Neurochem 12:629–663
Svennerholm L, Brane G, Karlsson I, Lekman A, Ramstroem I, Wikkelsoe C (2002) Alzheimer disease - effect of continuous intracerebroventricular treatment with GM1 ganglioside and a systematic activation programme. Demen geriatr cogn Disord 14:128–136
Walkley, Steven U (2003) Neurobiology and cellular pathogenesis of glycolipid storage diseases. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series B: Biological Sciences 358(1433):893–904
Wang X, Yin Z, Peng Y, Shen Y, Wei D (2005) Highly efficient conversion of polysialoganglioside to GM1 with Brevibacterium casei as a microbial biocatalyst. Biocatal Biotransformation 23:29–32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, YF., Wang, XD. & Wei, DZ. Development of a large scale process for the conversion of polysialogangliosides to monosialotetrahexosylganglioside with a novel strain of Brevibacterium casei producing sialidase. Biotechnol Lett 29, 885–889 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-007-9339-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-007-9339-0