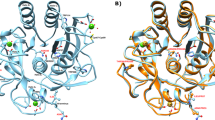
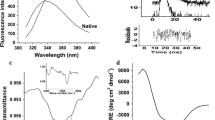
Abstract
We employed random mutagenesis to determine the region of the initial unfolding of hyper-alkaline-sensitive subtilisin, ALP I, that precedes the denaturation of the entire protein under highly alkaline conditions. This region comprises two α-helices and a calcium-binding loop. Stabilization of the region caused the stabilization of the entire protein at a high alkaline pH 12. The alkaline stability of this region was most effectively improved by hydrophobic interactions, followed by ionic interactions with Arg residues. The effect of mutations on the improvement was different with regard to the alkaline stability and thermostability. This indicated that different strategies were necessary to improve the alkaline stability and thermostability of the protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold U, Schierhorn A, Ulbrich-Hofmann R (1999) Modification of the unfolding region in bovine pancreatic ribonuclease and its influence on the thermal stability and proteolytic fragmentation. Eur J Biochem 259:470–475
Betzel C, Klupsch S, Papendorf G et’al (1992) Crystal structure of the alkaline proteinase Savinase from Bacillus lentus at 1.4 A resolution. J Mol Biol 223:427–445
Bryan PN (2000) Protein engineering of subtilisin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1543:203–222
Chang S, Cohen SN (1979) High frequency transformation of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts by plasmid DNA. Mol Gen Genet 168:111–115
Chou K-C, Howe WJ (2002) Prediction of the tertiary structure of the β-secretase zymogen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 292:702–708
Cunningham BC, Wells JA (1987) Improvement in the alkaline stability of subtilisin using an efficient random mutagenesis and screening procedure. Protein Eng 1:319–325
Eijsink VG, Bjork A, Gaseidnes S et’al (2004) Rational engineering of enzyme stability. J Biotechnol 113:105–120
Maeda H, Mizutani O, Yamagata Y et’al (2001) Alkaline-resistance model of subtilisin ALP I, a novel alkaline subtilisin. J Biochem 129:675–682
Mansfeld J, Vriend G, van der Burg B et’al (1999) Probing the unfolding region in a thermolysin-like protease by site-specific immobilization. Biochemistry 38:8240–8245
Makhatadze GI, Loladze VV, Ermolenko DN et’al (2003) Contribution of surface salt bridges to protein stability: guidelines for protein engineering. J Mol Biol 327:1135–1148
Schellenberger A, Ulbrich R (1989) Protein stabilization by blocking the native unfolding nucleus. Biomed Biochim Acta 48:63–67
Shiraishi T, Suzuki A, Yamane T et’al (1997) High-resolution crystal structure of M-protease: phylogeny aided analysis of the high-alkaline adaptation mechanism. Protein Eng 10:627–634
Tange T, Taguchi S, Kojima S et’al (1994) Improvement of a useful enzyme (subtilisin BPN′) by an experimental evolution system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 41:239–244
Yamagata Y, Ichishima E (1989) A new alkaline proteinase with pI 2.8 from alkalophilic Bacillus sp. Curr Microbiol 19:259–264
Yamagata Y, Isshiki K, Ichishima E (1995a) Subtilisin Sendai from alkalophilic Bacillus sp.: molecular and enzymatic properties of the enzyme and molecular cloning and characterization of the gene, aprS. Enzyme Microb Technol 17:653–663
Yamagata Y, Maeda H, Nakajima T et’al (2002) The molecular surface of proteolytic enzymes has an important role in stability of the enzymatic activity in extraordinary environments. Eur J Biochem 269:4577–4585
Yamagata Y, Sato T, Hanzawa S et’al (1995b) The structure of subtilisin ALP I from alkalophilic Bacillus sp. NKS-21. Curr Microbiol 30:201–209
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oguchi, Y., Maeda, H., Abe, K. et al. Hydrophobic interactions between the secondary structures on the molecular surface reinforce the alkaline stability of serine protease. Biotechnol Lett 28, 1383–1391 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-006-9100-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-006-9100-0