Abstract
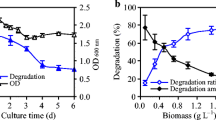
Dibutyl phthalate (DBP) was more efficiently degraded by cutinase compared to yeast esterase; i.e. almost 80% of initial DBP (500 mg l−1) was decomposed within 7.5 h, and nearly 50% of the degraded DBP disappeared within the initial 30 min. The toxicity of the final DBP degradation products were investigated using various recombinant bioluminescent bacteria. Butyl methyl phthalate, the major product of degradation by the esterase, was an oxidative toxic hazard that damaged protein synthesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N Barlow S Phillips D Wallace M Sar K Gaido P Foster (2003) ArticleTitleQuantitative changes in gene expression in fetal rat testes following exposure to di-butylphthalate Toxicol. Sci. 73 431–41 Occurrence Handle10.1093/toxsci/kfg087 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXktVCnsrk%3D Occurrence Handle12700402
S Belkin D Smulski A Vollmer T Dyk ParticleVan R LaRossa (1996) ArticleTitleOxidative stress detection with Escherichia coli harboring a katG′::lux fusion Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62 2252–2256 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XjvFGnsbY%3D Occurrence Handle8779563
C Cartwright S Owen I Thompson R Burns (2000) ArticleTitleBiodegradation of diethyl phthalate in soil by a novel pathway FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 186 27–34 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-1097(00)00111-7 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXisFGltrY%3D Occurrence Handle10779708
C Carvalho M Aires-Barros J Cabral (1999) ArticleTitleCutinase: from molecular level to bioprocess development Biotechnol. Bioeng. 66 17–34 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(1999)66:1<17::AID-BIT2>3.0.CO;2-F Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXnslKqsr0%3D Occurrence Handle10556791
S Choi M Gu (2001) ArticleTitlePhenolic toxicity -- Detection and classification through the use of a recombinant bioluminescent Escherichia coli Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 20 248–255 Occurrence Handle10.1897/1551-5028(2001)020<0248:PTDACT>2.0.CO;2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXnsV2ltg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11351423
J Flipsen A Appel H Hijden ParticleVan der C Verrips (1998) ArticleTitleMechanism of removal of immobilized triacylglycerol by lipolytic enzymes in a sequential laundry wash process Enzyme Microb. Technol. 23 274–280 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0141-0229(98)00050-7 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXlsFOgur4%3D
M Gu J Min E Kim (2002) ArticleTitleTocixity monitoring and classification of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals (EDCs) using recombinant bioluminescent bacteria Chemosphere 46 289–294 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00081-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXpt1ahsL4%3D Occurrence Handle11827287
C Harris P Henttu M Parker J Sumpter (1997) ArticleTitleThe estrogenic activity of phthalate esters in vitro Environ. Health Perspect. 105 802–810 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXnt1GjurY%3D Occurrence Handle9347895
Kolattukudy P,Purdy R,Maiti I,1981,Cutinase from fungi and pollen,Lowenstein J.M,Academics,New York,652-664
J Min E Kim R LaRossa M Gu (1999) ArticleTitleDistinct responses of a recA::luxCDABE Escherichia coli strain to direct and indirect DNA damaging agents Mutat. Res. 442 61–68 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjs1Sgsb0%3D Occurrence Handle10393274
E Mylchreest M Sar R Cattley P Foster (1999) ArticleTitleDisruption of androgen-regulated male reproductive development by di (n-butyl) phthalate during late gestation in rats is different from flutamide Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 156 81–95 Occurrence Handle10.1006/taap.1999.8643 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXit1yktbw%3D Occurrence Handle10198273
T Van Dyk D Smulski T Reed S Belkin A Vollmer R LaRossa (1995) ArticleTitleResponses to toxicants of an Escherichia coli strain carrying a uspA′::lux genetic fusion and an E.coli strain carrying a grpE′::lux fusion are similar Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61 4124–4127 Occurrence Handle8526529
A Vollmer S Belkin D Smulski T Dyk ParticleVan R LaRossa (1997) ArticleTitleDetection of DNA damage by use of Escherichia coli Carrying recA::lux, uvrA::lux, or alkA::lux reporter plamids Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63 2566–2571 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXktlers7c%3D Occurrence Handle9212407
R Wine L Li L Barnes D Gulati R Chapin (1997) ArticleTitleReproductive toxicity of di-n-butylphthalate in a continuous breeding protocol in Sprague--Dawley rats Environ. Health Perspect. 105 102–107 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXitleitb0%3D Occurrence Handle9074889
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, YH., Lee, J. Enzymatic degradation of dibutyl phthalate and toxicity of its degradation products . Biotechnol Lett 27, 635–639 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-005-3631-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-005-3631-7