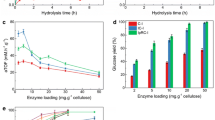
Abstract
Peptides (MW < 5 kDa) produced by 57 cellulolytic fungi can form free radicals. Scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) and IR spectroscopy showed that the peptide produced by Trichoderma pseudokoningii can break the hydrogen bond network of cellulose. The synergic action of these peptides and cellulases increased production of reducing sugars during degradation of native cellulose.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A Enoki H Tanaka G Fuse (1989) ArticleTitleRelationship between degradation of wood and production of H2O2 producing one-electron oxidases by brown-rot fungi Wood Sci. Technol. 23 1–12
PJ Gao (2003) ArticleTitleStudy progress in the mechanism of cellulase degradation and the structure and function of cellulase molecules Prog. Nat. Sci. 13 21–29
PJ Gao GJ Chen TH Wang YS Zhang J Liu (2001) ArticleTitleNon-hydrolytic disruption of crystalline structure of cellulose by cellulose binding domain and linker sequence of cellobiohydrolase from Penicillium janthinellum Acta Biochem. Biophys. Sin. 33 13–18
PJ Gao YB Qu X Zhao MT Zhu YC Duan (1997) ArticleTitleScreening microbial strain for improving the nutritional value of wheat and corn straws as animal feed Enzyme Microb. Tech. 20 581–584
B Halliwell JMC Gutteridge (1985) Hydroxyl radicals assayed by aromatic hydroxylation and deoxyribose degradation RA Greenwald (Eds) Handbook of Methods for Oxygen Radical Research CRC Press Boca Raton 177–180
J Liu XY Shen PJ Gao (1996) ArticleTitleShot fibre formation during cellulose degradation by cellulolytic fungi Biotechnol. Lett. 18 1235–1240
W Wang PJ Gao (2002) ArticleTitleA peptide-mediated and hydroxyl radical HO involved oxidative degradation of cellulose by brown-rot fungi Biodegradation 13 383–394
W Wang PJ Gao (2003) ArticleTitleFunction and mechanism of a low-molecular-weight peptide produced by Gloeophyllum trabeum in biodegradation of cellulose J. Biotechnol. 101 119–130
W Wang J Liu GJ Chen YS Zhang PJ Gao (2003) ArticleTitleFunction of a low molecular weight peptide from Trichoderma pseudokoningii S38 during cellulose biodegradation Curr. Microbiol. 46 371–379
YZ Zhang J Liu PJ Gao (1997) ArticleTitleStudy of super-microstructure of native cellulose by scanning tunnel electron microscope J. Electr. Microsc. 16 736–739
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, W., Liu, J., Wang, W. et al. Function of a low molecular peptide generated by cellulolytic fungi for the degradation of native cellulose. Biotechnol Lett 26, 1799–1802 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-004-4612-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-004-4612-y