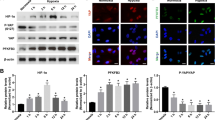
Abstract
In the present study, our aim was to explore the role of MUC4 in IL-4-stimulated conjunctival epithelial cells and the underlying mechanisms. Human recombinant IL-4 was employed in human conjunctival epithelial cells (HConEpic) cells, and MUC4 shRNA (sh-MUC4) was constructed to explore the functional role of MUC4. The protein level of MUC4, O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT), O-GlcNAc hydrolase (OGA), zonula occludens 1 (ZO-1), gap junction protein beta 2 (GJB2), claudin-8 (CLDN8), and E-cadherin were detected by Western blot in HConEpic cells, the interaction between MUC4 and OGT/OGA was assessed by co-immunoprecipitation (IP) and Western blot in 293T cells. Our results showed that IL-4 significantly up-regulated MUC4 and OGT protein levels in HConEpic cells, while down-regulated OGA protein level. Also, IL-4 down-regulated ZO-1, GJB2, CLDN8, and E-cadherin protein levels in HConEpic cells, while which was markedly reversed by sh-MUC4. Additionally, OGT inhibitor significantly reduced MUC4 protein level, and elevated ZO-1, GJB2, CLDN8, and E-cadherin protein levels in HConEpic cells, while OGA inhibitor resulted in the opposite results. Furthermore, in addition to the interaction between OGT/OGA and MUC4, Co-IP and Western blot also revealed the alteration of MUC4 O-GlcNAcylation in 293T cells treated with OGT/OGA inhibitor. Above findings suggested that OGT/OGA inhibitor regulated MUC4 protein level by affecting MUC4 O-GlcNAcylation to regulate ZO-1, GJB2, CLDN8, and E-cadherin protein levels in HConEpic cells, which was achieved via inhibiting the interaction between OGT/OGA and MUC4. This study may provide a better understanding of the pathogenesis of allergic conjunctivitis (AC).
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The supporting data used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author.
References
Ablamowicz AF, Nichols JJ (2016) Ocular surface membrane-associated mucins. Ocul Surf 14:331–341
Bhatia R et al (2023) Muc4 loss mitigates epidermal growth factor receptor activity essential for PDAC tumorigenesis. Oncogene 42:759–770. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02587-1
Brockhausen I, Yang JM, Burchell J, Whitehouse C, Taylor-Papadimitriou J (2010) Mechanisms underlying aberrant glycosylation of MUC1 mucin in breast cancer cells. FEBS J 233:607–617
Das S, Rachagani S, Sheinin Y, Smith LM, Gurumurthy CB, Roy HK, Batra SK (2016) Mice deficient in Muc4 are resistant to experimental colitis and colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Oncogene 35:2645–2654
Doan Ü, Aca S (2018) Investigation of possible risk factors in the development of seasonal allergic conjunctivitis. Int J Ophthalmol 11:78–83
Dogru M et al (2010) Alterations of the ocular surface epithelial mucins 1, 2, 4 and the tear functions in patients with atopic keratoconjunctivitis. Clin Exp Allergy 36:1556–1565
Elbatrawy AA, Kim EJ, Nam G (2020) O-GlcNAcase: emerging mechanism, substrate recognition and small-molecule inhibitors. ChemMedChem 15:1244–1257
Fauquert JL (2019) Diagnosing and managing allergic conjunctivitis in childhood: the allergist’s perspective. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 30:405–414
Hanson RL, Hollingsworth MA (2016) Functional consequences of differential O-glycosylation of MUC1, MUC4, and MUC16 (downstream effects on signaling). Biomolecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom6030034
Hennebicq-Reig S, Soudan BT, Tetaert D, Briand G, Richet C, Demeyer D, Degand P (1996) Capillary electrophoresis separation of mucin motif MUC 5AC glycopeptides from in vitro O-glycosylation reactions. Carbohydr Res 280:121–126
Horinaka M, Shoji J, Tomioka A, Tonozuka Y, Inada N, Yamagami S (2021) Alterations in mucin-associated gene expression on the ocular surface in active and stable stages of atopic and vernal keratoconjunctivitis. J Ophthalmol 2021:9914786
Irimura T, Denda K, Iida SI, Takeuchi H, Kato K (1999) Diverse glycosylation of MUC1 and MUC2: potential significance in tumor immunity. J Biochem 126:975–985
Kunert KS, Keane-Myers AM, Spurr-Michaud S, Tisdale AS, Gipson IK (2001) Alteration in goblet cell numbers and mucin gene expression in a mouse model of allergic conjunctivitis. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 42:2483–2489
Leonardi A, Daull P, Rosani U, Cavarzeran F, Salami E, Garrigue JS, Paola B (2022) Evidence of epithelial remodelling but not epithelial-mesenchymal transition by transcriptome profiling in vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Allergy 77:3460–3462
Li Y, Li R, Liu ZC (2014) Analysis of the correlation between tear film changes of allergic conjunctivitis and dry eye. Int Eye Sci 14:1272–1274
Li CL et al (2017a) Fibronectin induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells via activation of calpain. Oncol Lett 13:3889–3895
Li Y et al (2017b) O-GlcNAcylation modulates Bmi-1 protein stability and potential oncogenic function in prostate cancer. Oncogene 36:6293–6305
Liu J, Xing R, Shao J, Jiao S (2023) Relationship between MUC4 variants and metastatic recurrence in colorectal cancer. Int J Gen Med 16:5077–5087. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijgm.s437957
Martinez-Carrasco R, Argüeso P, Fini ME (2021) Membrane-associated mucins of the human ocular surface in health and disease. Ocul Surf 21:313–330
Martinez-Carrasco R, Rachagani S, Batra SK, Argüeso P, Fini ME (2023) Roles unveiled for membrane-associated mucins at the ocular surface using a Muc4 knockout mouse model. Sci Rep 13:13558. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-40491-0
Mukhopadhyay P et al (2013) MUC4 overexpression augments cell migration and metastasis through EGFR family proteins in triple negative breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 8:e54455
Nie H, Yi W (2019) O-GlcNAcylation, a sweet link to the pathology of diseases. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 20:437–448. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1900150
Pai P et al (2015) The canonical Wnt pathway regulates the metastasis-promoting mucin MUC4 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mol Oncol 10:224–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molonc.2015.10.005
Pflugfelder SC, Liu Z, Monroy D, Li DQ, Carraway KL (2000) Detection of sialomucin complex (MUC4) in human ocular surface epithelium and tear fluid. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41:1316–1326
Stephen HM, Adams TM, Lance W (2021) Regulating the regulators: mechanisms of substrate selection of the O-GlcNAc cycling enzymes OGT and OGA. Glycobiology 31:724–733
Wang Y et al (2017) O-GlcNAcylation destabilizes the active tetrameric PKM2 to promote the Warburg effect. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:13732–13737
Ya QI, Qian WU, Gang YU (2015) Tear film stability in allergic conjunctivitis children without symptoms of dry eye. Ophthalmol China 94:e1648
Ying L et al (2012) Developmental regulation of protein O-GlcNAcylation, O-GlcNAc transferase, and O-GlcNAcase in mammalian brain. PLoS ONE 7:e43724
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WWX designed the study and drafted the paper; WWX, ZJO, YT performed the experiments; LWX, XWP analyzed the data; XWP revised the paper. All authors read and approved the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
All authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Human Ethics
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, WW., Ouyang, ZJ., Tan, Y. et al. MUC4 O-GlcNAcylation Regulates the Epithelial Phenotype in Conjunctival Epithelial Cells. Biochem Genet (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-024-10791-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-024-10791-9