Abstract
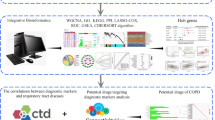
Sjogren’s syndrome (SS) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by dry mouth and dry eyes. Its pathogenic mechanism is currently unclear. This study aims to integrate weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) and machine learning to identify key genes associated with SS. We downloaded 3 publicly available datasets from the GEO database comprising the gene expression data of 231 SS and 78 control cases, including GSE84844, GSE48378 and GSE51092, and carried out WGCNA to elucidate differences in the abundant genes. Candidate biomarkers for SS were then identified using a LASSO regression model. Totally 6 machine-learning models were subsequently utilized for validating the biological significance of major genes according to their expression. Finally, immune cell infiltration of the SS tissue was assessed using the CIBERSORT algorithm. A weighted gene co-expression network was built to divide genes into 10 modules. Among them, blue and red modules were most closely associated with SS, and showed significant enrichment in type I interferon signaling, cellular response to type I interferon and response to virus, etc. Combined machine learning identified 5 hub genes, including OAS1, EIF2AK2, IFITM3, TOP2A and STAT1. Immune cell infiltration analysis showed that SS was associated with CD8+ T cell, CD4+ T cell, gamma delta T cell, NK cell and dendritic cell activation. WGCNA was combined with machine learning to uncover genes that may be involved in SS pathogenesis, which can be utilized for developing SS biomarkers and appropriate therapeutic targets.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included in GEO.
References
Bedford JG, O’Keeffe M, Reading PC, Wakim LM (2019) Rapid interferon independent expression of IFITM3 following T cell activation protects cells from influenza virus infection. PLoS One 14(1):e0210132. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0210132
Chen L, Lu D, Sun K, Xu Y, Hu P, Li X, Xu F (2019) Identification of biomarkers associated with diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer patients based on integrated bioinformatics analysis. Gene 692:119–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2019.01.001
Cornec D, Jamin C, Pers JO (2014) Sjögren’s syndrome: where do we stand, and where shall we go? J Autoimmun 51:109–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2014.02.006
Delaleu N, Nguyen CQ, Tekle KM, Jonsson R, Peck AB (2013) Transcriptional landscapes of emerging autoimmunity: transient aberrations in the targeted tissue’s extracellular milieu precede immune responses in Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Res Ther 15(5):R174. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar4362
Fang K, Zhang K, Wang J (2015) Network-assisted analysis of primary Sjögren’s syndrome GWAS data in Han Chinese. Sci Rep 5:18855. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18855
Fernandez-Ruiz R, Niewold TB (2022) Type I interferons in autoimmunity. J Invest Dermatol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2021.11.031
Gandolfo S, De Vita S (2019) Emerging drugs for primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 24(2):121–132. https://doi.org/10.1080/14728214.2019.1634052
Gao L, Zhang LJ, Li SH, Wei LL, Luo B, He RQ, Xia S (2018) Role of miR-452-5p in the tumorigenesis of prostate cancer: a study based on the cancer genome Atl(TCGA), gene expression omnibus (GEO), and bioinformatics analysis. Pathol Res Pract 214(5):732–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2018.03.002
Guha M, Saare M, Maslovskaja J, Kisand K, Liiv I, Haljasorg U, Peterson P (2017) DNA breaks and chromatin structural changes enhance the transcription of autoimmune regulator target genes. J Biol Chem 292(16):6542–6554. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.764704
Kang X, Song C, Du X, Zhang C, Liu Y, Liang L, Yin Y (2015) PTEN stabilizes TOP2A and regulates the DNA decatenation. Sci Rep 5:17873. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17873
Kühnl A, Musiol A, Heitzig N, Johnson DE, Ehrhardt C, Grewal T, Rescher U (2018) Late endosomal/lysosomal cholesterol accumulation is a host cell-protective mechanism inhibiting endosomal escape of influenza A virus. mBio. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01345-18
Langfelder P, Horvath S (2008) WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform 9:559. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-9-559
Li H, Reksten TR, Ice JA, Kelly JA, Adrianto I, Rasmussen A, Sivils KL (2017) Identification of a Sjögren’s syndrome susceptibility locus at OAS1 that influences isoform switching, protein expression, and responsiveness to type I interferons. PLoS Genet 13(6):e1006820. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006820
Li W, Zhao Y, Wang D, Ding Z, Li C, Wang B, Yuan B (2021) Transcriptome research identifies four hub genes related to primary myelofibrosis: a holistic research by weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Aging (Albany NY) 13(19):23284–23307. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.203619
Liu Z, Chu A (2021) Sjögren’s Syndrome and viral infections. Rheumatol Ther 8(3):1051–1059. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40744-021-00334-8
Liu Y, Ma J, Song JS, Zhou HY, Li JH, Luo C, Zhao HX (2022) DNA topoisomerase II alpha promotes the metastatic characteristics of glioma cells by transcriptionally activating β-catenin. Bioengineered 13(2):2207–2216. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.2023985
Lopez Velazquez M, Highland KB (2018) Pulmonary manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjögren’s syndrome. Curr Opin Rheumatol 30(5):449–464. https://doi.org/10.1097/bor.0000000000000531
Mavragani CP (2017) Mechanisms and new strategies for primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Annu Rev Med 68:331–343. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-med-043015-123313
Morimoto S, Tsuda M, Bunch H, Sasanuma H, Austin C, Takeda S (2019) Type II DNA topoisomerases cause spontaneous double-strand breaks in genomic DNA. Genes (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10110868
Nikolov NP, Illei GG (2009) Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s syndrome. Curr Opin Rheumatol 21(5):465–470. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOR.0b013e32832eba21
Retamozo S, Brito-Zerón P, Ramos-Casals M (2019) Prognostic markers of lymphoma development in primary Sjögren syndrome. Lupus 28(8):923–936. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203319857132
Seo GS, Lee JK, Yu JI, Yun KJ, Chae SC, Choi SC (2010) Identification of the polymorphisms in IFITM3 gene and their association in a Korean population with ulcerative colitis. Exp Mol Med 42(2):99–104. https://doi.org/10.3858/emm.2010.42.2.011
Seror R, Ravaud P, Bowman SJ, Baron G, Tzioufas A, Theander E, Vitali C (2010) EULAR Sjogren’s syndrome disease activity index: development of a consensus systemic disease activity index for primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 69(6):1103–1109. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.110619
Stefanski AL, Tomiak C, Pleyer U, Dietrich T, Burmester GR, Dörner T (2017) The diagnosis and treatment of Sjögren’s syndrome. Dtsch Arztebl Int 114(20):354–361. https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2017.0354
Sutormin DA, Galivondzhyan AK, Polkhovskiy AV, Kamalyan SO, Severinov KV, Dubiley SA (2021) Diversity and functions of type II topoisomerases. Acta Naturae 13(1):59–75. https://doi.org/10.32607/actanaturae.11058
Tao Z, Shi A, Li R, Wang Y, Wang X, Zhao J (2017) Microarray bioinformatics in cancer- a review. J buon 22(4):838–843
Thalayasingam N, Baldwin K, Judd C, Ng WF (2021) New developments in Sjogren’s syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford) 60(Supplement_6):vi53–vi61. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keab466
Umazume T, Thomas WM, Campbell S, Aluri H, Thotakura S, Zoukhri D, Makarenkova HP (2015) Lacrimal gland inflammation deregulates extracellular matrix remodeling and alters molecular signature of epithelial stem/progenitor cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 56(13):8392–8402. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.15-17477
Wellington D, Yin Z, Abdel-Haq A, Zhang L, Forbester J, Kite K, Dong T (2021) IFITM3-specific antibody reveals IFN preferences and slow IFN induction of the antiviral factor IFITM3 in humans. Eur J Immunol 51(3):742–745. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.202048706
Weng W, Zhang Z, Huang W, Xu X, Wu B, Ye T, Lin Z (2020) Identification of a competing endogenous RNA network associated with prognosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell Int 20:231. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-01243-6
Wu F, Dassopoulos T, Cope L, Maitra A, Brant SR, Harris ML, Chakravarti S (2007) Genome-wide gene expression differences in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis from endoscopic pinch biopsies: insights into distinctive pathogenesis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 13(7):807–821. https://doi.org/10.1002/ibd.20110
Wu W, Chen Y, Huang L, Li W, Tao C, Shen H (2020) Effects of AKT1 E17K mutation hotspots on the biological behavior of breast cancer cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 13(3):332–346
Wu H, Chen X, Gu F, Zhang P, Xu S, Liu Q, Wei W (2021) CP-25 alleviates antigen-induced experimental Sjögren’s syndrome in mice by inhibiting JAK1-STAT1/2-CXCL13 signaling and interfering with B-cell migration. Lab Invest 101(8):1084–1097. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41374-020-0453-0
Xu J, Yang Y, Chen D, Lu Z, Ge J, Li X, Gao X (2021) Co-Existence of sarcoidosis and Sjögren’s syndrome with hypercalcemia and renal involvement: a case report and literature review. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 21(4):768–776. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871530320666200619133654
Yánez DC, Sahni H, Ross S, Solanki A, Lau CI, Papaioannou E, Crompton T (2019) IFITM proteins drive type 2 T helper cell differentiation and exacerbate allergic airway inflammation. Eur J Immunol 49(1):66–78. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201847692
Yánez DC, Ross S, Crompton T (2020) The IFITM protein family in adaptive immunity. Immunology 159(4):365–372. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.13163
Yang J, Wang J, Tian S, Wang Q, Zhao Y, Wang B, Ma J (2021) An integrated analysis of tumor purity of common central nervous system tumors in children based on machine learning methods. Front Genet 12:707802. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.707802
Yao Q, Song Z, Wang B, Qin Q, Zhang JA (2019) Identifying key genes and functionally enriched pathways in Sjögren’s syndrome by weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Front Genet 10:1142. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.01142
Yu R, Zhang J, Zhuo Y, Hong X, Ye J, Tang S, Zhang Y (2021) Identification of diagnostic signatures and immune cell infiltration characteristics in rheumatoid arthritis by integrating bioinformatic analysis and machine-learning strategies. Front Immunol 12:724934. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.724934
Zhao J, Guo C, Ma Z, Liu H, Yang C, Li S (2020) Identification of a novel gene expression signature associated with overall survival in patients with lung adenocarcinoma: a comprehensive analysis based on TCGA and GEO databases. Lung Cancer 149:90–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.09.014
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Funding
Nature Science Foundation of Hainan (823QN254, China); Nature Science Foundation of Shanghai (21ZR1449200, China); The New Interdisciplinary Subjects of Pudong New District Health Committee, grant number (PWXx2020-04, China); Shanghai Pujiang Program (13PJC004); Innovation research team of high-level local universities in Shanghai (SHSWU-ZDCX20212801).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DMX and CW conceived and designed the study. QL and KWW and HL prepared the manuscript, and had equal contribution to the study. HW prepared the tables and Figs. DMX, CW, QL and KWW reviewed and revised the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This study does not involve animal and/or human tissue/individual data/participants, resulting in no ethics-related issues. No permissions were required to collect any repository data involved in the present study.
Consent for Publication
All authors agree to publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Q., Wu, K., Li, H. et al. Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis and Machine Learning Validation for Identifying Major Genes Related to Sjogren’s Syndrome. Biochem Genet (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-024-10750-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-024-10750-4