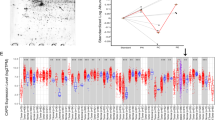
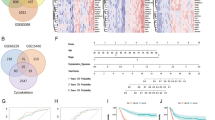
Abstract
Phospholipase C Beta 1 (PLCB1) regulates the abundance of PI(4,5)P2 in the plasma membrane and is implicated in various kinds of cancers. This study aimed to investigate the role and underlying mechanisms of PLCB1 in gastric cancer. Herein, it was found that PLCB1 mRNA and protein were highly expressed in gastric cancer, and high levels of PLCB1 were correlated with poor outcomes of patients with gastric cancer via the GEPIA database. Moreover, our results revealed that PLCB1 depletion inhibited gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Meanwhile, PLCB1 overexpression resulted in an inverse result. Furthermore, PLCB1 mediated actin cytoskeleton rearrangement and activated the RhoA/LIMK/Cofilin pathway. Besides, PLCB1 promoted the Epithelial–Mesenchymal transition process via activating ATK signaling. In conclusion, PLCB1 promoted gastric cancer cell migratory and invasive abilities via regulating actin cytoskeleton rearrangement and Epithelial–Mesenchymal transition process. These findings imply that targeting PLCB1 may be a potential strategy to improve the prognosis of gastric cancer patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azadi S, Mohammadi E, Tafazzoli-Shadpour M, Tabatabaei M (2022) Effects of chemically EGFR targeting on non-targeted physical cell behaviors in 2D and 3D microfluidic cultures of invasive and non-invasive breast cancer cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 622:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.07.013
Baj J, Korona-Głowniak I (2020) Mechanisms of the Epithelial–Mesenchymal transition and tumor microenvironment in helicobacter pylori-induced gastric cancer. Cells 9:1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9041055
Banik I, Ghosh A (2023) P38 mediates tumor suppression through reduced autophagy and actin cytoskeleton changes in NRAS-mutant melanoma. Cancers 15:877. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030877
Dahl EF, Wu SC, Healy CL, Harsch BA, Shearer GC, O’Connell TD (2018) Subcellular compartmentalization of proximal Gα(q)-receptor signaling produces unique hypertrophic phenotypes in adult cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem 293:8734–8749. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.002283
Desprairies C, Valence S, Maurey H, Helal SI, Weckhuysen S, Soliman H, Mefford HC, Spentchian M, Héron D, Leguern E, Nava C, Bouilleret V, Moretti R, Mignot C (2020) Three novel patients with epileptic encephalopathy due to biallelic mutations in the PLCB1 gene. Clin Genet 97:477–482. https://doi.org/10.1111/cge.13696
Ha SD, Lewin N, Li SSC, Kim SO (2021) HDAC8 activates AKT through upregulating PLCB1 and suppressing DESC1 expression in MEK1/2 inhibition-resistant cells. Cells 10:1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051101
Janmey PA, Bucki R, Radhakrishnan R (2018) Regulation of actin assembly by PI(4,5)P2 and other inositol phospholipids: an update on possible mechanisms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 506:307–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.07.155
Kankanamge D, Ubeysinghe S, Tennakoon M, Pantula PD, Mitra K, Giri L, Karunarathne A (2021) Dissociation of the G protein βγ from the Gq-PLCβ complex partially attenuates PIP2 hydrolysis. J Biol Chem 296:100702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100702
Li J, Zhao X, Wang D, He W, Zhang S, Cao W, Huang Y, Wang L, Zhou S, Luo K (2016) Up-regulated expression of phospholipase C, β1 is associated with tumor cell proliferation and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther 9:1697–1706. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s97189
Li S, Cong X, Gao H, Lan X, Li Z, Wang W, Song S, Wang Y, Li C, Zhang H, Zhao Y, Xue Y (2019) Tumor-associated neutrophils induce EMT by IL-17a to promote migration and invasion in gastric cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-1003-0
Liang S, Guo H, Ma K, Li X, Wu D, Wang Y, Wang W, Zhang S, Cui Y, Liu Y, Sun L, Zhang B, Xin M, Zhang N, Zhou H, Liu Y, Wang J, Liu L (2021) A PLCB1-PI3K-AKT signaling axis activates EMT to promote cholangiocarcinoma progression. Cells 81:5889–5903. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells1005110110.1158/0008-5472.can-21-1538
Lu G, Chang JT, Liu Z, Chen Y, Li M, Zhu JJ (2016) Phospholipase C beta 1: a candidate signature gene for proneural subtype high-grade glioma. Mol Neurobiol 53:6511–6525. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201701284R10.1007/s12035-015-9518-2
Lu ML, Zhang Y, Li J, Fu Y, Li WH, Zhao GF, Li XH, Wei L, Liu GB, Huang H (2019) MicroRNA-124 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation and suppresses tumor growth by interacting with PLCB1 and regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23:121–136. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201901_16756
Ratti S, Marvi MV, Mongiorgi S, Obeng EO, Rusciano I, Ramazzotti G, Morandi L, Asioli S, Zoli M, Mazzatenta D, Suh PG, Manzoli L, Cocco L (2022) Impact of phospholipase C β1 in glioblastoma: a study on the main mechanisms of tumor aggressiveness. Cell Mol Life Sci 79:195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-022-04198-1
Sengelaub CA, Navrazhina K, Ross JB, Halberg N, Tavazoie SF (2016) PTPRN2 and PLCβ1 promote metastatic breast cancer cell migration through PI(4,5)P2-dependent actin remodeling. Cells 35:62–76. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells1005110110.15252/embj.201591973
Strassheim D, Shafer SH, Phelps SH, Williams CL (2000) Small cell lung carcinoma exhibits greater phospholipase C-beta1 expression and edelfosine resistance compared with non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Res 60:2730–2736
Wang H, Xia Y, Zhang Y (2021) Diagnostic significance of serum lncRNA HOTAIR and its predictive value for the development of chronic complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetol Metab Syndr 13:97. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-021-00719-3
Wang H, Luo Y, Ou S, Ni T, Chu Z, Feng X, Dai X, Zhang X, Liu Y (2023) Celastrus orbiculatus Thunb. extract inhibits EMT and metastasis of gastric cancer by regulating actin cytoskeleton remodeling. Cancers (Basel) 301:115737. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers1503087710.1016/j.jep.2022.115737
Wei W, Cappellini A, Mongiorgi S, Finelli C, Fazio A, Ratti S, Marvi MV, Curti A, Salvestrini V, Pellagatti A, Billi AM, Suh PG, McCubrey JA, Boultwood J, Manzoli L, Cocco L, Follo MY (2020) Phospholipase C beta1 (PI-PLCbeta1)/Cyclin D3/protein kinase C (PKC) alpha signaling modulation during iron-induced oxidative stress in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Cancer Cell Int 34:15400–15416. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-021-02261-810.1096/fj.202000933RR
Wong MCS, Huang J, Chan PSF, Choi P, Lao XQ, Chan SM, Teoh A, Liang P (2021) Global Incidence and Mortality of Gastric Cancer, 1980–2018. JAMA Netw Open 4:e2118457. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.18457
Xu ZW, Liu NN, Wang XY, Ding BC, Zhang HF, Li Y, Sun WY (2021) Effect of PLC-β1/CaM signaling pathway mediated by AT1R on the occurrence and development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int 21:587. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-021-02261-8
Zhang T, Song X, Liao X, Wang X, Zhu G, Yang C, Xie X (2019) Distinct prognostic values of phospholipase C beta family members for non-small cell lung carcinoma. BioMed Res Int 2019:4256524. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4256524
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YW and ZT participated in the design of the study and drafted the manuscript. WZ, LW, JJ, LG, and ML helped with study data collection and manuscript preparation. LJ, YW, ZT and YB conceived the study, participated in its design and coordination, and helped to draft the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All of the authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Ethical Approval
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Tianjin Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated Hospital.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Tu, Z., Zhao, W. et al. PLCB1 Enhances Cell Migration and Invasion in Gastric Cancer Via Regulating Actin Cytoskeletal Remodeling and Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Biochem Genet 61, 2618–2632 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10396-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10396-8