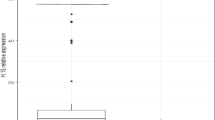
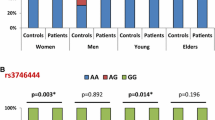
Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, progressive, inflammatory, autoimmune disease that could be disabling throughout its course. It affects people in their most reproductive years with relatively high morbidity and mortality. Long non-coding RNAs became one of the epigenetic mechanisms to prove a link to RA pathogenesis and development, including H19 and MALAT1 genes. These two genes’ expressions had proved to increase in multiple diseases, attracting attention to their polymorphisms and their possible risk role. Assess the association between H19 SNP (rs2251375) and MALAT1 SNP (rs3200401) and the susceptibility of RA and its disease activity. In this pilot study, 200 hundred subjects (100 RA patients and 100 healthy controls) were investigated for a possible link between the polymorphisms H19 SNP (rs2251375) and MALAT1 SNP (3200401) and RA susceptibility and disease activity. RA-related investigations and clinical assessment were done. Real-time PCR genotyping of both SNPs was done using TaqMan® MGB probes. There was no association between the SNPs and risk of developing RA. However, both SNPs had a significant association with high disease activity. H19 SNP (rs2251375) heterozygous genotype CA had an association with elevated levels of ESR (p = 0.04) and higher DAS28-ESR score (p = 0.03). MALAT1 (rs3200401) C allele had an association with elevated ESR (p = 0.001), DAS28-ESR (p = 0.03), and DAS28-CRP (p = 0.007), while CC genotype had an association with DAS28-CRP (p = 0.015). Linkage disequilibrium and haplotyping of the alleles of both SNPs were analyzed as both genes are present on chromosome 11, but no significant association was found between any of the combinations of the alleles (p > 0.05), denoting that (rs2251375) and (rs3200401) are not in linkage disequilibrium. There is no association between H19 SNP (rs2251375) and MALAT1 SNP (rs3200401) and the susceptibility of RA. However, there is an association between H19 SNP (rs2251375) genotype CA and MALAT1 SNP (rs3200401) genotype CC with RA high disease activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO et al (2010) 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 62(9):2569–2581
Bouwland-Both MI, Van Mil NH, Stolk L, Eilers PHC, Verbiest MMPJ, Heijmans BT et al (2013) DNA methylation of IGF2DMR and H19 is associated with fetal and infant growth: the generation R study. PLoS ONE 8(12):e81731. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0081731
Bullock J, Rizvi SAA, Saleh AM, Ahmed SS, Do DP, Ansari RA et al (2019) Rheumatoid arthritis: a brief overview of the treatment. Med Princ Pract 27(6):501–507
Calabresi E, Petrelli F, Bonifacio AF, Puxeddu I, Alunno A (2018) One year in review 2018: pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 36:175–184
Chen X, Luo X, Wei Y, Sun H, Dai L, Tangzhou Y et al (2021) LncRNA H19 induces immune dysregulation of BMMSCs, at least partly, by inhibiting IL-2 production. Mol Med. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10020-021-00326-y
Ding LL, Li X, Lei YM, Xia LP, Lu J, Shen H (2020) Effect of interleukin-34 on secretion of angiogenesis cytokines by peripheral blood mononuclear cells of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Investig 49(1–2):81–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/08820139.2019.1649281
Eftekharian MM, Noroozi R, Komaki A, Mazdeh M, Ghafouri-Fard S, Taheri M (2019) MALAT1 genomic variants and risk of multiple sclerosis. Immunol Investig 48(5):549–554. https://doi.org/10.1080/08820139.2019.1576728
El-Ghany NSA, Siam IM, Monir AM (2019) Gender impact on rheumatoid arthritis disease characteristics in a cohort of Egyptian patients. Med J Cairo Univ 87(3):1895–9
El Saman A, Mohamed ER, Khalifa A, Meghezel ZM, Radwan ARA (2020) Evaluation of awareness, knowledge and attitudes regarding common rheumatic diseases (rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematous) in Sohag Governorate. Egypt J Community Med 38(2):25–36
Elwazir MY, Hussein MH, Toraih EA, Al Ageeli E, Esmaeel SE, Fawzy MS et al (2022) Association of angio-LncRNAs MIAT rs1061540/MALAT1 rs3200401 molecular variants with Gensini Score in coronary artery disease patients undergoing angiography. Biomolecules 12:137. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12010137
Gao Y, Li S, Zhang Z, Yu X, Zheng J (2018) The role of long non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of RA, SLE, and SS. Front Med 5(July):1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2018.00193/full
Giannini D, Antonucci M, Petrelli F, Bilia S, Alunno A, Puxeddu I (2020) One year in review 2020: pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 38(3):387–397
Hofmann P, Sommer J, Theodorou K, Kirchhof L, Fischer A, Li Y et al (2018) Long non-coding RNA H19 regulates endothelial cell aging via inhibition of STAT3 signalling. Cardiovasc Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvy206/5073048
Huang W, Li X, Huang C, Tang Y, Zhou Q, Chen W (2022) LncRNAs and rheumatoid arthritis: from identifying mechanisms to clinical investigation. Front Immunol 12(January):1–17
Ismail NM, Toraih EA, Almars AI, Al Ageeli E, Fawzy MS, Maher SA (2022) Genotype triad for HOTAIR rs10783618, LINC-ROR rs1942347, and MALAT1 rs3200401 as molecular markers in systemic lupus erythematous. Diagnostics 12:1197–210
Kim JW, Kong J, Lee S, Yoo S, Koh JH, Kim W (2020) Angiogenic cytokines can reflect the synovitis severity and treatment response to biologics in rheumatoid arthritis. Exp Mol Med. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-020-0443-8
Klein K, Gay S (2015) Epigenetics in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 27(1):76–82
Kondo T, Aoki H, Otsuka Y, Kawaguchi Y, Waguri-Nagaya Y, Aoyama M (2022) Insulin-like growth factor 2 promotes osteoclastogenesis increasing inflammatory cytokine levels under hypoxia. J Pharmacol Sci 149(3):93–99
Li Z, Li X, Jiang C, Qian W, Tse G, Chan MTV et al (2018) Long non-coding RNAs in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Prolif 51(1):e12404. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12404
Liu B, Zhang T-N, Knight JK, Goodwin JE (2019) The glucocorticoid receptor in cardiovascular health and disease. Cells 8(10):1227
Lou Y, Han M, Liu H, Niu Y, Liang Y, Guo J et al (2020) Essential roles of S100A10 in Toll-like receptor signaling and immunity to infection. Cell Mol Immunol 17(10):1053–1062. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-019-0278-1
Martin-Trujillo A, Van RJGI, Timmer TCG, Rodríguez FM, Huizinga TWJ, Tak PP et al (2010) Loss of imprinting of IGF2 characterises high IGF2 mRNA-expressing type of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 69(6):1239–1242
Mcwilliams DF, Kiely PDW, Young A, Joharatnam N, Wilson D, Walsh DA (2018) Interpretation of DAS28 and its components in the assessment of inflammatory and non-inflammatory aspects of rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Rheumatol 2(8):1–12
Mohammad HMF, Al Ageeli EA, Kattan SW, Abdelghany AA, Hassan R, Toraih EA et al (2021) Long non-coding RNAs gene variants as molecular markers for diabetic retinopathy risk and response to anti-VEGF therapy. Pharmgenomics Pers Med 14:997–1014
Okada Y, Eyre S, Suzuki A, Kochi Y, Yamamoto K (2019) Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis: 2018 status. Ann Rheum Dis 78(4):446–453
Pearson MJ, Jones SW (2016) Review: long noncoding RNAs in the regulation of inflammatory pathways in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 68(11):2575–2583
Petrelli F, Mariani FM, Alunno A, Puxeddu I (2022) Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: one year in review 2022. Clin Exp Rheumatol 40(3):475–482
Qanbari S (2020) On the extent of linkage disequilibrium in the genome of farm animals. Front Genet 10(January):1–11
Ramakrishnan AP (2013) Linkage disequilibrium. In: Maloy S, Hughes K, editors. Brenner's Encyclopedia of Genetics, 2nd edn. San Diego: Academic Press, pp 252–253
Said MA, van de Vegte YJ, Zafar MM, van der Ende MY, Raja GK, Verweij N et al (2019) Contributions of interactions between lifestyle and genetics on coronary artery disease risk. Curr Cardiol Rep 21(9):89
Sallam RA, Saad BS, El Wassefy MA, EL Kady BA (2021) Effect of vascular endothelial growth factor gene polymorphisms on disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Egypt Rheumatol Rehabil. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43166-021-00098-7
Testa D, Calvacchi S, Petrelli F, Giannini D, Bilia S, Alunno A et al (2021) One year in review 2021: pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 39(3):445–452
Thanapati S, Ganu M, Giri P, Kulkarni S, Sharma M, Babar P et al (2017) Impaired NK cell functionality and increased TNF-α production as biomarkers of chronic chikungunya arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Immunol 78(4):370–374
Tsai C-Y, Hsieh S-C, Lu M-C, Yu C-L (2018) Aberrant non-coding RNA expression profiles as biomarker/bio-signature in autoimmune and inflammatory rheumatic diseases. J Lab Precis Med 3:51–51
Wang JZ, Xiang JJ, Wu LG, Bai YS, Chen ZW, Yin XQ et al (2017) A genetic variant in long non-coding RNA MALAT1 associated with survival outcome among patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma: a survival cohort analysis. BMC Cancer. 3;17(1):167. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-017-3151-6
Wang XM, Li XM, Song N, Zhai H, Gao XM, Yang YN (2019) Long non-coding RNAs H19, MALAT1 and MIAT as potential novel biomarkers for diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Biomed Pharmacother 118:109208
Wu H, Chen S, Li A, Shen K, Wang S, Wang S et al (2021) LncRNA expression profiles in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis: emerging biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Front Immunol 12(December):1–12
Zhang X, Hamblin MH, Yin KJ (2017) The long noncoding RNA Malat 1: its physiological and pathophysiological functions. RNA Biol 14(12):1705–1714. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2017.1358347
Zhao G, Su Z, Song D, Mao Y, Mao X (2016) The long noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response through its interaction with NF-κB. FEBS Lett 590(17):2884–2895. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12315
Zhou JZ, Li JJ, Hua DJ, Huang SC, Sun QQ, Huang H et al (2017) A study on associations of single-nucleotide polymorphisms within H19 and HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) with genetic susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in a Chinese population. Inflamm Res 66(6):515–521
Zhu R, Liu X, He Z (2018) Long non-coding RNA H19 and MALAT1 gene variants in patients with ischemic stroke in a northern Chinese Han population. Mol Brain 11(1):1–7
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
There is no funding of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EHE-S: design the protocol, collect and analyze the data, write the manuscript, and final revision and review the manuscript. AFA-H: collect, analyze and interpret the samples and data, write the manuscript, and final revision and review the manuscript. SEA-DY: acquisition of data, drafting the article and final revision, and reviewing the manuscript. MHA-S: sample collection, drafting the main manuscript, and reviewing the manuscript and final revision. HHO: Design the idea of the study, analyze the data, write the main manuscript and review the manuscript with final approval. All authors have been contributed equally to this work. All authors were involved in the decision to submit the manuscript for publication and had the right to accept or reject comments or suggestions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
All authors have not any competing interests.
Ethical Approval
Ethical approval for the study was secured by the research ethics committee of the faculty of medicine, Suez Canal University. The study was conducted according to Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to Participate
All participants provided an informed written consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
El-Sayed, E.H., Fathy, A., Al-Deen Younes, S.E. et al. Long Non-coding RNA Genes Polymorphisms H19 (rs2251375) and MALAT1 (rs3200401) Association with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Their Correlation with Disease Activity in a Cohort of Egyptian Patients: A Pilot Study. Biochem Genet 61, 2443–2456 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10383-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-023-10383-z