Abstract
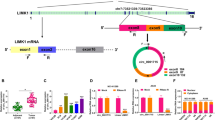
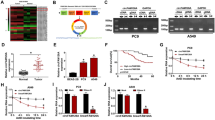
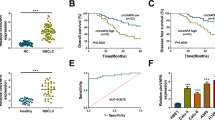
Lung cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer and the leading reason for tumor-related mortality, while non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most usual type of lung cancer. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have emerged as vital regulators in the development of human cancers, including NSCLC. We aimed to explore the functions of circRNA leukemia inhibitory factor receptor (circLIFR) in NSCLC progression. Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was used to quantify the expression of circLIFR, microRNA-429 (miR-429), and Elav-like family member 2 (CELF2) in NSCLC tissues and cells. Cell proliferation capability of NSCLC cells was determined by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and colony formation assays. The flow cytometry assay was performed to evaluate cell-cycle distribution and apoptosis of NSCLC cells. The abilities of migration and invasion were measured by transwell assay. In addition, the activities of caspase 3 and caspase 9 were measured by the assay kits. The interaction relationship between miR-429 and circLIFR or CELF2 was analyzed by dual-luciferase reporter, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP), and RNA pull-down assays. The expression levels of related proteins were examined by Western Blot assay. The xenograft experiment was established to explore the role of circLIFR in vivo. CircLIFR, circular, and stable transcript in NSCLC cells, was decreased more than 2 folds in NSCLC tissues and cells than controls (P < 0.0001). Importantly, overexpression of circLIFR impeded cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and inactivated protein kinase B (AKT)/phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)-signaling pathways while enhanced apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest in NSCLC cells, which was overturned by upregulation of miR-429 or silencing of CELF2. Furthermore, the upregulation of circLIFR inhibited NSCLC tumor growth in vivo. Overexpression of circLIFR could suppress NSCLC progress by acting as a sponge of miR-429 to regulate the expression of CELF2 and PTEN/AKT-signaling pathways in NSCLC.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The analyzed datasets generated during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Armwood S, Juma BF, Ombito JO, Majinda RR, Gwebu ET (2018) Effect of erythrinaline alkaloids from Erythrina lysistemon on human recombinant caspase-3. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol 12:183–187
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer J Clin 68:394–424
Chen J, Wang L, Matyunina LV, Hill CG, McDonald JF (2011) Overexpression of miR-429 induces mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition (MET) in metastatic ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol 121:200–205
Chen X, Zeng K, Xu M et al (2018) SP1-induced lncRNA-ZFAS1 contributes to colorectal cancer progression via the miR-150-5p/VEGFA axis. Cell Death Dis 9:982
Chen T, Shao S, Li W, Liu Y, Cao Y (2019) The circular RNA hsa-circ-0072309 plays anti-tumour roles by sponging miR-100 through the deactivation of PI3K/AKT and mTOR pathways in the renal carcinoma cell lines. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47:3638–3648
Dong Y, He D, Peng Z et al (2017) Circular RNAs in cancer: an emerging key player. J Hematol Oncol 10:2
Ersahin T, Tuncbag N, Cetin-Atalay R (2015) The PI3K/AKT/mTOR interactive pathway. Mol BioSyst 11:1946–1954
Fan B, Jiao B-H, Fan F-S et al (2015) Downregulation of miR-95-3p inhibits proliferation, and invasion promoting apoptosis of glioma cells by targeting CELF2. Int J Oncol 47:1025–1033
Fumarola C, Bonelli MA, Petronini PG, Alfieri RR (2014) Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in non small cell lung cancer. Biochem Pharmacol 90:197–207
Govindan R, Page N, Morgensztern D et al (2006) Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. J Clin Oncol 24:4539–4544
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH et al (2013) Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 495:384
Lang Y, Xu S, Ma J et al (2014) MicroRNA-429 induces tumorigenesis of human non-small cell lung cancer cells and targets multiple tumor suppressor genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 450:154–159
Li J, Yang J, Zhou P et al (2015) Circular RNAs in cancer: novel insights into origins, properties, functions and implications. Am J Cancer Res 5:472
Liu X, Liu Y, Wu S et al (2014) Tumor-suppressing effects of miR-429 on human osteosarcoma. Cell Biochem Biophys 70:215–224
Martini M, De Santis MC, Braccini L, Gulluni F, Hirsch E (2014) PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: an updated review. Ann Med 46:372–383
Meng S, Zhou H, Feng Z et al (2017) CircRNA: functions and properties of a novel potential biomarker for cancer. Mol Cancer 16:94
Pan H, Li T, Jiang Y et al (2018) Overexpression of circular RNA ciRS-7 abrogates the tumor suppressive effect of miR-7 on gastric cancer via PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem 119:440–446
Ramalingam S, Ramamoorthy P, Subramaniam D, Anant S (2012) Reduced expression of RNA binding protein CELF2, a putative tumor suppressor gene in colon cancer. Immuno-Gastroenterology 1:27
Rong D, Sun H, Li Z et al (2017) An emerging function of circRNA-miRNAs-mRNA axis in human diseases. Oncotarget 8:73271
Suzuki H, Takeuchi M, Sugiyama A et al (2012) Alternative splicing produces structural and functional changes in CUGBP2. BMC Biochem 13:6
Wang J, Li H (2018) CircRNA circ_0067934 silencing inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of NSCLC cells and correlates with unfavorable prognosis in NSCLC. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:3053–3060
Wang Y, Zhu W, Levy DE (2006) Nuclear and cytoplasmic mRNA quantification by SYBR green based real-time RT-PCR. Methods 39:356–362
Wang Y, Li M, Zang W et al (2013) MiR-429 up-regulation induces apoptosis and suppresses invasion by targeting Bcl-2 and SP-1 in esophageal carcinoma. Cell Oncol 36:385–394
Wang J, Liu L, Sun Y et al (2018) miR-615-3p promotes proliferation and migration and inhibits apoptosis through its potential target CELF2 in gastric cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 101:406–413
Xiao P, Liu W, Zhou H (2016) miR-429 promotes the proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer cells via targeting DLC-1. Oncol Lett 12:2163–2168
Yan L, Zheng M, Wang H (2019) Circular RNA hsa_circ_0072309 inhibits proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells via targeting miR-492. Cancer Manag Res 11:1033
Ye Z-B, Ma G, Zhao Y-H et al (2015) miR-429 inhibits migration and invasion of breast cancer cells in vitro. Int J Oncol 46:531–538
Yeung YT, Fan S, Lu B et al (2019) CELF2 suppresses non-small cell lung carcinoma growth by inhibiting the PREX2-PTEN interaction. Carcinogenesis. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgz113
Zhu W, He J, Chen D et al (2014) Expression of miR-29c, miR-93, and miR-429 as potential biomarkers for detection of early stage non-small lung cancer. PLoS ONE 9:e87780
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was not received funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and Methodology: XL and XP; Formal analysis and Data curation: XP and JW; Validation and Investigation: JW and XL; Writing—original draft preparation and Writing—review and editing: JW, XL and XP; Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
The present study was approved by the ethical review committee of Peking University Shenzhen Hospital.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Lai, X. & Peng, X. CircLIFR Inhibits Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Progression by Acting as a miR-429 Sponge to Enhance CELF2 Expression. Biochem Genet 61, 725–741 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-022-10285-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-022-10285-6