Abstract
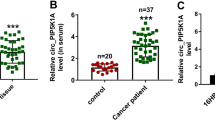
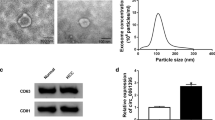
The deregulation of circular RNAs (circRNAs) is involved in cancer development. CircRNA polo-like kinase 1 (circPLK1) was reported to promote breast cancer development. However, the role of circPLK1 in malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is unclear. The expression of circPLK1, miR-1294, and high mobility group AT-hook 1 (HMGA1) mRNA was measured by quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR). Cell viability was detected by CCK-8 assay. Colony formation ability was monitored by colony formation assay. Cell proliferation was detected by EdU assay. Cell migration and cell invasion were monitored by transwell assay. Cancer cell stemness was investigated by sphere formation assay. The protein levels of marker proteins and HMGA1 expression were measured by western blot analysis. The binding relationship between miR-1294 and circPLK1 or HMGA1 was validated by pull-down assay, dual-luciferase reporter assay or RIP assy. Animal study was performed to disclose the role of circPLK1 in vivo. Exosomes were identified by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA). CircPLK1 was upregulated in MPM tumor tissues and cell lines. CircPLK1 knockdown suppressed the proliferation, migration, invasion and stemness of MPM cells. CircPLK1 contained a binding site for miR-1294 and thus bound to miR-1294 to sequester its expression. Inhibition of miR-1294 reversed the effects of circPLK1 knockdown. HMGA1 was a target of miR-1294, and circPLK1 bound to miR-1294 to increase the expression of HMGA1. MiR-1294 restoration also suppressed the proliferation, migration, invasion and stemness of MPM cells, while these effects were abolished by HMGA1 overexpression. In addition, circPLK1 knockdown inhibited tumor growth in vivo. CircPLK1 was overexpressed in exosomes derived from serum of MPM patients. CircPLK1 knockdown inhibited MPM cell proliferation, migration, invasion and stemness by targeting the miR-1294/HMGA1 pathway.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Baas P, Fennell D, Kerr KM, Van Schil PE, Haas RL, Peters S et al (2015) Malignant pleural mesothelioma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 26(Suppl 5):v31-39
Beckett P, Edwards J, Fennell D, Hubbard R, Woolhouse I, Peake MD (2015) Demographics, management and survival of patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma in the National Lung Cancer Audit in England and Wales. Lung Cancer 88(3):344–348
Belousova EA, Filipenko ML, Kushlinskii NE (2018) Circular RNA: new regulatory molecules. Bull Exp Biol Med 164(6):803–815
Cao XP, Cao Y, Zhao H, Yin J, Hou P (2019) HMGA1 promoting gastric cancer oncogenic and glycolytic phenotypes by regulating c-myc expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 516(2):457–465
Chang ZG, Yang LY, Wang W, Peng JX, Huang GW, Tao YM et al (2005) Determination of high mobility group A1 (HMGA1) expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: a potential prognostic marker. Dig Dis Sci 50(10):1764–1770
Chen H, Liu L, Li X, Shi Y, Liu N (2018) MicroRNA-1294 inhibits the proliferation and enhances the chemosensitivity of glioma to temozolomide via the direct targeting of TPX2. Am J Cancer Res 8(2):291–301
Chen M, Xu K, Li B, Wang N, Zhang Q, Chen L et al (2020) HMGA1 Regulates the stem cell-like properties of circulating tumor cells from GIST patients via Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Onco Targets Ther 13:4943–4956
Cinausero M, Rihawi K, Cortiula F, Follador A, Fasola G, Ardizzoni A (2019) Emerging therapies in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 144:102815
Fu F, Wang T, Wu Z, Feng Y, Wang W, Zhou S et al (2018) HMGA1 exacerbates tumor growth through regulating the cell cycle and accelerates migration/invasion via targeting miR-221/222 in cervical cancer. Cell Death Dis 9(6):594
Ismail-Khan R, Robinson LA, Williams CC Jr, Garrett CR, Bepler G, Simon GR (2006) Malignant pleural mesothelioma: a comprehensive review. Cancer Control 13(4):255–263
Johnson TG, Schelch K, Cheng YY, Williams M, Sarun KH, Kirschner MB et al (2018) Dysregulated expression of the microRNA miR-137 and its target YBX1 contribute to the invasive characteristics of malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Thorac Oncol 13(2):258–272
Kan XQ, Li YB, He B, Cheng S, Wei Y, Sun J (2020) MiR-1294 acts as a tumor inhibitor in cervical cancer by regulating FLOT1 expression. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. https://doi.org/10.23812/20-10A
Khodayari N, Mohammed KA, Lee H, Kaye F, Nasreen N (2016) MicroRNA-302b targets Mcl-1 and inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in malignant pleural mesothelioma cells. Am J Cancer Res 6(9):1996–2009
Klonisch T, Wiechec E, Hombach-Klonisch S, Ande SR, Wesselborg S, Schulze-Osthoff K et al (2008) Cancer stem cell markers in common cancers - therapeutic implications. Trends Mol Med 14(10):450–460
Kong Y, Yang L, Wei W, Lyu N, Zou Y, Gao G et al (2019) CircPLK1 sponges miR-296-5p to facilitate triple-negative breast cancer progression. Epigenomics 11(10):1163–1176
Lin G, Wang S, Zhang X, Wang D (2020) Circular RNA circPLK1 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by regulating miR-4500/IGF1 axis. Cancer Cell Int 20(1):593
Liu K, Li L, Rusidanmu A, Wang Y, Lv X (2015) Down-regulation of MiR-1294 is related to dismal prognosis of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through elevating C-MYC expression. Cell Physiol Biochem 36(1):100–110
Renganathan A, Kresoja-Rakic J, Echeverry N, Ziltener G, Vrugt B, Opitz I et al (2014) GAS5 long non-coding RNA in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Mol Cancer 13:119
Robb T, Reid G, Blenkiron C (2017) Exploiting microRNAs as cancer therapeutics. Target Oncol 12(2):163–178
Wang M, Yu F, Wu W, Zhang Y, Chang W, Ponnusamy M et al (2017) Circular RNAs: a novel type of non-coding RNA and their potential implications in antiviral immunity. Int J Biol Sci 13(12):1497–1506
Xu T, Wu J, Han P, Zhao Z, Song X (2017) Circular RNA expression profiles and features in human tissues: a study using RNA-seq data. BMC Genom 18(Suppl 6):680
Yuan Q, Yu H, Chen J, Song X, Sun L (2020) Antitumor effect of miR-1294/pyruvate kinase M2 signaling cascade in osteosarcoma cells. Onco Targets Ther 13:1637–1647
Zalcman G, Mazieres J, Margery J, Greillier L, Audigier-Valette C, Moro-Sibilot D et al (2016) Bevacizumab for newly diagnosed pleural mesothelioma in the Mesothelioma Avastin Cisplatin Pemetrexed Study (MAPS): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 387(10026):1405–1414
Zanin R, Pegoraro S, Ros G, Ciani Y, Piazza S, Bossi F et al (2019) HMGA1 promotes breast cancer angiogenesis supporting the stability, nuclear localization and transcriptional activity of FOXM1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38(1):313
Funding
This study was supported by Chongqing Science and Health Joint Medical Research Project (NO. 2021MSXM214).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YJ designed and supervised the study. QZ and ZW conducted the experiments and drafted the manuscript. HC and DG collected and analyzed the data. WX and SB contributed the methodology and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10528_2022_10186_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Fig. S1 CircPLK1 knockdown arrested cancer cell cycle arrest. (A and B) The effect of si-circPLK1#1 on cell cycle was determined by flow cytometry assay. **P<0.01. Supplementary file1 (TIF 1045 KB).
10528_2022_10186_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Fig. S2 The screening of HMGA1 from the target genes of miR-1294. (A and B) The expression of several genes potentially targeted by miR-1294 in MSTO-211H and H2052 cells after miR-1294 overexpression was checked by qPCR. ***P<0.001. Supplementary file2 (TIF 248 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Wang, Z., Cai, H. et al. CircPLK1 Acts as a Carcinogenic Driver to Promote the Development of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma by Governing the miR-1294/HMGA1 Pathway. Biochem Genet 60, 1527–1546 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-022-10186-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-022-10186-8