Abstract
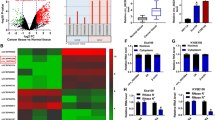
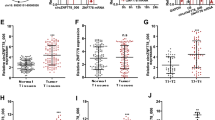
In the previous studies, circular RNA (circRNA) has been shown to be closely related to the occurrence and development of various cancers. However, the role and mechanism of circ-ATIC in the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is not yet clear. Quantitative real-time PCR was used to detect the expression levels of circ-ATIC, microRNA (miR)-326 and inhibitor of DNA binding 1 (ID1) in tissues (n = 50) and cells. Cell counting kit 8 assay, colony formation assay, flow cytometry, wound-healing assay and transwell assay were performed to measure the proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion of cells. In addition, the oxidative stress of cells was evaluated by detecting the productions of superoxide dismutase and malondialdehyde. Animal studies were implied to explore the role of circ-ATIC in ESCC tumor growth. The relationship between circ-ATIC and miR-326 or ID1 was determined by dual-luciferase reporter assay and RNA immunoprecipitation assay. Additionally, the protein expression of ID1 was examined by western blot assay. Circ-ATIC was found to be upregulated in ESCC tissues and cells. Silenced circ-ATIC suppressed the proliferation, migration, invasion, promoted the apoptosis and oxidative stress of ESCC cells. The tumor growth of ESCC also was inhibited by circ-ATIC knockdown. Furthermore, we found that circ-ATIC could sponge miR-326, and miR-326 could target ID1. The rescue experiments revealed that miR-326 inhibitor could reverse the negative regulation of circ-ATIC silencing on ESCC progression, and ID1 overexpression also inverted the inhibitory effect of miR-326 on ESCC progression. In addition, we confirmed that the expression of ID1 was positively regulated by circ-ATIC. Our study showed that circ-ATIC facilitated the progression of ESCC by regulating the miR-326/ID1 axis, indicating that circ-ATIC might be a target for ESCC treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in the article.
Abbreviations
- ESCC:
-
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- ID1:
-
Inhibitor of DNA binding 1
References
Barbetta A, Hsu M, Tan KS, Stefanova D, Herman K, Adusumilli PS, Bains MS, Bott MJ, Isbell JM, Janjigian YY, Ku GY, Park BJ, Wu AJ, Jones DR, Molena D (2018) Definitive chemoradiotherapy versus neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy followed by surgery for stage II to III esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 155(2710–21):e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2018.01.086
Barrett SP, Salzman J (2016) Circular RNAs: analysis, expression and potential functions. Development 143:1838–1847. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.128074
Chen LL, Yang L (2015) Regulation of circRNA biogenesis. RNA Biol 12:381–388. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2015.1020271
Chen X, Yu J, Tian H, Shan Z, Liu W, Pan Z, Ren J (2019) Circle RNA hsa_circRNA_100290 serves as a ceRNA for miR-378a to regulate oral squamous cell carcinoma cells growth via Glucose transporter-1 (GLUT1) and glycolysis. J Cell Physiol 234:19130–19140. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28692
Codipilly DC, Qin Y, Dawsey SM, Kisiel J, Topazian M, Ahlquist D, Iyer PG (2018) Screening for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: recent advances. Gastrointest Endosc 88:413–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2018.04.2352
Deng W, Zhang W, Yang J, Ni W, Yu S, Li C, Chang X, Zhou Z, Chen D, Feng Q, Chen X, Lin Y, Zhu K, Zheng X, He J, Gao S, Xue Q, Mao Y, Cheng G, Sun K, Liu X, Fang D, Chen J, Xiao Z (2019) Nomogram to predict overall survival for thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients after radical esophagectomy. Ann Surg Oncol 26:2890–2898. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-019-07393-w
Fan Z, Bai Y, Zhang Q, Qian P (2020) CircRNA circ_POLA2 promotes lung cancer cell stemness via regulating the miR-326/GNB1 axis. Environ Toxicol 35:1146–1156. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22980
Gaman MA, Cozma MA, Dobrica EC, Cretoiu SM, Gaman AM, Diaconu CC (2021) Liquid biopsy and potential liquid biopsy-based biomarkers in philadelphia-negative classical myeloproliferative neoplasms: a systematic review. Life (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/life11070677
Gong J, Jiang H, Shu C, Hu MQ, Huang Y, Liu Q, Li RF, Wei YZ (2019) Integrated analysis of circular RNA-associated ceRNA network in cervical cancer: observational Study. Medicine (baltimore) 98:e16922. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000016922
Han L, Cui D, Li B, Xu WW, Lam AKY, Chan KT, Zhu Y, Lee NPY, Law SYK, Guan XY, Qin YR, Chan KW, Ma S, Tsao SW, Cheung ALM (2019) MicroRNA-338-5p reverses chemoresistance and inhibits invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting Id-1. Cancer Sci 110:3677–3688. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.14220
Hirano H, Kato K (2019) Systemic treatment of advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: chemotherapy, molecular-targeting therapy and immunotherapy. Jpn J Clin Oncol 49:412–420. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyz034
Hou Y, Liu H, Pan W (2020) Knockdown of circ_0003340 induces cell apoptosis, inhibits invasion and proliferation through miR-564/TPX2 in esophageal cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.112142
Hsiao KY, Sun HS, Tsai SJ (2017) Circular RNA—new member of noncoding RNA with novel functions. Exp Biol Med (maywood) 242:1136–1141. https://doi.org/10.1177/1535370217708978
Huang FL, Yu SJ (2018) Esophageal cancer: risk factors, genetic association, and treatment. Asian J Surg 41:210–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asjsur.2016.10.005
Huang L, Wang Y, Chen J, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Ma Y, Chen X, Liu W, Li Z, Zhao L, Shan B, Dong X, Li D, Shao S, Song Y, Zhan Q, Liu X (2019) Long noncoding RNA PCAT1, a novel serum-based biomarker, enhances cell growth by sponging miR-326 in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis 10:513. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1745-4
Huang E, Fu J, Yu Q, Xie P, Yang Z, Ji H, Wang L, Luo G, Zhang Y, Li K (2020) CircRNA hsa_circ_0004771 promotes esophageal squamous cell cancer progression via miR-339-5p/CDC25A axis. Epigenomics 12:587–603. https://doi.org/10.2217/epi-2019-0404
Hui CM, Cheung PY, Ling MT, Tsao SW, Wang X, Wong YC, Cheung AL (2006) Id-1 promotes proliferation of p53-deficient esophageal cancer cells. Int J Cancer 119:508–514. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.21874
Jia B, Yin X, Wang Y, Qian J, He Y, Yang C, Yu G, Guo B, Meng X (2020) CircRNA-PTN sponges miR-326 to promote proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther 13:4893–4903. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S251300
Kristensen LS, Hansen TB, Veno MT, Kjems J (2018) Circular RNAs in cancer: opportunities and challenges in the field. Oncogene 37:555–565. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.361
Li R, Wu B, Xia J, Ye L, Yang X (2019) Circular RNA hsa_circRNA_102958 promotes tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer via miR-585/CDC25B axis. Cancer Manag Res 11:6887–6893. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S212180
Liang H, Huang H, Li Y, Lu Y, Ye T (2020) CircRNA_0058063 functions as a ceRNA in bladder cancer progression via targeting miR-486-3p/FOXP4 axis. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20193484
Liu J, Hu Y, Hu W, Xie X, Ela Bella A, Fu J (2010) Expression and prognostic relevance of Id1 in stage III esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biomark 8:67–72. https://doi.org/10.3233/DMA-2011-0831
Liu W, Ma W, Yuan Y, Zhang Y, Sun S (2018) Circular RNA hsa_circRNA_103809 promotes lung cancer progression via facilitating ZNF121-dependent MYC expression by sequestering miR-4302. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 500:846–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.172
Maciejewska I, Sakowicz-Burkiewicz M, Pawelczyk T (2014) Id1 expression level determines the differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells. J Dent Res 93:576–581. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034514530164
Murakami Y, Hamai Y, Emi M, Hihara J, Imano N, Takeuchi Y, Takahashi I, Nishibuchi I, Kimura T, Okada M, Nagata Y (2018) Long-term results of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy using cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil followed by esophagectomy for resectable, locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Radiat Res 59:616–624. https://doi.org/10.1093/jrr/rry047
Patop IL, Kadener S (2018) circRNAs in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 48:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gde.2017.11.007
Rodriguez Viales R, Diotel N, Ferg M, Armant O, Eich J, Alunni A, Marz M, Bally-Cuif L, Rastegar S, Strahle U (2015) The helix-loop-helix protein id1 controls stem cell proliferation during regenerative neurogenesis in the adult zebrafish telencephalon. Stem Cells 33:892–903. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.1883
Sachdeva R, Wu M, Smiljanic S, Kaskun O, Ghannad-Zadeh K, Celebre A, Isaev K, Morrissy AS, Guan J, Tong J, Chan J, Wilson TM, Al-Omaishi S, Munoz DG, Dirks PB, Moran MF, Taylor MD, Reimand J, Das S (2019) ID1 is critical for tumorigenesis and regulates chemoresistance in glioblastoma. Cancer Res 79:4057–4071. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-1357
Shi Y, Fang N, Li Y, Guo Z, Jiang W, He Y, Ma Z, Chen Y (2020) Circular RNA LPAR3 sponges microRNA-198 to facilitate esophageal cancer migration, invasion, and metastasis. Cancer Sci 111:2824–2836. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.14511
Su CM, Su YH, Chiu CF, Chang YW, Hong CC, Yu YH, Ho YS, Wu CH, Yen CS, Su JL (2014) Vascular endothelial growth factor-C upregulates cortactin and promotes metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 21(Suppl 4):S767–S775. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-4009-7
Sun M, Zhao W, Chen Z, Li M, Li S, Wu B, Bu R (2019) Circ_0058063 regulates CDK6 to promote bladder cancer progression by sponging miR-145-5p. J Cell Physiol 234:4812–4824. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27280
Tsai CH, Yang MH, Hung AC, Wu SC, Chiu WC, Hou MF, Tyan YC, Wang YM, Yuan SF (2016) Identification of Id1 as a downstream effector for arsenic-promoted angiogenesis via PI3K/Akt, NF-kappaB and NOS signaling. Toxicol Res (camb) 5:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5tx00280j
Xian ZY, Hu B, Wang T, Cai JL, Zeng JY, Zou Q, Zhu PX (2020) CircABCB10 silencing inhibits the cell ferroptosis and apoptosis by regulating the miR-326/CCL5 axis in rectal cancer. Neoplasma 67:1063–1073. https://doi.org/10.4149/neo_2020_191024N1084
Zhang Y, Tang Q, Huang XM, Liao DZ (2020a) Circular RNA circCNOT6L regulates cell development through modulating miR-384/FN1 axis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24:3674–3685. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202004_20830
Zhang Z, Li X, Xiong F, Ren Z, Han Y (2020b) Hsa_circ_0012563 promotes migration and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating XRCC1/EMT pathway. J Clin Lab Anal. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.23308
Zheng Y, Chen Y, Jiang H, Zhang H, Wang H, Xu J, Yu Z (2020) Circ_0058063 upregulates GLUT1 expression and promotes glucose-uptake in esophageal squamous-cell carcinomas. J Thorac Dis 12:925–931. https://doi.org/10.21037/jtd.2019.12.57
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all the patients and family members participating in this work for their cooperation and patience. This study was supported by Shijiazhuang No.1 Hospital.
Funding
The author(s) reported there is no funding associated with the work featured in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BZ participated in the design of the work, methodology, data interpretation, carried out the statistical analysis and drafted the manuscript. WC and ZL participated in the methodology, data interpretation, and analysis for the work. YZ, QZ and BL participated in data interpretation and methodology. JL and CL performed the experiments and analyzed and interpreted the data. XZ analyzed interpreted the data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The design of this protocol follows the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki, approved by the Ethics Committee of Shijiazhuang No.1 Hospital. (No. SJZ-20201643).
Consent for Publication
All patients in this study provided their consent for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B., Chu, W., Li, Z. et al. Circ-ATIC Serves as a Sponge of miR-326 to Accelerate Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression by Targeting ID1. Biochem Genet 60, 1585–1600 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-021-10167-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-021-10167-3