Abstract
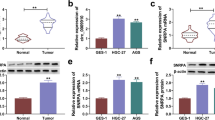
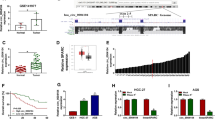
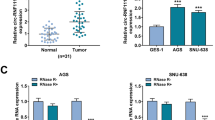
Gastric cancer (GC) is a prevalent and heterogeneous malignancy in the digestive system. Increasing studies have suggested that circular RNAs are implicated in GC pathogenesis. This study aimed to explore the biological role and underlying mechanism of circRNA zinc finger protein 131 (circZNF131) in GC. The expression pattern of circZNF131, microRNA-186-5p (miR-186-5p), and 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2, 6-bisphosphatase 2 (PFKFB2) mRNA in GC tissues and cells was detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. The stability of circZNF131 was verified using ribonuclease R assay. Functional experiments were performed by colony formation assay for cloning ability analysis, transwell assay and wounding healing assay for cell metastasis, and flow cytometry for cell apoptosis. Glycolysis metabolism was investigated by determining the levels of glucose uptake and lactate production. The protein detection of apoptosis- or glycolysis-associated markers, PFKFB2, and Ki-67 was implemented by western blot or immunohistochemistry. Dual-luciferase reporter assay was conducted to identify the interaction between miR-186-5p and circZNF131 or PFKFB2. The role of circZNF131 on tumor growth in nude mice was investigated via xenograft tumor assay. Expression analysis indicated that circZNF131 was upregulated in GC tissues and cells in a stable structure. Functional analyses showed that circZNF131 knockdown suppressed GC cell colony formation ability, migration, invasion and glycolysis metabolism, and induced cell apoptosis. Mechanically, miR-186-5p was a target of circZNF131, and miR-186-5p could bind to PFKFB2. Rescue experiments presented that miR-186-5p inhibition reversed the effects of circZNF131 knockdown on GC cell growth and glycolysis, and PFKFB2 overexpression abolished the impacts of miR-186-5p restoration on GC cell progression. Moreover, circZNF131 could positively modulate PFKFB2 expression via sponging miR-186-5p. In vivo, circZNF131 knockdown hindered GC tumor growth by regulating the miR-186-5p/PFKFB2 axis. circZNF131 could exert an oncogenic role in GC malignant development through the miR-186-5p/PFKFB2 axis, which might provide novel targets for GC treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Please contact the correspondence author for the data request.
References
Akram M (2013) Mini-review on glycolysis and cancer. J Cancer Educ 28:454–457
Azarbarzin S, Safaralizadeh R, Khojasteh MB, Baghbanzadeh A, Baradaran B (2020) Current perspectives on the dysregulated microRNAs in gastric cancer. Mol Biol Rep 47:7253–7264
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Bolha L, Ravnik-Glavac M, Glavac D (2017) Circular RNAs: biogenesis, function, and a role as possible cancer biomarkers. Int J Genom 2017:6218353
Cui N, Liu J, Xia H, Xu D (2019) LncRNA SNHG20 contributes to cell proliferation and invasion by upregulating ZFX expression sponging miR-495-3p in gastric cancer. J Cell Biochem 120:3114–3123
Eun JW, Kim HS, Shen Q, Yang HD, Kim SY, Yoon JH, Park WS, Lee JY, Nam SW (2018) MicroRNA-495-3p functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating multiple epigenetic modifiers in gastric carcinogenesis. J Pathol 244:107–119
Fang X, Wen J, Sun M, Yuan Y, Xu Q (2019) CircRNAs and its relationship with gastric cancer. J Cancer 10:6105–6113
Farazi TA, Hoell JI, Morozov P, Tuschl T (2013) MicroRNAs in human cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol 774:1–20
Ganapathy-Kanniappan S, Geschwind JF (2013) Tumor glycolysis as a target for cancer therapy: progress and prospects. Mol Cancer 12:152
Han B, Chao J, Yao H (2018) Circular RNA and its mechanisms in disease: from the bench to the clinic. Pharmacol Ther 187:31–44
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, Kjems J (2013) Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 495:384–388
Hayes J, Peruzzi PP, Lawler S (2014) MicroRNAs in cancer: biomarkers, functions and therapy. Trends Mol Med 20:460–469
Hsiao KY, Sun HS, Tsai SJ (2017) Circular RNA—new member of noncoding RNA with novel functions. Exp Biol Med 242:1136–1141
Huang GM, Zang HL, Geng YX, Li YH (2020) LncRNA FAM83A-AS1 aggravates the malignant development of esophageal cancer by binding to miR-495-3p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol, Sci 24:9408–9415
Hui C, Tian L, He X (2020) Circular RNA circNHSL1 contributes to gastric cancer progression through the miR-149-5p/YWHAZ axis. Cancer Manag Res 12:7117–7130
Ishiguro H, Kimura M, Takeyama H (2014) Role of microRNAs in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 20:5694–5699
Jiang C, Chen X, Alattar M, Wei J, Liu H (2015) MicroRNAs in tumorigenesis, metastasis, diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 22:291–301
Li T, Shao Y, Fu L, Xie Y, Zhu L, Sun W, Yu R, Xiao B, Guo J (2018) Plasma circular RNA profiling of patients with gastric cancer and their droplet digital RT-PCR detection. J Mol Med 96:85–96
Liu H, Chen K, Wang L, Zeng X, Huang Z, Li M, Dong P, Chen X (2019a) miR-613 inhibits Warburg effect in gastric cancer by targeting PFKFB2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 515:37–43
Liu J, Song S, Lin S, Zhang M, Du Y, Zhang D, Xu W, Wang H (2019) Circ-SERPINE2 promotes the development of gastric carcinoma by sponging miR-375 and modulating YWHAZ. Cell Prolif 52:e12648
Liu J, Liu H, Zeng Q, Xu P, Liu M, Yang N (2020a) Circular RNA circ-MAT2B facilitates glycolysis and growth of gastric cancer through regulating the miR-515-5p/HIF-1alpha axis. Cancer Cell Int 20:171
Liu Y, Jiang Y, Xu L, Qu C, Zhang L, Xiao X, Chen W, Li K, Liang Q, Wu H (2020b) circ-NRIP1 promotes glycolysis and tumor progression by regulating miR-186-5p/MYH9 axis in gastric cancer. Cancer Manag Res 12:5945–5956
Ma Y, Zhang D, Wu H, Li P, Zhao W, Yang X, Xing X, Li S, Li J (2020) Circular RNA PRKCI silencing represses esophageal cancer progression and elevates cell radiosensitivity through regulating the miR-186-5p/PARP9 axis. Life Sci 259:118168
Ning Y, Bai Z (2020) DSCAM-AS1 accelerates cell proliferation and migration in osteosarcoma through miR-186-5p/GPRC5A signaling. Cancer Biomark 30:29–39
Niu Q, Dong Z, Liang M, Luo Y, Lin H, Lin M, Zhong X, Yao W, Weng J, Zhou X (2020) Circular RNA hsa_circ_0001829 promotes gastric cancer progression through miR-155-5p/SMAD2 axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 39:280
Ouyang Y, Li Y, Huang Y, Li X, Zhu Y, Long Y, Wang Y, Guo X, Gong K (2019) CircRNA circPDSS1 promotes the gastric cancer progression by sponging miR-186-5p and modulating NEK2. J Cell Physiol 234:10458–10469
Ouyang J, Long Z, Li G (2020) Circular RNAs in gastric cancer: potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Biomed Res Int 2020:2790679
Ozcan SC, Sarioglu A, Altunok TH, Akkoc A, Guzel S, Guler S, Imbert-Fernandez Y, Muchut RJ, Iglesias AA, Gurpinar Y, Clem AL, Chesney JA, Yalcin A (2020) PFKFB2 regulates glycolysis and proliferation in pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem 470:115–129
Pan X, Li H, Tan J, Weng X, Zhou L, Weng Y, Cao X (2020) miR-1297 suppresses osteosarcoma proliferation and aerobic glycolysis by regulating PFKFB2. Onco Targets Ther 13:11265–11275
Panda AC (2018) Circular RNAs act as miRNA sponges. Adv Exp Med Biol 1087:67–79
Qu S, Yang X, Li X, Wang J, Gao Y, Shang R, Sun W, Dou K, Li H (2015) Circular RNA: a new star of noncoding RNAs. Cancer Lett 365:141–148
Qu J, Yang J, Chen M, Wei R, Tian J (2020) CircFLNA acts as a sponge of miR-646 to facilitate the proliferation, metastasis, glycolysis, and apoptosis inhibition of gastric cancer by targeting PFKFB2. Cancer Manag Res 12:8093–8103
Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, van Grieken NC, Lordick F (2020) Gastric cancer. Lancet 396:635–648
Tang J, Hu Y, Zhang C, Gong C (2021) miR-4636 inhibits tumor cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and serves as a candidate clinical biomarker for gastric cancer. Oncol Lett 21:33
Wang H, Sun G, Xu P, Lv J, Zhang X, Zhang L, Wang S, Cao J, Xia Y, Xuan Z, Li B, Huang X, Jiang T, Fang L, Xu Z (2020) Circular RNA TMEM87A promotes cell proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer by elevating ULK1 via sponging miR-142-5p. J Gastroenterol 56:125–138
Wei G, Zhu J, Hu HB, Liu JQ (2020) Circular RNAs: promising biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Gene 771:145365
Yan C, Kong X, Gong S, Liu F, Zhao Y (2020) Recent advances of the regulation roles of MicroRNA in glioblastoma. Int J Clin Oncol 25:1215
Yang G, Zhang Y, Yang J (2019) Identification of potentially functional CircRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in gastric carcinoma using bioinformatics analysis. Med Sci Monit 25:8777–8796
Yoon H, Kim N (2015) Diagnosis and management of high risk group for gastric cancer. Gut Liver 9:5–17
Yuan X, Yang T, Xu Y, Ou S, Shi P, Cao M, Zuo X, Liu Q, Yao J (2020) SNHG10 promotes cell proliferation and migration in gastric cancer by targeting miR-495-3p/CTNNB1 axis. Dig Dis Sci 66:2627–2636
Zhang XY, Zhang PY (2017) Gastric cancer: somatic genetics as a guide to therapy. J Med Genet 54:305–312
Zhao ZJ, Shen J (2017) Circular RNA participates in the carcinogenesis and the malignant behavior of cancer. RNA Biol 14:514–521
Zhong Y, Du Y, Yang X, Mo Y, Fan C, Xiong F, Ren D, Ye X, Li C, Wang Y, Wei F, Guo C, Wu X, Li X, Li Y, Li G, Zeng Z, Xiong W (2018) Circular RNAs function as ceRNAs to regulate and control human cancer progression. Mol Cancer 17:79
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XS was responsible for drafting the manuscript. XS, XZ, and PH contributed to the analysis and interpretation of data. XS, TJ, YQ, and JZ contributed in the data collection. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
Written informed consent was obtained from patients with approval by the Institutional Review Board in Jinan Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10528_2021_10165_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary file1 Supplementary Figure 1. The expression of candidate miRNAs and genes in GC tissues. (A and B) The expression of candidate miRNAs (miR-186-5p, miR-448, miR-605-3p, miR-545-5p, and miR-4766-5p) and genes (PFKFB2, CASK, ERBB4, HMGA2, and FOXK1) in GC tissues and adjacent normal tissues was examined by qRT-PCR assay (TIF 184 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, X., Zhu, X., Hu, P. et al. Knockdown circZNF131 Inhibits Cell Progression and Glycolysis in Gastric Cancer Through miR-186-5p/PFKFB2 Axis. Biochem Genet 60, 1567–1584 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-021-10165-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-021-10165-5