Abstract
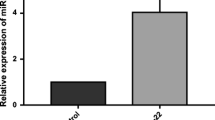
Psoriasis is considered as a common chronic and relapsing inflammatory skin disease. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) were found to be related with psoriasis pathogenesis. Nevertheless, the function of miR-617 in psoriasis is still unclear. The miR-617 RNA level was detected using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR). Western blot analysis examined the protein level. Cell proliferation was analyzed via cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. Flow cytometry analysis detected cell cycle and apoptosis. The relationship between miR-617 and forkhead box protein O4 (FOXO4) was confirmed through dual luciferase assay. The miR-617 was up-regulated in psoriatic skin tissues and interleukin-22 (IL-22)-stimulated immortalized human keratinocyte HaCaT cells. Moreover, miR-617 mimics promoted proliferation, cell cycle, and suppressed apoptosis in IL-22-stimulated HaCaT cells. However, miR-617 inhibitor showed opposite effects. Additionally, FOXO4 was a target of miR-617. FOXO4 was down-regulated in psoriatic skin tissues and IL-22-stimulated HaCaT cells. Negative correlation between miR-617 and FOXO4 was identified. FOXO4 overexpression alleviated the effects of miR-617 proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis in the IL-22-stimulated HaCaT cells. These results demonstrate that miR-617 increases the growth of IL-22-stimulated keratinocytes through targeting FOXO4, which provides a new therapeutic target for psoriasis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Boehncke WH, Schon MP (2015) Psoriasis. Lancet 386(9997):983–994
Bracken CP, Scott HS, Goodall GJ (2016) A network-biology perspective of microRNA function and dysfunction in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 17(12):719–732
Capon F (2017) The genetic basis of psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 18(12):2526
Chandra A, Ray A, Senapati S et al (2015) Genetic and epigenetic basis of psoriasis pathogenesis. Mol Immunol 64(2):313–323
Chen L, Tang Y, Wang J et al (2013) miR-421 induces cell proliferation and apoptosis resistance in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma via downregulation of FOXO4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 435(4):745–750
Cheng H, Xu M, Liu X et al (2016) TWEAK/Fn14 activation induces keratinocyte proliferation under psoriatic inflammation. Exp Dermatol 25(1):32–37
Ding X, Duan H, Luo H (2020) Identification of core gene expression signature and key pathways in colorectal cancer. Front Genet 11:45
Eyerich S, Eyerich K, Pennino D et al (2009) Th22 cells represent a distinct human T cell subset involved in epidermal immunity and remodeling. J Clin Invest 119(12):3573–3585
Feng S, Wang L, Liu W et al (2018) MiR-126 correlates with increased disease severity and promotes keratinocytes proliferation and inflammation while suppresses cells' apoptosis in psoriasis. J Clin Lab Anal 32(9):e22588
Geller S, Xu H, Lebwohl M et al (2018) Malignancy risk and recurrence with psoriasis and its treatments: a concise update. Am J Clin Dermatol 19(3):363–375
Hao JQ (2014) Targeting interleukin-22 in psoriasis. Inflammation 37(1):94–99
Hawkes JE, Nguyen GH, Fujita M et al (2016) microRNAs in psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 136(2):365–371
Huang H, Tindall DJ (2007) Dynamic FoxO transcription factors. J Cell Sci 120(Pt 15):2479–2487
Ji Y, Wang D, Zhang B et al (2019) MiR-361-3p inhibits beta-amyloid accumulation and attenuates cognitive deficits through targeting BACE1 in Alzheimer's disease. J Integr Neurosci 18(3):285–291
Katoh M, Igarashi M, Fukuda H et al (2013) Cancer genetics and genomics of human FOX family genes. Cancer Lett 328(2):198–206
Li J, Hu L, Tian C et al (2015) microRNA-150 promotes cervical cancer cell growth and survival by targeting FOXO4. BMC Mol Biol 16:24
Li H, Ouyang R, Wang Z et al (2016) MiR-150 promotes cellular metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting FOXO4. Sci Rep 6:39001
Liakou AI, Zouboulis CC (2015) Links and risks associated with psoriasis and metabolic syndrome. Psoriasis (Auckl) 5:125–128
Liu Q, Wu DH, Han L et al (2017) Roles of microRNAs in psoriasis: Immunological functions and potential biomarkers. Exp Dermatol 26(4):359–367
Liu X, Zhang Z, Sun L et al (2011) MicroRNA-499-5p promotes cellular invasion and tumor metastasis in colorectal cancer by targeting FOXO4 and PDCD4. Carcinogenesis 32(12):1798–1805
Lovendorf MB, Zibert JR, Gyldenlove M et al (2014) MicroRNA-223 and miR-143 are important systemic biomarkers for disease activity in psoriasis. J Dermatol Sci 75(2):133–139
Meisgen F, Xu N, Wei T et al (2012) MiR-21 is up-regulated in psoriasis and suppresses T cell apoptosis. Exp Dermatol 21(4):312–314
Otsuka K, Ochiya T (2014) Genetic networks lead and follow tumor development: microRNA regulation of cell cycle and apoptosis in the p53 pathways. Biomed Res Int 2014:749724
Parisi R, Symmons DP, Griffiths CE et al (2013) Global epidemiology of psoriasis: a systematic review of incidence and prevalence. J Invest Dermatol 133(2):377–385
Riffo-Campos AL, Riquelme I, Brebi-Mieville P (2016) Tools for sequence-based miRNA target prediction: what to choose? Int J Mol Sci 17(12):1987
Ritchlin CT, Colbert RA, Gladman DD (2017) Psoriatic arthritis. N Engl J Med 376(10):957–970
Rongna A, Yu P, Hao S et al (2018) MiR-876-5p suppresses cell proliferation by targeting Angiopoietin-1 in the psoriasis. Biomed Pharmacother. 103:1163–1169
Roubille C, Richer V, Starnino T et al (2015) The effects of tumour necrosis factor inhibitors, methotrexate, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroids on cardiovascular events in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis 74(3):480–489
Shen H, Tian Y, Yao X et al (2017) MiR-99a inhibits keratinocyte proliferation by targeting Frizzled-5 (FZD5) / FZD8 through beta-catenin signaling in psoriasis. Pharmazie 72(8):461–467
Shenoy A, Blelloch RH (2014) Regulation of microRNA function in somatic stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15(9):565–576
Shukla GC, Singh J, Barik S (2011) MicroRNAs: Processing, Maturation, Target Recognition and Regulatory Functions. Mol Cell Pharmacol 3(3):83–92
Soonthornchai W, Tangtanatakul P, Meephansan J et al (2019) Down-regulation of miR-155 after treatment with narrow-band UVB and methotrexate associates with apoptosis of keratinocytes in psoriasis. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. https://doi.org/10.12932/AP-031218-0451
Sun Y, Zhang J, Zhou Z et al (2015) CCN1, a pro-inflammatory factor, aggravates psoriasis skin lesions by promoting keratinocyte activation. J Invest Dermatol 135(11):2666–2675
Vide J, Magina S (2017) Moderate to severe psoriasis treatment challenges through the era of biological drugs. An Bras Dermatol 92(5):668–674
Wang R, Wang FF, Cao HW et al (2019a) MiR-223 regulates proliferation and apoptosis of IL-22-stimulated HaCat human keratinocyte cell lines via the PTEN/Akt pathway. Life Sci 230:28–34
Wang Y, Yu X, Wang L et al (2018) miR-320b is down-regulated in psoriasis and modulates keratinocyte proliferation by targeting AKT3. Inflammation 41(6):2160–2170
Wang C, Zong J, Li Y et al (2019b) MiR-744-3p regulates keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation via targeting KLLN in psoriasis. Exp Dermatol 28(3):283–291
Wawrzycki B, Pietrzak A, Grywalska E et al (2019) Interleukin-22 and its correlation with disease activity in plaque psoriasis. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 67(2):103–108
Zai W, Chen W, Wu Z et al (2019) Targeted interleukin-22 gene delivery in the liver by polymetformin and penetratin-based hybrid nanoparticles to treat nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(5):4842–4857
Zhang Y, Tu C, Zhang D et al (2015) Wnt/beta-catenin and Wnt5a/Ca pathways regulate proliferation and apoptosis of keratinocytes in psoriasis lesions. Cell Physiol Biochem 36(5):1890–1902
Zhao X, Li R, Qiao M et al (2018) MiR-548a-3p promotes keratinocyte proliferation targeting PPP3R1 after being induced by IL-22. Inflammation 41(2):496–504
Zhao L, Lu X, Cao Y (2013) MicroRNA and signal transduction pathways in tumor radiation response. Cell Signal 25(7):1625–1634
Zhu H, Hou L, Liu J et al (2016) MiR-217 is down-regulated in psoriasis and promotes keratinocyte differentiation via targeting GRHL2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 471(1):169–176
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by Scientific research fund support program of Southwest Medical University of Sichuan Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TL conceived and designed the experiments, XMF analyzed and interpreted the results of the experiments, YML performed the experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The animal experimental processes were performed in accordance with World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki and approved by Clinical Trial Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10528_2020_9997_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
Fig.S1. (A) IL-22R expression was measured in the IL-22-stimulated HaCaT cells (n=3) using qRT-PCR. (B) Western blot analysis was performed to confirm the p27 protein level. n=3. **, p<0.01. (364 kB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T., Feng, X. & Liao, Y. miR-617 Promotes the Growth of IL-22-Stimulated Keratinocytes Through Regulating FOXO4 Expression. Biochem Genet 59, 547–559 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-020-09997-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-020-09997-4