Abstract
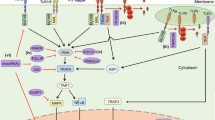
Infection of microbial pathogen triggers the innate immune system, and the induction of interferons (IFNs) play a vital role in host antiviral response. Stimulator of interferon genes (STING) was identified as a crucial regulator of the DNA sensing pathway, and activates both nuclear factor-κB and interferon regulatory factor 3 transcription pathways to evoke IFNs production. In this study, we studied the upregulation of STING mRNA expression, induced by IFN-γ in human keratinocytes (HaCaT). STING promoter assays clarified that a gamma-activated sequence (GAS), located at − 7 to − 15-bp, is required for IFN-γ-upregulated promoter activity. Furthermore, an electrophoretic mobility shift assay showed that signal transducers and activators of transcription 1 (STAT1) attach to the GAS motif on the human STING promoter region. This indicates that IFN-γ/Janus kinases/STAT1 signaling is essential for the STING upregulation in human keratinocytes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boehm U, Klamp T, Groot M, Howard JC (1997) Cellular responses to interferon-gamma. Annu Rev Immunol 15:749–795
Bowie AG, Unterholzner L (2008) Viral evasion and subversion of pattern-recognition receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 8:911–922
Chen H, Sun H, You F, Sun W, Zhou X, Chen L, Yang J, Wang Y, Tang H, Guan Y, Xia W, Gu J, Ishikawa H, Gutman D, Barber G, Qin Z, Jiang Z (2011) Activation of STAT6 by STING is critical for antiviral innate immunity. Cell 147:436–446
de Prati AC, Ciampa AR, Cavalieri E, Zaffini R, Darra E, Menegazzi M, Suzuki H, Mariotto S (2005) STAT1 as a new molecular target of anti-inflammatory treatment. Curr Med Chem 12:1819–1828
Gao P, Ascano M, Zillinger T, Wang W, Dai P, Serganov AA, Gaffney BL, Shuman S, Jones RA, Deng L, Hartmann G, Barchet W, Tuschl T, Patel DJ (2013) Structure-function analysis of STING activation by c[G(2′,5′)pA(3′,5′)p] and targeting by antiviral DMXAA. Cell 154:748–762
Ho SN, Hunt HD, Horton RM, Pullen JK, Pease LR (1989) Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene 77:51–59
Ishikawa H, Barber GN (2008) STING is an endoplasmic reticulum adaptor that facilitates innate immune signalling. Nature 455:674–678
Ishikawa H, Barber GN (2011) The STING pathway and regulation of innate immune signaling in response to DNA pathogens. Cell Mol Life Sci 68:1157–1165
Ishikawa H, Ma Z, Barber GN (2009) STING regulates intracellular DNA-mediated, type I interferon-dependent innate immunity. Nature 461:788–792
Kalali BN, Köllisch G, Mages J, Müller T, Bauer S, Wagner H, Ring J, Lang R, Mempel M, Ollert M (2008) Double-stranded RNA induces an antiviral defense status in epidermal keratinocytes through TLR3-, PKR-, and MDA5/RIG-I-mediated differential signaling. J Immunol 181:2694–2704
Karim R, Meyers C, Backendorf C, Ludigs K, Offringa R, van Ommen GJ, Melief CJ, van der Burg SH, Boer JM (2011) Human papillomavirus deregulates the response of a cellular network comprising of chemotactic and proinflammatory genes. PLoS ONE 6:e17848
Kemp MG, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Sancar A (2015) UV Light potentiates STING (stimulator of interferon genes)-dependent innate immune signaling through deregulation of ULK1 (Unc51-like kinase 1). J Biol Chem 290:12184–12194
Kimura K, Matsuzaki Y, Nishikawa Y, Kitamura H, Akasaka E, Rokunohe D, Nakano H, Imaizumi T, Satoh K, Sawamura D (2012) Characterization of retinoic acid-inducible gene-I (RIG-I) expression corresponding to viral infection and UVB in human keratinocytes. J Dermatol Sci 66:64–70
Ma F, Li B, Yu Y, Iyer SS, Sun M, Cheng G (2015) Positive feedback regulation of type I interferon by the interferon-stimulated gene STING. EMBO Rep 16:202–212
Rani MR, Ransohoff RM (2005) Alternative and accessory pathways in the regulation of IFN-beta-mediated gene expression. J Interferon Cytokine Res 25:788–798
Staab J, Herrmann-Lingen C, Meyer T (2013) A rapid conformational rearrangement of STAT1 dimers is required for termination rather than for amplification of interferon-γ signaling. JAKSTAT 2:e23576
Steiner E, Holzmann K, Pirker C, Elbling L, Micksche M, Sutterlüty H, Berger W (2006) The major vault protein is responsive to and interferes with interferon-gamma-mediated STAT1 signals. J Cell Sci 119:459–469
Sun L, Wu J, Du F, Chen X, Chen ZJ (2013) Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway. Science 339:786–791
Takeuchi O, Akira S (2010) Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 140:805–820
Thompson MR, Kaminski JJ, Kurt-Jones EA, Fitzgerald KA (2011) Pattern recognition receptors and the innate immune response to viral infection. Viruses 3:920–940
Wu J, Sun L, Chen X, Du F, Shi H, Chen C, Chen ZJ (2013) Cyclic GMP-AMP is an endogenous second messenger in innate immune signaling by cytosolic DNA. Science 339:826–830
Yoshizumi M, Nakamura T, Kato M, Ishioka T, Kozawa K, Wakamatsu K, Kimura H (2008) Release of cytokines/chemokines and cell death in UVB-irradiated human keratinocytes, HaCaT. Cell Biol Int 32:1405–1411
Zhong B, Yang Y, Li S, Wang YY, Li Y, Diao F, Lei C, He X, Zhang L, Tien P, Shu HB (2008) The adaptor protein MITA links virus-sensing receptors to IRF3 transcription factor activation. Immunity 29:538–550
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms. Yukiko Tamura and Ikuko Takahashi for their technical assistance. This work was supported by KAKENHI (26461675).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishikawa, Y., Matsuzaki, Y., Kimura, K. et al. Modulation of Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING) Expression by Interferon-γ in Human Keratinocytes. Biochem Genet 56, 93–102 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-017-9832-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-017-9832-7