Abstract
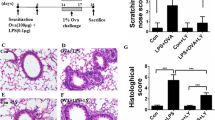
This study aimed to investigate the effects of the 5-HT7 receptor agonist (LP44) and antagonist (SB269970) on LPS-induced in vivo tissue damage and cell culture by molecular methods. This study was conducted in two steps. For in vivo studies, 24 female rats were divided into four groups. Group I: healthy; II (2nd h): LPS 5 mg/kg administered intraperitoneally (i.p.); III (4th h): LPS 5 mg/kg administered i.p.; IV (8th h): LPS 5 mg/kg administered i.p. For in vitro studies, we used the A549 cell line. Groups: I control (healthy) (2–4 h); II LPS: 1 µg/ml E. Coli O55:B5 strain (2–4 h); III agonist (LP44) 10−9 M (2–4 h); IV antagonist (SB269970) 10−9 M (2–4 h); V LPS+agonist 10−9 M (LP44 1 µg/ml) (2–4 h); VI LPS+antagonist 10−9 M (2–4 h). In molecular analyses, we determined increased TNF-α, IL-1β, NF-κB, and 5-HT7 mRNA expressions in rat lung tissues and increased TNF-α, iNOS, and 5-HT7 mRNA expressions in the A549 cell line. In in vitro parameters, LP44 agonist administration-related decrease was observed. Our study showed that lung 5-HT7 receptor expression is increased in LPS-induced endotoxemia. All this data suggest that 5-HT7 receptor overexpression is an important protective mechanism during LPS-induced sepsis-related cell damage.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akça AGH (2007) Immuniteye Genel Bakış ve Paraziter Hastalıklarda Immunite. Tıbbi ve Veteriner Immunoparazitoloji, Türkiye: Parazitoloji Derneği Yayınları. Yayın No:21. İzmir, p 430–431
Aladağ MA, Türköz Y, Özerol İH (2000) Nitrik oksit ve nörofizyopatolojik etkileri. Turkiye Klinikleri J Med Sci 20(2):107–111
Albayrak A, Halici Z, Cadirci E, Polat B, Karakus E, Bayir Y et al (2013) Inflammation and peripheral 5-HT7 receptors: the role of 5-HT7 receptors in carrageenan induced inflammation in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 715(1–3):270–279
Albrecht EW, Stegeman CA, Heeringa P, Henning RH, van Goor H (2003) Protective role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. J Pathol 199(1):8–17
Baeuerle PA (1998) Pro-inflammatory signaling: last pieces in the NF-κB puzzle? Curr Biol 8(1):R19–R22
Benedict CR, Mathew B, Rex KA, Cartwright J Jr, Sordahl LA (1986) Correlation of plasma serotonin changes with platelet aggregation in an in vivo dog model of spontaneous occlusive coronary thrombus formation. Circ Res 58(1):58–67
Bhatia M, Moochhala S (2004) Role of inflammatory mediators in the pathophysiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Pathol 202(2):145–156
Buras JA, Holzmann B, Sitkovsky M (2005) Animal models of sepsis: setting the stage. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4(10):854–865
Cadirci E, Halici Z, Bayir Y, Albayrak A, Karakus E, Polat B et al (2013) Peripheral 5-HT7 receptors as a new target for prevention of lung injury and mortality in septic rats. Immunobiology 218(10):1271–1283
Cazzola M, Matera MG (2000) 5-HT modifiers as a potential treatment of asthma. Trends Pharmacol Sci 21(1):13–16
Chen X-M, O’Hara SP, Nelson JB, Splinter PL, Small AJ, Tietz PS et al (2005) Multiple TLRs are expressed in human cholangiocytes and mediate host epithelial defense responses to Cryptosporidium parvum via activation of NF-κB. J Immunol 175(11):7447–7456
Damas P, Ledoux D, Nys M, Vrindts Y, De Groote D, Franchimont P et al (1992) Cytokine serum level during severe sepsis in human IL-6 as a marker of severity. Ann Surg 215(4):356
Dean B, Pavey G, Thomas D, Scarr E (2006) Cortical serotonin7, 1D and 1F receptors: effects of schizophrenia, suicide and antipsychotic drug treatment. Schizophr Res 88(1–3):265–274
Dejager L, Pinheiro I, Dejonckheere E, Libert C (2011) Cecal ligation and puncture: the gold standard model for polymicrobial sepsis? Trends Microbiol 19(4):198–208
Demling RH, Wong C, Fox R, Hechtman H, Huval W (1985) Relationship of increased lung serotonin levels to endotoxin-induced pulmonary hypertension in sheep. Effect of a serotonin antagonist. Am Rev Respir Dis 132(6):1257–1261
Dupont LL, Bracke KR, De Maeyer JH, Compan V, Joos GF, Lefebvre RA et al (2014) Investigation of 5-HT 4 receptors in bronchial hyperresponsiveness in cigarette smoke-exposed mice. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 28(1):60–67
El Nehir S, Karakaya S (2004) Radical scavenging and iron-chelating activities of some greens used as traditional dishes in Mediterranean diet. Int J Food Sci Nutr 55(1):67–74
Eskandari MK, Bolgos G, Miller C, Nguyen DT, DeForge LE, Remick DG (1992) Anti-tumor necrosis factor antibody therapy fails to prevent lethality after cecal ligation and puncture or endotoxemia. J Immunol 148(9):2724–2730
Evans GF, Snyder YM, Butler LD, Zuckerman SH (1989) Differential expression of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor in murine septic shock models. Circ Shock 29(4):279–290
Hernekamp JF, Hu S, Schmidt K, Walther A, Kneser U, Kremer T (2013) Cinanserin reduces plasma extravasation after burn plasma transfer in rats. Burns J Int Soc Burn Inj 39(6):1226–1233
Kang Q, Chen Y, Zhang X, Yu G, Wan X, Wang J et al (2015) Heat shock protein A12B protects against sepsis-induced impairment in vascular endothelial permeability. J Surg Res 202(1):87–94
Kürkçü E (2008) Deneysel olarak oluşturulmuş meme tümörlerinde curcumin’in arginaz enzim aktivitesi, ornitin ve nitrik oksit düzeylerine etkisi
Kuşcuoğlu U (2004) Deneysel omurilik yaralanmasında agmatin’in doza bağlı nöroprotektif etkilerinin incelenmesi. İstanbul
Kuyumcu A, Düzgün AP, Özmen MM, Besler HT (2004) Travma ve enfeksiyonda nitrik oksidin rolü. Turk J Trauma Emerg Surg 10(3):149–159
Leon-Ponte M, Ahern GP, O’Connell PJ (2007) Serotonin provides an accessory signal to enhance T-cell activation by signaling through the 5-HT7 receptor. Blood 109(8):3139–3146
Leopoldo M, Lacivita E, Berardi F, Perrone R, Hedlund PB (2011) Serotonin 5-HT7 receptor agents: structure-activity relationships and potential therapeutic applications in central nervous system disorders. Pharmacol Ther 129(2):120–148
Lepoivre M, Fieschi F, Coves J, Thelander L, Fontecave M (1991) Inactivation of ribonucleotide reductase by nitric oxide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 179(1):442–448
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Livermore S, Zhou Y, Pan J, Yeger H, Nurse CA, Cutz E (2015) Pulmonary neuroepithelial bodies are polymodal airway sensors: evidence for CO2/H+ sensing. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 308(8):L807–L815
Maleki-Dizaji N, Eteraf-Oskouei T, Fakhrjou A, Maljaie SH, Garjani A (2010) The effects of 5HT3 receptor antagonist granisetron on inflammatory parameters and angiogenesis in the air-pouch model of inflammation. Int Immunopharmacol 10(9):1010–1016
Mossner R, Lesch KP (1998) Role of serotonin in the immune system and in neuroimmune interactions. Brain Behav Immun 12(4):249–271
Nilsson T, Longmore J, Shaw D, Pantev E, Bard JA, Branchek T et al (1999) Characterisation of 5-HT receptors in human coronary arteries by molecular and pharmacological techniques. Eur J Pharmacol 372(1):49–56
Nishiyama T (2009) Acute effects of sarpogrelate, a 5-HT2A receptor antagonist on cytokine production in endotoxin shock model of rats. Eur J Pharmacol 614(1–3):122–127
Özkan C, Akgül Y (2010) Deneysel Nefrotoksisite Oluşturulan Tavşanlarda Nitrik Oksit Donörü (L-Arginin) ve Nitrik Oksit Sentaz İnhibitörlerinin (Aminoguanidin, L-NAME) Bazı Biyokimyasal Parametrelere Etkileri. Yüzüncü Yıl Üniversitesi Veteriner Fakültesi Dergisi 21(1):35–41
Reinhart K, Daniels R, Kissoon N, O’Brien J, Machado FR, Jimenez E (2013) The burden of sepsis-a call to action in support of World Sepsis Day 2013. J Crit Care 28(4):526–528
Ruggieri AJ, Levy RJ, Deutschman CS (2010) Mitochondrial dysfunction and resuscitation in sepsis. Crit Care Clin 26(3):567–575
Schabbauer G (2012) Polymicrobial sepsis models: CLP versus CASP. Drug Discov Today Dis Models 9(1):e17–e21
Segura P, Vargas M, Córdoba-Rodríguez G, Chávez J, Arreola J, Campos-Bedolla P et al (2010) Role of 5-HT2A, 5-HT4 and 5-HT7 receptors in the antigen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness in guinea-pigs. Clin Exp Allergy 40(2):327–338
Shishodia S, Aggarwal BB (2004) Nuclear factor-κB: a friend or a foe in cancer? Biochem Pharmacol 68(6):1071–1080
Tizard IR (2004) Veterinary immunology: an introduction, 7th edn. Saunders, Readfield, pp 293–299
Tosi MF (2005) Innate immune responses to infection. J Allergy Clin Immunol 116(2):241–249
Türköz YÖE (1997) Nitrik oksit’in etkileri ve patolojik rolleri
Ullmer C, Schmuck K, Kalkman HO, Lubbert H (1995) Expression of serotonin receptor mRNAs in blood vessels. FEBS Lett 370(3):215–221
Waddick KG, Uckun FM (1999) Innovative treatment programs against cancer: II. Nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) as a molecular target. Biochem Pharmacol 57(1):9–17
Yang GB, Qiu CL, Zhao H, Liu Q, Shao Y (2006) Expression of mRNA for multiple serotonin (5-HT) receptor types/subtypes by the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of rhesus macaques. J Neuroimmunol 178(1–2):24–29
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the TUBITAK 1001 project (TUBITAK-112S627) and was conducted in the pharmacology of the Faculty of Medicine at Ataturk University, 25240 Erzurum/Turkey. This study is a part of Master thesis of Gulsen AYAZ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None of the authors has a commercial interest, financial interest, and/or other relationship with manufacturers of pharmaceuticals, laboratory supplies, and/or medical devices or with commercial providers of medically related services.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayaz, G., Halici, Z., Albayrak, A. et al. Evaluation of 5-HT7 Receptor Trafficking on In Vivo and In Vitro Model of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Inflammatory Cell Injury in Rats and LPS-Treated A549 Cells. Biochem Genet 55, 34–47 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-016-9769-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-016-9769-2