Abstract
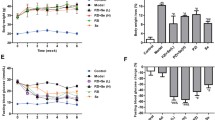
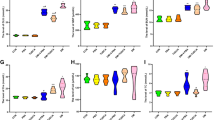
Selenium and exendin-4 exert antidiabetic effects by unknown mechanisms. Herein, we investigated their effects on the expression of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R), insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1), and Raf-1 in the livers of rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetic rats were injected intraperitoneally with exendin-4 (0.03 μg/kg body weight) twice daily or treated with 5 ppm selenium as sodium selenite in drinking water for 4 weeks. Both selenium and exendin-4 reduced the hyperglycemia in diabetic rats. Induction of diabetes mellitus resulted in decreased level of GLP-1R and increased levels of IRS-1 and Raf-1 in the liver. Treatment of diabetic rats with selenium or exendin-4 resulted in increased level of GLP-1R and decreased levels of IRS-1 and Raf-1 in the liver, compared with the levels in diabetic rats. Therefore, the antidiabetic actions of selenium and exendin-4 involve their effects on GLP-1R, IRS-1, and Raf-1 levels in the liver.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbaraly TN, Arnaud J, Rayman MP, Hininger-Favier I, Roussel A, Berr C, Fontbonne A (2010) Plasma selenium and risk of dysglycemia in an elderly French population: results from the prospective epidemiology of vascular ageing study. Nutr Metab (Lond) 7(21):1–7
Algotar AM, Stratton MS, Xu MJ, Dalkin BL, Nagle RB, Hsu CH, Ahmann FR, Clark LC, Stratton SP (2011) Dose-dependent effects of selenized yeast on total selenium levels in prostatic tissue of men with prostate cancer. Nutr Cancer 63(1):1–5
Ban K, Noyan-Ashraf H, Hoefer J, Steffen-Sebastian B, Drucker DJ, Mansoor H (2008) Cardioprotective and vasodilatory actions of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor are mediated through both glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor-dependent and -independent pathways. Circulation 117(18):2340–2350
Bergmann U, Funatomi H, Kornmann M, Beger HG, Korc M (1996) Increased expression of insulin receptor substrate-1 in human pancreatic cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 220(3):886–890
Bjorkhem-Bergman L, Torndal UB, Eken S, Nystrom C, Capitanio A, Larsen EH, Bjornstedt M, Eriksson LC (2005) Selenium prevents tumor development in a rat model for chemical carcinogenesis. Carcino 26(1):125–131
Bleys J, Navas-Acien A, Guallar E (2007) Serum selenium and diabetes in US adults. Diabetes Care 30(4):829–834
Campbell SC, Aldibbiat A, Marriotta CE, Landya C, Tomader A, Ferrisc WF, Butlerd CS, Shawb JA, Macfarlanea WM (2008) Selenium stimulates pancreatic β-cell gene expression and enhances islet function. FEBS Lett 582(15):2333–2337
Douillet C, Tabib A, Bost M, Accominotti M, Borson-Chazot F, Ciavatti M (1999) Selenium in diabetes: effects of selenium on nephropathy in type I streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Trace Elem Exp Med 12:379–392
Drucker DJ (2003) Glucagon-like peptide-1 and the islet β-cell: augmentation of cell proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis. Endocrinology 144:5145–5148
Drucker DJ (2007) The role of gut hormones in glucose homeostasis. J Clin Invest 117(1):24–32
Elliott RM, Morgan LM, Tredger JA, Deacon S, Wright J, Marks V (1993) Glucagon-like peptide-1(7–36) amide and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide secretion in response to nutrient ingestion in man: acute post-prandial and 24 h secretion patterns. J Endocrinol 138:159–166
Fehmann HC, Goke R, Goke B (1992) Glucagon-like peptide-1(7–37)/(7–36) amide is a new incertin. Mol Cell Endocrinol 85(1–2):C39–C44
Fürnsinn C, Englisch R, Ebner K, Nowotny P, Vogl C, Waldhäusl W (1996) Insulin-like vs. non-insulin-like stimulation of glucose metabolism by vanadium, tungsten, and selenium compounds in rat muscle. Life Sci 23:1989–2000
Ghosh R, Mukherjee B, Chatterjee M (1994) A novel effect of selenium on streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Diabetes Res 25(4):165–171
Goke R, Fehmann HC, Linn T, Schmidt H, Krause M, Eng J, Goke B (1993) Exendin-4 is a high potency agonist and truncated exendin-(9–39)-amide an antagonist at the glucagon-like peptide 1-(7–36)-amide receptor of insulin-secreting β-cells. J Biol Chem 268(26):19650–19655
Grankvist K, Marklund SL, Täljedal IB (1981) Cu, Zn-superoxide dismutase, Mn-superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase in pancreatic islets and other tissues in the mouse. Biochem J 199:393–398
Hara K, Yonezawa K, Sakaue J, Ando A, Kotani K, Kitamura T, Kitamura Y, Ueda H, Stephens L, Jackson TR (1994) 1-Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity is required for insulin-stimulated glucose transport but not for RAS activation in CHO cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 91:7415–7419
Harmon JS, Bogdani M, Parazzoli SD, Mak SS, Oseid EA, Berghmans M, Leboeuf RC, Robertson RP (2009) Beta-cell-specific overexpression of glutathione peroxidase preserves intranuclear MafA and reverses diabetes in db/db mice. Endocrinology 150:4855–4862
Hei YJ, Farahbakhshian S, Chen X, Battell ML, McNeill JH (1998) Stimulation of MAP kinase and S6 kinase by vanadium and selenium in rat adipocytes. Mol Cell Biochem 178(1–2):367–375
Hong G, Xinjun W, Zhiguo Z, Yisheng Y, Jun Y, Xiaoying L, Guang N (2007) GLP-1 amplifies insulin signaling by up-regulation of IRβ, IRS-1 and Glut4 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Endocrine 32(1):90–95
Iizuka Y, Sakurai E, Maeda K, Hikichi N (1993) Effects of selenium on the glycolysis and gluconeogenesis system in rat liver. Yakugaku Zasshi 113(7):525–531
Kljai K, Runje R (2001) Selenium and glycogen levels in diabetic patients. Biol Trace Elem Res 83:223–229
Laakso M, Malkki M, Kekäläinen P, Kuusisto J, Deeb S (1994) Insulin receptor substrate-1 variants in non-insulin-dependent diabetes. J Clin Invest 94(3):1141–1146
Labunskyy VM, Lee BC, Handy DE, Loscalzo J, Hatfield DL, Gladyshev VN (2011) Both maximal expression of selenoproteins and selenoprotein deficiency can promote development of type 2 diabetes-like phenotype in mice. Antioxid Redox Signal 14:2327–2336
Lei XG, Cheng WH (2005) New roles for an old selenoenzyme: evidence from glutathione peroxidase-1 null and overexpressing mice. J Nutr 135:2295–2298
Lippman SM, Klein EA, Goodman PJ, Lucia MS, Thompson IM, Ford LG, Parnes HL, Minasian LM, Gaziano JM, Hartline JA, Parsons JK, Bearden JD 3rd, Crawford ED, Goodman GE, Claudio J, Winquist E, Cook ED, Karp DD, Walther P, Lieber MM, Kristal AR, Darke AK, Arnold KB, Ganz PA, Santella RM, Albanes D, Taylor PR, Probstfield JL, Jagpal TJ, Crowley JJ, Meyskens FL Jr, Baker LH, Coltman CA Jr (2009) Effect of selenium and vitamin E on risk of prostate cancer and other cancers: the selenium and vitamin E cancer prevention trial (SELECT). JAMA 301:39–51
Lortz S, Tiedge M, Nachtwey T, Karlsen AE, Nerup J, Lenzen S (2000) Protection of insulin-producing RINm5F cells against cytokine-mediated toxicity through overexpression of antioxidant enzymes. Diabetes 49:1123–1130
Maiese K, Morhan SD, Chong ZZ (2007) Oxidative stress biology and cell injury during type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Neurovasc Res 4(1):63–71
McClung JP, Roneker CA, Mu W, Lisk DJ, Langlas P, Lu F, Lei XG (2004) Development of insulin resistance and obesity in mice overexpressing cellular glutathione peroxidase. PNAS 101:8852–8857
McNeill JH, Delgatty HL, Battell ML (1991) Insulinlike effects of sodium selenate in streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes 40(12):1675–1678
Moriscot C, Richard M, Favrot MC, Benhamou PY (2003) Protection of insulin-secreting INS-1 cells against oxidative stress through adenoviral-mediated glutathione peroxidase overexpression. Diabetes Metab 29:145–151
Mukherjee B, Anbazhagan S, Roy A, Ghosh R, Chatterjee M (1998) Novel implications of the potential role of selenium on antioxidant status in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Biomed Pharmacother 52(2):89–95
Mysore TB, Shinkel TA, Collins J, Salvaris EJ, Fisicaro N, Murray-Segal LJ, Johnson LE, Lepore DA, Walters SN, Stokes R, Chandra AP, O’Connell PJ, d’Apice AJ, Cowan PJ (2005) Overexpression of glutathione peroxidase with two isoforms of superoxide dismutase protects mouse islets from oxidative injury and improves islet graft function. Diabetes 54:2109–2116
Navarro-Alarcon M, Lopez G, Perez-Valero V, Lopez-Martinez C (1999) Serum and urine selenium concentrations as indicators of body status in patients with diabetes mellitus. Sci Total Environ 228:79–85
Rajpathak S, Rimm E, Morris JS, Hu F (2005) Toenail selenium and cardiovascular disease in men with diabetes. J Am Coll Nutr 24:250–256
Rasekh HR, Potmis RA, Nonavinakere VK, Early JL, Iszard MB (1991) Effect of selenium on plasma glucose of rats: role of insulin and glucocorticoids. Toxicol Lett 58(2):199–207
Schnedl WJ, Ferber S, Johnson JH, Newgard CB (1994) STZ transport and cytotoxicity. Specific enhancement in GLUT2-expressing cells. Diabetes 43(11):1326–1333
Sesti G, Federici M, Hribal ML, Lauro D, Sbraccia P, Lauro R (2001) Defects of the insulin receptor substrate (IRS) system in human metabolic disorders. FASEB J 15(12):2099–2111
Stapleton SR (2000) Selenium: an insulin-mimetic. Cell Mol Life Sci 57(13–14):1874–1879
Stranges S, Marshall JR, Natarajan R, Donahue RP, Trevisan M, Combs GF, Cappuccio FP, Ceriello A, Reid ME (2007) Effects of long-term selenium supplementation on the incidence of type 2 diabetes: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 47(4):217–223
Trumper A, Trumper K, Horsch D (2002) Mechanisms of mitogenic and anti-apoptotic signaling by glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide in β (INS-1)-cells. J Endocrinol 174:233–246
Wang XD, Vatamaniuk MZ, Wang SK, Roneker CA, Simmons RA, Lei XG (2008) Molecular mechanisms for hyperinsulinemia induced by overproduction of selenium-dependent glutathione peroxidase-1 in mice. Diabetologia 51:1515–1524
Xu G, Kaneto H, Laybutt DR, Duvivier-Kali VF, Trivedi N, Suzuma K, King GL, Weir GC, Bonner-Weir S (2007) Down regulation of GLP-1 and GIP receptor expression by hyperglycemia. Diabetes 56:1551–1558
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a research fund from the National Council for Scientific Research (CNRS), Lebanon, to M.E.M. (Grant No. 01-11-08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barakat, G.M., Moustafa, M.E. & Bikhazi, A.B. Effects of Selenium and Exendin-4 on Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor, IRS-1, and Raf-1 in the Liver of Diabetic Rats. Biochem Genet 50, 922–935 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-012-9532-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-012-9532-2