Abstract
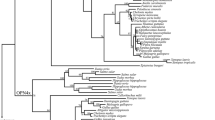
A newly discovered melanopsin gene (Opn4) encodes a member of the opsins, melanopsin. Two melanopsin genes, mammalian-like Opn4m and Xenopus-like Opn4x, have been described in nonmammalian vertebrates, but the underlying evolutionary mechanisms behind the duplication of melanopsin genes remain unclear. We conducted a comprehensive evolutionary analysis within a phylogenetic framework. In our phylogenetic tree, the duplication of Opn4m and Opn4x probably occurred prior to the emergence of vertebrates, and subsequently Opn4x disappeared in the lineages leading to mammalian species. Evolutionary analyses show strong purifying selection during melanopsin evolution. We also provide evidence that Opn4x underwent positive selection after the early gene duplication events. It has been indicated that functional divergence and altered functional constraints occurred between Opn4m and Opn4x duplicates with the identification of positively selected amino acids. Our findings highlight the evolutionary malleability in vertebrate melanopsin genes and provide a genetic basis for comparative studies of functional properties of these two melanopsins.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped Blast and PSI-Blast: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–33402
Bagnara J, Hadley ME (1973) Chromatophores and color change: the comparative physiology of animal pigmentation. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Bellingham J, Chaurasia SS, Melyan Z, Liu C, Cameron MA, Tarttelin EE, Iuvone PM, Hankins MW, Tosini G, Lucas RJ (2006) Evolution of melanopsin photoreceptors: discovery and characterization of a new melanopsin in nonmammalian vertebrates. PLoS Biol 4:e254
Berson DM, Dunn FA, Takao M (2002) Phototransduction by retinal ganglion cells that set the circadian clock. Science 295:1070–1073
Bockaert J, Pin JP (1999) Molecular tinkering of G protein-coupled receptors: an evolutionary success. EMBO J 18:1723–1729
Drivenes O, Soviknes AM, Ebbesson LO, Fjose A, Seo HC, Helvik JV (2003) Isolation and characterization of two teleost melanopsin genes and their differential expression within the inner retina and brain. J Comp Neurol 456:84–93
Frigato E, Vallone D, Bertolucci C, Foulkes NS (2006) Isolation and characterization of melanopsin and pinopsin expression within photoreceptive sites of reptiles. Naturwissenschaften 93:379–385
Fujii R (2000) The regulation of motile activity in fish chromatophores. Pigment Cell Res 13:300–319
Gribaldo S, Casane D, Lopez P, Philippe H (2003) Functional divergence prediction from evolutionary analysis: a case study of vertebrate hemoglobin. Mol Biol Evol 20:1754–1759
Gu X (1999) Statistical methods for testing functional divergence after gene duplication. Mol Biol Evol 16:1664–1667
Gu X (2001) Maximum-likelihood approach for gene family evolution under functional divergence. Mol Biol Evol 18:453–464
Gu X (2006) A simple statistical method for estimating type-II (cluster-specific) functional divergence of protein sequences. Mol Biol Evol 23:1937–1945
Gu X, Vander Velden K (2002) Diverge: phylogeny-based analysis for functional-structural divergence of a protein family. Bioinformatics 18:500–501
Hankins MW, Peirson SN, Foster RG (2008) Melanopsin: an exciting photopigment. Trends Neurosci 31:27–36
Hattar S, Liao HW, Takao M, Berson DM, Yau KW (2002) Melanopsin-containing retinal ganglion cells: architecture, projections, and intrinsic photosensitivity. Science 295:1065–1070
Hermann R, Poppeb L, Pilbákb S, Bodena C, Maurera J, Webera S, Lerch A (2005) Predicted 3D-structure of melanopsin, the non-rod, non-cone photopigment of the mammalian circadian clock, from Djungarian hamsters (Phodopus sungorus). Neurosci Lett 376:76–80
Jenkins A, Munoz M, Tarttelin EE, Bellingham J, Foster RG, Hankins MW (2003) VA opsin, melanopsin, and an inherent light response within retinal interneurons. Curr Biol 13:1269–1278
Jones CD, Begun DJ (2005) Parallel evolution of chimeric fusion genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:11373–11378
Lucas RJ, Freedman MS, Munoz M, Garcia-Fernandez JM, Foster RG (1999) Regulation of the mammalian pineal by non-rod, non-cone, ocular photoreceptors. Science 284:505–507
Lucas RJ, Hattar S, Takao M, Berson DM, Foster RG, Yau KW (2003) Diminished pupillary light reflex at high irradiances in melanopsin-knockout mice. Science 299:245–247
Madabushi S, Gross AK, Philippi A, Meng EC, Wensel TG, Lichtarge O (2004) Evolutionary trace of G protein-coupled receptors reveals clusters of residues that determine global and class-specific functions. J Biol Chem 279:8126–8132
Massingham T, Goldman N (2005) Detecting amino acid sites under positive selection and purifying selection. Genetics 169:1753–1762
Menon ST, Han M, Sakmar TP (2001) Rhodopsin: structural basis of molecular physiology. Physiol Rev 81:1659–1688
Notredame C, Higgins DG, Heringa J (2000) T-Coffee: A novel method for fast and accurate multiple sequence alignment. J Mol Biol 302:205–217
Oliphant LW (1988) Cytology and pigments of non-melanophore chromatophores in the avian iris. Prog Clin Biol Res 256:65–82
Oshima N (2001) Direct reception of light by chromatophores of lower vertebrates. Pigment Cell Res 14:312–319
Palczewski K, Kumasaka T, Hori T, Behnke CA, Motoshima H, Fox BA, Trong IL, Teller DC, Okada T, Stenkamp RE, Yamamoto M, Miyano M (2000) Crystal structure of rhodopsin: a G protein-coupled receptor. Science 289:739–745
Panda S, Sato TK, Castrucci AM, Rollag MD, DeGrip WJ, Hogenesch JB, Provencio I, Kay SA (2002) Melanopsin (Opn4) requirement for normal light-induced circadian phase shifting. Science 298:2213–2216
Pires SS, Shand J, Bellingham J, Arrese C, Turton M, Peirson S, Foster RG, Halford S (2007) Isolation and characterization of melanopsin (Opn4) from the Australian marsupial Sminthopsis crassicaudata (fat-tailed dunnart). Proc Biol Sci 274:2791–2799
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) Modeltest: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817–818
Provencio I, Cooper HM, Foster RG (1998a) Retinal projections in mice with inherited retinal degeneration: implications for circadian photoentrainment. J Comp Neurol 395:417–439
Provencio I, Jiang G, De Grip WJ, Hayes WP, Rollag MD (1998b) Melanopsin: an opsin in melanophores, brain, and eye. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:340–345
Provencio I, Rodriguez IR, Jiang G, Hayes WP, Moreira EF, Rollag MD (2000) A novel human opsin in the inner retina. J Neurosci 20:600–605
Rambaut A (1996) Se-Al. http://evolve.zoo.ox.ac.uk/Se-Al/Se-Al.html
Rollag MD (1996) Amphibian melanophores become photosensitive when treated with retinal. J Exp Zool 275:20–26
Ruby NF, Brennan TJ, Xie X, Cao V, Franken P, Heller HC, O’Hara BF (2002) Role of melanopsin in circadian responses to light. Science 298:2211–2213
Sawyer S (1989) Statistical tests for detecting gene conversion. Mol Biol Evol 6:526–538
Swofford DL (2003) PAUP: Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (and other methods), version 4. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
Taylor JS, Braasch I, Frickey T, Meyer A, Van de Peer Y (2003) Genome duplication, a trait shared by 22,000 species of ray-finned fish. Genome Res 13:382–390
Terakita A, Yamashita T, Shichida Y (2000) Highly conserved glutamic acid in the extracellular IV–V loop in rhodopsins acts as the counterion in retinochrome, a member of the rhodopsin family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:14263–14267
Wang Y, Gu X (2001) Functional divergence in the caspase gene family and altered functional constraints: statistical analysis and prediction. Genetics 158:1311–1320
Yang Z (2007) PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol Biol Evol 24:1586–1591
Yang Z, Nielsen R, Goldman N, Pedersen AM (2000) Codon-substitution models for heterogeneous selection pressure at amino acid sites. Genetics 155:431–449
Yang Z, Wong WS, Nielsen R (2005) Bayes empirical Bayes inference of amino acid sites under positive selection. Mol Biol Evol 22:1107–1118
Yokoyama S, Radlwimmer FB (2001) The molecular genetics and evolution of red and green color vision in vertebrates. Genetics 158:1697–1710
Yokoyama S, Starmer WT, Takahashi Y, Tada T (2006) Tertiary structure and spectral tuning of UV and violet pigments in vertebrates. Gene 365:95–103
Zhang J (1999) Performance of likelihood ratio tests of evolutionary hypotheses under inadequate substitution models. Mol Biol Evol 16:868–875
Zhang J (2004) Frequent false detection of positive selection by the likelihood method with branch-site models. Mol Biol Evol 21:1332–1339
Zhang J, Nielsen R, Yang Z (2005) Evaluation of an improved branch-site likelihood method for detecting positive selection at the molecular level. Mol Biol Evol 22:2472–2479
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Huabin Zhao, Dr. Aleksei Chmura and Dr. Dong Dong for their kind comments and manuscript editing. This study was funded by grants under the Key Construction Program of the National “985” Project and “211” Project awarded to SZ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, C., Zhang, J., Qiao, J. et al. Positive Selection and Functional Divergence After Melanopsin Gene Duplication. Biochem Genet 50, 235–248 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-011-9466-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-011-9466-0