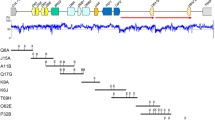
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC), with its extraordinary levels of genetic variation, is thought to be an essential aspect of the ability of an organism to recognize different parasites and pathogens. It has also been proposed to regulate reproductive processes in many aspects. Here we examine the genetic variation of the second exon of the MHC class II B genes of the crested ibis, an endangered species known to descend from just two breeding pairs rediscovered in 1981. Only five alleles are identified by single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) analysis of 36 samples taken from both wild and captive populations, and a comparatively low level of divergence between MHC alleles is observed. We suggest that representative sampling of individuals with most of the different MHC allele genotypes to constitute a founder population, together with the monitoring of the pathogen status of candidate sites before release, is of great importance for raising the success rate of reintroduction for the crested ibis.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bassam, B. J., Caetano-Anolles, G., and Gresshoff, P. M. (1991). Fast and sensitive silver staining of DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 196(1):80–83.
Bird Life International (2001). Threatened Birds of Asia: The Bird Life International Red Data Book, Bird Life International, Cambridge, UK.
Brown, J. H., Jardetzky, T. S., Gorga, J. C., Stem, L. J., Urban, R. G., Strominger, J. L., and Wiley, D. C. (1993). Three-dimensional structure of the human class II histocompatibility antigen HLA-DRI. Nature 364:33–39.
Ding, C. Q., and Liu, D. P. (2002). Crested Ibis Nipponia nippon. Chin. J. Zool. 37:84.
Edwards, S. V., Grahn, M., and Potts, W. K. (1995). Dynamics of Mhc evolution in birds and crocodilians: Amplification of class II genes with degenerate primers. Mol. Ecol. 4:719–729.
Edwards, S. V., and Potts, W. K. (1996). Polymorphism of gene in the major histocompatibility complex (MHC): Implications for conservation genetics of vertebrates. In Smith, T. B., and Wayne, R. K. (eds.), Molecular Genetic Approaches in Conservation, Oxford University Press, New York, pp. 214–236.
Fan, G. L., Yang, Z. Q., Gao, G. G., Bin, J. J., Qiao, H. L., Huang, Z. X., and Hou, Y. F. (2004). The histopathological observations of young crested ibis infected with Escherichia coli. Chin. J. Zool. 39(3):44–46.
Fan, G. L., Zhou, H. C., Yang, M. Q., Pu, P., Yang, Z. Q., Cao, Y. H., Fu, W. K., and Lu, B. Z. (2001). The pathological observation of young crested ibis newcaste disease. J. Northwest Sci. Tech. Univ. Agric. For. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 29(6):79–82.
Frankham, R., Ballou, J. D., and Briscoe, D. A. (2002). Introduction to Conservation Genetics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
Guillemot, F., Billault, A., Pourquie, O., Behar, G., Chausse, A. M., Zoorob, R., Kreibich, G., and Auffray, C. (1988). A molecular map of the chicken major histocompatibility complex: The class II genes are closely linked to the class I genes and the nucleolar organizer. EMBO J 7(9):2775–2785.
Hancock, J. A., Kushlan, J. A., and Kahl, M. P. (1992). Storks, Ibises, and Spoonbills of the World, Academic, London.
Hedrick, P. W. (1996). Conservation genetics and molecular techniques: A perspective. In Smith, T. B., and Wayne, R. K. (eds.), Molecular Genetic Approaches in Conservation, Oxford University Press, New York, pp. 459–477.
Hedrick, P. W., and Kim, T. J. (2000). Genetics of complex polymorphisms: Parasites and maintenance of MHC variation. In Singh, R. S., and Krimbas, C. B. (eds.), Evolution Genetics: From Molecules to Morphology, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, pp. 204–234.
Hedrick, P. W., Lee, R., and Parker, K. M. (2000a). Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) variation in the endangered Mexican wolf and related canids. Heredity 85:617–624.
Hedrick, P. W., Parker, K. M., Gutierrez-Espeleta, G. A., Rattink, A., and Lievers, K. (2000b). Major histocompatibility complex variation in the Arabian oryx. Evolution 54:2145–2151.
Hedrick, P. W., Parker, K. M., Miller, E. L., and Miller, P. L. (1999). Major histocompatibility complex variation in the endangered Przewalski’s horse. Genetics 152:1701–1710.
Hess, C. M., and Edwards, S. V. (2002). The evolution of the major histocompatibility complex in birds. Bioscience 52(5):423–431.
Hoelzel, A. R., Stephens, J. C., and O’Brien, S. J. (1999). Molecular genetic diversity and evolution at the MHC DQB locus in four species of pinnipeds. Mol. Biol. Evol. 16(5):611–618.
Jeffery, D. J. M., and Bangham, C. R. M. (2000). Do infectious diseases drive MHC diversity? Microb. Infect. 2:1335–1341.
Jukes, T. H., and Cantor, C. R. (1969). Evolution of protein molecules. In Munro, H. N. (ed.), Mammalian Protein Metabolism, Academic, New York, pp. 21–132.
Kumar, S., Tamura, K., Jakobsen, I. B., and Nei, M. (2001). MEGA2: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Software. Arizona State University, Tempe.
Langefors, A., Lohm, J., Grahn, M., Andersen, O., and von Schantz, T. (2001). Association between major histocompatibility complex class II B alleles and resistance to Aeromons salmonicida in Atlantic salmon. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 268:479–485.
Liu, Y. Z. (1981). Rediscovery of crested ibis Nipponia nippon in Qinling Mountain. Chin. J. Zool. 27:237.
Lohm, J., Grahn, M., Langefors, A., Andersen, O., Storset, A., and von Schantz, T. (2002). Experimental evidence for major histocompatibility complex allele-specific resistance to a bacterial infection. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 2114:2029–2034.
Lokki, M. L., and Laitinen, T. (2001). Role of major histocompatibility complex class III genes in recurrent spontaneous abortions. Front. Biosci. 6:E23–E29.
Mikko, S., Spencer, M., Morris, B., Stabile, S., Basu, T., Stormont, C., and Andersson, L. (1997). A comparative analysis of Mhc DRB3 polymorphism in the American bison (Bison bison). J. Hered. 88:499–503.
Nei, M., and Gojobori, T. (1986). Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol. Biol. Evol. 3:418–426.
Parham, P. (1999). Virtual reality in the MHC. Immunol. Rev. 167:5–15.
Paterson, S., Wilson, K., and Pemberton, J. M. (1998). Major histocompatibility complex variation associated with juvenile survival and parasite resistance in a large unmanaged ungulate population (Ovis aries L.). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95:3714–3719.
Penn, D. J., and Potts, W. K. (1998). How do major histocompatibility complex genes influence odor and mating preferences? Adv. Immunol. 69:411–436.
Richardson, D. S., and Westerdahl, H. (2003). MHC diversity in two Acrocephalus species: The outbred great reed warbler and the inbred Seychelles warbler. Mol. Ecol. 12:3523–3529.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., and Maniatis, T. (1989). Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn., Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York.
Sunnucks, P., Wilson, A. C. C., Beheregaray, L. B., Zenger, K., French, J., and Taylor, A. C. (2000). SSCP is not so difficult: The application and utility of single-stranded conformation polymorphism in evolutionary biology and molecular ecology. Mol. Ecol. 9:1699–1710.
Thompson, J. D., Gibson, T. J., Plewniak, F., Jeanmougin, F., and Higgins, D. G. (1997). The Clustal X Windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 25:4876–4882.
Wang, S. (1998). China Red Data Book of Endangered Animals: Aves, Science Press, Beijing.
Xi, Y. M., Lu, B. Z., and Fujihara, N. (2001). Captive rearing and breeding of the crested ibis, Nipponia nippon. J. Poult. Sci. 38:213–224.
Xi, Y. M., Lu, B. Z., Zhang, Y. M., and Fujihara, N. (2002). Restoration of the crested ibis, Nipponia nippon. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 22:193–200.
Xu, Y. X., Pitcovski, J., Peterson, L., Auffray, C., Bourlet, Y., Gerndt, B. M., Nordskog, A. W., Lamont, S. J., and Warner, C. M. (1989). Isolation and characterization of three class II major histocompatibility complex genomic clones from the chicken. J. Immunol. 142(6):2122–2132.
Yamashina, Y. (1975). The feeding of Japanese crested ibis. In Temple, S. A. (ed.), Endangered Birds, University of Wisconsin Press, Madison, pp. 161–164.
Zhang, B., Fang, S. G., and Xi, Y. M. (2004). Low genetic diversity in the endangered crested ibis Nipponia nippon and implications for conservation. Bird Conserv. Int. 14:183–190.
Zhou, H. C., Fan, G. L., Cao, Y. H., Fu, W. K., Lu, B. Z., and Xi, Y. M. (2000). The pathological diagnosis of the death of a domesticated crested ibis. Acta Univ. Agric. Boreali-Occidentalis 28(2):60–63.
Zhou, H. C., Fan, G. L., Lin, Q., Yang, M. Q., Zhang, L. L., Cao, Y. H., Lou, X. R., and Lu, B. Z. (2001a). The pathological observations of crested ibis Eustrongyloides sp. J. Northwest Sci. Tech. Univ. Agric. For. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 29(5):27–29.
Zhou, H. C., Yang, M. Q., Fan, G. L., Fu, W. K., Cao, Y. H., Li, H. L., and Zheng, J. J. (2001b). The pathological diagnosis of the death of the two crested ibis. J. Northwest Sci. Tech. Univ. Agric. For. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 29(3):69–72.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to Shaanxi Crested Ibis Breeding Centre for providing all the samples used in this study, as well as to Dr. Wan Q.H., Dr. Wu H., Dr. Wu H.L., Dr. Xu Y.C., and Mr. Wood for their valuable comments on the manuscript. This work was supported by a grant from the State Key Basic Research and Development Plan of P.R. China (No. G2000046906) and a special grant for crested ibis from the State Forestry Administration, P.R. China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B., Fang, SG. & Xi, YM. Major Histocompatibility Complex Variation in the Endangered Crested Ibis Nipponia nippon and Implications for Reintroduction. Biochem Genet 44, 110–120 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-006-9018-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-006-9018-1