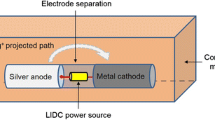
The antimicrobial effect of direct electric current passing through metal implantable medical devices was evaluated. An in vitro study showed that the maximum antimicrobial effect on S. aureus (54.2% average microbial growth inhibition) was achieved at a current of 300 μA applied for 1 min; the maximum antimicrobial effect on E. coli (57.3% average microbial growth inhibition), at 150 μA for 3 min; on P. aeruginosa (40.8%), at 150 μA for 1 min. The study showed that the use of metal medical implants as electrodes has an antimicrobial effect on various pathogenic microorganisms. Thus, exposure to direct electric current can be used for antibacterial treatment of orthopedic implants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bushnev, S. V., Zagorodnyi, N. V., Burtsev, A. V., Stogov, M. V., Ovchinnikov, E. N., and Gubin, A. V., “Import substitution of products for traumatology and orthopedics in the Russian Federation: Challenges and unresolved issues,” Gen. Ortoped., 26, No. 2, 161-165 (2020).
Goriainov, V., Cook, R., Latham, J. M., Dunlop, D. G., and Oreffo, R. O. C., “Bone and metal: An orthopaedic perspective on osseointegration of metals,” Acta Biomater., 10, No. 10, 4043-4057 (2014).
Katsuura, Y. and Qureshi, S. A., “Additive manufacturing for metal applications in orthopaedic surgery,” J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg., 28, No. 8, e349-e355 (2020).
Kaur, M. and Singh, K., “Review on titanium and titanium based alloys as biomaterials for orthopaedic applications,” Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl., 102, 844-862 (2019).
Guillory, R. J. 2nd, Sikora-Jasinska, M., Drelich, J. W., and Goldman, J., “In vitro corrosion and in vivo response to zinc implants with electropolished and anodized surfaces,” ACS Appl. Mater. Interf., 11, No. 22, 19884-19893 (2019).
Hallock, K., Vaughn, N. H., Juliano, P., and Marks, J. G. Jr., “Metal hypersensitivity and orthopedic implants: Survey of orthopedic surgeons,” Dermatitis, 28, No. 1, 76-80 (2017).
Rony, L., Lancigu, R., and Hubert, L., “Intraosseous metal implants in orthopedics: A review,” Morphologie, 102, No. 339, 231-242 (2018).
Kumar, S., Nehra, M., Kedia, D., Dilbaghi, N., Tankeshwar, K., and Kim, K. H., “Nanotechnology-based biomaterials for orthopaedic applications: Recent advances and future prospects,” Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl., 106, 110154 (2020).
Lewallen, E. A., Riester, S. M., Bonin, C. A., Kremers, H. M., Dudakovic, A., Kakar, S., Cohen, R. C., Westendorf, J. J., Lewallen, D. G., and Wijnen, A. J., “Biological strategies for improved osseointegration and osteoinduction of porous metal orthopedic implants,” Tissue Eng. Part B Rev., 21, No. 2, 218-230 (2015).
Tran, P. A., O’Brien-Simpson, N., Palmer, J. A., Bock, N., Reynolds, E. C., Webster, T. J., Deva, A., Morrison, W. A., and O’Connor. A. J., “Selenium nanoparticles as anti-infective implant coatings for trauma orthopedics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and epidermidis: In vitro and in vivo assessment,” Int. J. Nanomed., 14, 4613-4624 (2019).
Gayuk, V. D., Klyushin, N. M., and Burnashov, S. I., “Soft tissue inflammation around the transosseous elements and wire-induced osteomyelitis (literature review),” Gen. Ortoped., 25, No. 3, 407-412 (2019).
Soldatov, Yu. P., Stogov, M. V., Ovchinnikov, E. N., Gubin, A. V., and Gorodnova, N. V., “Ilizarov apparatus for external fixation: Evaluation of clinical efficacy and safety (literature review),” Gen. Ortoped., 25, No. 4, 588-599 (2019).
Haseeb, M., Butt, M. F., Altaf, T., Muzaffar, K., Gupta, A., and Jallu, A., “Indications of implant removal: A study of 83 cases,” Int. J. Health Sci. (Qassim), 11, No. 1, 1-7 (2017).
Peña-Martinez, V., Lara-Arias, J., Vilchez-Cavazos, F., Álvarez-Lozano, E., Montes de Oca-Luna, R., and Mendoza-Lemus, Ó., “Interosseous electrostimulation in a model of lengthening with external fixation,” Cir. Cir., 85, No. 2, 127-134 (2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Meditsinskaya Tekhnika, Vol. 55, No. 5, Sep.-Oct., 2021, pp. 16-19.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ovchinnikov, E.N., Godovykh, N.V., Dyuryagina, O.V. et al. Antimicrobial Efficacy of Exposure of Medical Metal Implants to Direct Electric Current. Biomed Eng 55, 323–327 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10527-022-10128-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10527-022-10128-z