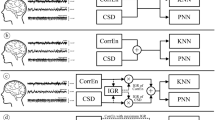
Electroencephalographic (EEG) diagnosis of neurological disorders is based on correlation analysis of epilepsy. This analysis compares the frequency of sharp and slow waves of EEG activity. The procedure is implemented in special filters that detect pathology. A mathematical model of the process and results of mathematical modeling are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. R. Zenkov, Clinical Electroencephalography: Manual for Physicians [in Russian], MEDpress-inform, Moscow (2004).
V. A. Zherebtsova, Systemic Analysis of Mechanisms of Organization of Higher Psychic Functions in Ontogenesis: Doctoral dissertation [in Russian], Tula (2004).
V. A. Zherebtsova, A. F. Indyukhin, E. M. Sokolov, A. A. Khadartsev, V. P. Vasil’ev, and V. I. Morozov, “A Method of Diagnosis of Long-Latency Evoked Brain Potential and a Device for Its Implementation”, RF Patent No. 2240036 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Meditsinskaya Tekhnika, Vol. 46, No. 1, Jan.-Feb., 2012, pp. 22–25.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishina, L.M., Indyukhin, A.A., Indyukhin, A.F. et al. A Subsystem for Electroencephalographic Diagnosis of Epilepsy. Biomed Eng 46, 21–24 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10527-012-9257-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10527-012-9257-x