Abstract
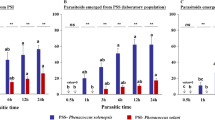
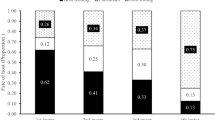
Synopeas myles (Walker) (Hymenoptera: Platygastridae) is a parasitoid of the swede midge, Contarinia nasturtii (Kieffer) (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae), in Europe. We conducted the first thorough investigation of this parasitoid’s biology. Contrary to the biology reported for all platygastrids to date, exposure of late-instar host larvae to parasitism as opposed to eggs or early larvae yielded more S. myles offspring. Superparasitism was relatively common in the field and among groups of females in the laboratory, but was much less common among single females, providing preliminary evidence for self-discrimination. Observation of immature stages of S. myles inside living hosts revealed that supernumerary larvae in superparasitized hosts were probably eliminated by physical combat soon after hatching. With increasing levels of superparasitism, sex ratios of offspring became more female-biased and their mean development time increased. The probability that offspring would emerge from a host and the size of offspring were unaffected by increasing levels of superparasitism.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abram PK, Haye T, Mason PG, Cappuccino N, Boivin G, Kuhlmann U (2012) Identity, distribution, and seasonal phenology of parasitoids of the swede midge, Contarinia nasturtii (Kieffer) (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) in Europe. Biol Control (in press)
Affolter F (1990) Étude structurelle et dynamique du complexe d’hymenoptères parasitoides s’attaquent aux cécidomyies des céreales Sitodiplosis mosellana (Géhin) et Contarinia tritici (Kirby) (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae). PhD thesis, faculty of sciences, Université de Neuchâtel, Switzerland
Austin AD, Johnson NF, Dowton M (2005) Systematics, evolution, and biology of scelionid and platygastrid wasps. Annu Rev Entomol 50:553–582
Bai B, Mackauer M (1992) Influence of superparasitism on development rate and adult size in a solitary parasitoid wasp, Aphidius ervi. Funct Ecol 6:302–307
Bigler F, Babendreier D, Kuhlmann U (2006) Environmental impact of invertebrates for biological control of arthropods: methods and risk assessment. CAB Publishing, Wallingford, UK
Buhl PN, Sarfati MS, Brockerhoff EG, Kelly D (2008) Description, phenology and biology of Zelostemma chionochloae Buhl sp. nov., a platygastrid parasitoid of Eucalyptodiplosis chionochloae (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) in New Zealand. New Zeal J Zool 35:255–264
Cameron PJ, Hill RL, Bain J, Thomas WP (1989) A review of biological control of invertebrate pests and weeds in New Zealand 1874 to 1987. CAB International, Wallingford, UK
Chau NNB, Maeto K (2008) Intraspecific larval competition in Meteorus pulchricornis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), a solitary endoparasitoid of lepidopteran larvae. Appl Entomol Zool 43:159–165
Chen M, Shelton AM (2007) Impact of soil type, moisture, and depth on swede midge (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) pupation and emergence. Environ Entomol 36:1349–1355
Chen M, Shelton AM, Hallett RH, Hoepting CA, Kikkert JR, Wang P (2011) Swede midge (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae), ten years of invasion of crucifer crops in North America. J Econ Entomol 104:709–716
Clausen CP (1940) Entomophagous insects. McGraw-Hill, London, UK
Clausen CP (1978) Cecidomyiidae (Itonididae). In: Clausen CP (ed) Introduced parasites and predators of arthropod pests and weeds: a world review. Agriculture handbook No. 480. United States Department of Agriculture, Washington, D. C., USA, pp 316–318
Darrouzet E, Imbert E, Chevrier C (2003) Self-superparasitism consequences for offspring sex ratio in the solitary ectoparasitoid Eupelmus vuilleti. Entomol Exp Appl 109:167–171
Desouhant E, Driessen G, Amat I, Bernstein C (2005) Host and food searching in a parasitic wasp Venturia canescens: a trade-off between current and future reproduction? Anim Behav 70:145–152
Duncan RE, Ulmer BJ, Peña JE, Lapointe SL (2007) Reproductive biology of Fidiobia dominica (Hymenoptera: Platygastridae), an egg parasitoid of Diaprepes abbreviatus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Environ Entomol 36:376–382
Duso C, Boaria A, Surian L, Buhl PN (2011) Seasonal abundance of the nearctic gall midge Obolodiplosis robiniae in Italy and the impact of its antagonist Platygaster robiniae on pest populations. Ann Ent Soc Am 104:180–191
Eller FJ, Tumlinson JH, Lewis WJ (1990) Intraspecific competition in Microplitis croceipes (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), a parasitoid of Heliothis species (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Ann Ent Soc Am 83:504–508
Fellowes M, Alphen J, Jervis MA (2005) Foraging behaviour. In: Jervis MA (ed) Insects as natural enemies. Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 1–62
Fisher RC (1971) Aspects of the physiology of endoparasitic hymenoptera. Biol Rev 46:243–278
Godfray HCJ (1994) Parasitoids: behavioral and evolutionary ecology. Princeton University Press, Princeton, USA
Gonzalez PI, Montoya P, Perez-Lachaud G, Cancino J, Liedo P (2007) Superparasitism in mass reared Diachasmimorpha longicaudata (Ashmead) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), a parasitoid of fruit flies (Diptera: Tephritidae). Biol Control 40:320–326
Harvey JA, Harvey IF, Thompson DJ (1993) The effect of superparasitism on development of the solitary parasitoid wasp, Venturia canescens (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae). Ecol Entomol 18:203–208
Hegazi E, Khafagi W (2008) The effects of host age and superparasitism by the parasitoid, Microplitis rufiventris on the cellular and humoral immune response of Spodoptera littoralis larvae. J Invertebr Pathol 98:79–84
Hymenoptera Online Database, Ohio State University (2011). http://hol.osu.edu/. Accessed 25 Oct 2011
Jervis MA, Kidd NAC (1986) Host-feeding strategies in hymenopteran parasitoids. Biol Rev 61:395–434
Jervis MA, Heimpel GE, Ferns PN, Harvey JA, Kidd NAC (2001) Life-history strategies in parasitoid wasps: a comparative analysis of ‘ovigeny’. J Anim Ecol 70:442–458
Keller S, Schweizer C (1994) Populationsdynamische untersuchungen an der erbsengallmücke Contarinia pisi Winn. (Dipt., Cecidomyiidae) und ihrer parasitoide. J Appl Entomol 118:281–299
Kim I-K, Park J-D, Shin S-C, Park I-K (2011) Prolonged embryonic stage and synchronized life-history of Platygaster robiniae (Hymenoptera: Platygastridae), a parasitoid of Obolodiplosis robiniae (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae). Biol Control 57:24–30
Least significant difference between ranks (2011). Department of Obstetrics, University of Hong Kong. http://department.obg.cuhk.edu.hk/researchsupport/Least_sig_diff_rank.asp. Accessed 2 Dec 2011
Mackauer M (1990) Host discrimination and larval competition in solitary endoparasitoids. In: Mackauer M, Ehler L, Roland J (eds) Critical issues in biological control. Intercept, Andover, UK, pp 41–62
Mamaev BM, Krivosheina NP (1993) The larvae of the gall midges (Diptera, Cecidomyiidae): comparative morphology, biology, keys. Brookfield, Rotterdam
Montoya P, Cancino J, Perez-Lachaud G, Liedo P (2011) Host size, superparasitism, and sex ratio in mass-reared Diachasmimorpha longicaudata, a fruit fly parasitoid. BioControl 56:11–17
Ogah EO, Odebiyi JA, Omoloye AA, Nwilene FE (2010) Parasitism and development of Platygaster diplosisae (Hymenoptera: Platygastridae) on the African rice gall midge Orseolia oryzivora (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae). Int J Trop Insect Sci 30:93–100
Olfert O, Doane JF, Braun MP (2003) Establishment of Platygaster tuberosula, an introduced parasitoid of the wheat midge, Sitodiplosis mosellana. Can Entomol 135:303–308
Onagbola EO, Fadamiro HY, Mbata GN (2007) Longevity, fecundity, and progeny sex ratio of Pteromalus cerealellae in relation to diet, host provision, and mating. Biol Control 40:222–229
Patterson JT (1927) Polyembryony in animals. Q Rev Bio 2:399–426
Potting RPJ, Snellen HM, Vet LEM (1997) Fitness consequences of superparasitism and mechanism of host discrimination in the stemborer parasitoid Cotesia flavipes. Entomol Exp Appl 82:341–348
Sampson BJ, Rinehart TA, Liburd OE, Stringer SJ, Spiers JM (2006) Biology of parasitoids (Hymenoptera) attacking Dasineura oxycoccana and Prodiplosis vaccinii (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) in cultivated blueberries. Ann Entomol Soc Am 99:113–120
Sandanayaka WRM, Ramankutty P (2007) Temperature dependent emergence and survival of Platygaster demades (Hymenoptera: Platygastridae), parasitoid of apple leaf curling midge. Biol Control 42:41–47
Ueno T (1997) Effects of superparasitism, larval competition, and host feeding on offspring fitness in the parasitoid Pimpla nipponica (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 90:682–688
van Alphen JJM, Visser ME (1990) Superparasitism as an adaptive strategy for insect parasitoids. Annu Rev Entomol 35:59–79
van Baaren J, Boivin G, Nénon J-P (1994) Intra- and interspecific host discrimination in two closely related egg parasitoids. Oecologia 100:325–330
van Baaren J, Landry BL, Boivin G (1999) Sex allocation and larval competition in a superparasitizing solitary egg parasitoid: competing strategies for an optimal sex ratio. Funct Ecol 13:66–71
van Driesche RG (1983) Meaning of percent parasitism in studies of insect parasitoids. Environ Entomol 12:1611–1622
Vlug HJ (1995) Catalogue of the Platygastridae (Platygastroidea) of the world (Insecta: Hymenoptera). SPB Acadamy, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Williams CT, Okhidievbie O, Harris KM, Ukwungwu MN (1999) The host range, annual cycle and parasitoids of the African rice gall midge Orseolia oryzivora (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) in central and southeast Nigeria. Bull Entomol Res 89:589–597
Zhao He X, Wang Q (2011) Phenological dynamics of Dasineura mali (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) and its parasitoid Platygaster demades (Hymenoptera: Platygasteridae) in apple orchards. J Econ Entomol 104:1640–1646
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Danielle Fife, Edna Quan, and Daniel Peach for assistance in the laboratory and field. The culture material provided by Lauren Des Marteux and Dr. Rebecca Hallett (University of Guelph) is greatly appreciated. We would also like to acknowledge the two anonymous reviewers who provided helpful comments on the manuscript. This research was funded by Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada. P. Abram received financial support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada and the Ontario Ministry of Training, Colleges, and Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Stefano Colazza
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abram, P.K., Haye, T., Mason, P.G. et al. Biology of Synopeas myles, a parasitoid of the swede midge, Contarinia nasturtii, in Europe. BioControl 57, 789–800 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-012-9459-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-012-9459-x