Abstract
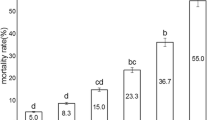
Larvicidal effects of interaction between Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis (Bti), temephos and Leptolegnia chapmanii zoospores on larvae of Aedes aegypti were determined under laboratory and seminatural conditions. In laboratory bioassays, two concentrations of Bti (0.012, 0.027 ppm), two of temephos (0.00035, 0.001 ppm), and a single concentration of L. chapmanii zoospores (6.1 × 104 zoospores ml−1) were evaluated. Trials under field-like conditions were performed in a single container and then placed either in the shade or in direct exposure to sunlight. We evaluated concentrations of Bti and temephos at 3-fold those normally used in laboratory tests: 0.09 and 0.003 ppm, respectively, plus 1.8 × 105 zoospores ml−1 of L. chapmanii. The combined effect of sublethal concentrations of Bti, temephos, and L. chapmanii zoospores thus indicated that this fungus is not inhibited by the larvicides and also demonstrated the synergistic effect of the action of L. chapmanii when used together with Bti and temephos.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
We acknowledge that all taxa of oomycete water molds are now classified among the Kingdom Chromista (=Straminipila) and formally excluded from the true fungi. For the sake of convenience, however, we continue to refer to oomycetes in this paper in the historically sense as fungi.
References
Andersen AH, Jensen E, Geat S (1981) Two-way analysis of variance with correlated errors. Int Stat Rev 49:153–169
Anderson TE, Hajek AE, Roberts DW, Preisler HK, Robertson JL (1989) Colorado potato beetle (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae): effects of combinations of Beauveria bassiana with insecticides. J Econ Entomol 82:83–89
Barjan C, Fedorko A, Kmitowa K (1995) Reactions of entomopathogenic fungi to pesticides. Pol Ecol Stud 21:69–88
Batista Filho A, Alves SB, Alves LFA, Pereira RM, Augusto NT (1998) Formulação de entomopatógenos. In: Alves SB (ed) Controle microbiano de insectos. FEALQ, Sao Paulo, pp 917–956
Becnel JJ, García JJ, Johnson M (1996) Effects of three larvicides on the production of Aedes albopictus based on removal of pupal exuviae. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 12:499–502
Braga IA, Lima JBP, Soares SS, Valle D (2004) Aedes aegypti resistance to temephos during 2001 in several municipalities in the states of Rio de Janeiro, Sergite and Alagoas, Brazil. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 99:199–203
Castellanos DO (1997) Importancia en la patogenicidad de la acción enzimática del hongo Beauveria bassiana sobre la broca del café. Rev Col Entomol 23:65–71
Federici BA, Park HW, Bideschi DK, Wirth MC, Johson JJ, Sakano Y, Tang M (2007) Developing recombinant bacteria for control of mosquito larvae. In: Floore TG (ed) Biorational control of mosquitoes, vol 7. Am Mosq Control Assoc, Allen Press, Inc., pp 164–175
Ferron P (1985) Fungal control. In: Kerkut GA, Gilbert LI (eds) Comprehensive insect physiology, biochemistry and pharmacology. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 313–346
Fukuda T, Willis OR, Barnard DR (1997) Parasites of the Asian tiger mosquito and other container-inhabiting mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) in north central Florida. J Med Entomol 84:226–233
Fumasa A (2000) Relatorio da reuniã de avaliacão do monitoramento da resistência das populacões de Aedes aegypti do País. Fundacão Nacional de Saúde, Ministerio de Saude, Brasília
Gerberg E, Barnard D, Ward R (1994) Manual for mosquito rearing and experimental techniques. Bulletin No 5, J Am Mosq Control Assoc, p 98
Johnson RA, Wichern DW (1982) Applied multivariate statistical analysis. Prentice-Hall, New Jersey
Lacey LA (2007) Bacillus thurigiensis serovariety israelensis and Bacillus sphaericus for mosquito control. In: Floore TG (ed) Biorational control of mosquitoes, vol 7. Am Mosq Control Assoc, Allen Press, Inc., pp 133–163
Lima JBP, Pereira Da Cunha M, Silva RCS Jr, Gallardo AKR, Soares SS, Braga IA, Ramos RP, Valle D (2003) Resistance of Aedes aegypti to organophosphates in several municipalities in the state of Rio de Janeiro and Espírito Santo, Brazil. Am J Trop Med Hyg 68:329–333
Littell R, Milliken G, Stroup W, Wolfinger R (1996) SAS system, for mixed models. SAS Institute, Cary, USA
López Lastra CC, Steciow MM, García JJ (1999) Registro más austral del hongo Leptolegnia chapmanii (Oomycetes: Saprolegniales) como patógeno de larvas de mosquitos (Diptera: Culicidae). Rev Iberoam Micol 16:143–145
López Lastra CC, Scorsetti AC, Marti GA, García JJ (2004) Host range and specificity of an Argentinean isolate of the aquatic fungus Leptolegnia chapmanii (Oomycetes: Saprolegniales), a pathogen of mosquito larvae (Diptera: Culicidae). Mycopathologia 158:311–315
Lord JC, Fukuda T (1988) An ultrastructural study of the invasion of Culex quinquefasciatus larvae by Leptolegnia chapmanii (Oomycetes: Saprolegniales). Mycopathologia 104:67–73
Mardini LBLF, Torres MAN, Silveira GL, Atz AMV (2000) Simulium spp. control program im Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 95:211–214
Mc Innis T Jr, Zattau WC (1982) Experimental infection of mosquito larvae by a species of the aquatic fungus Leptolegnia. J Invertebr Pathol 39:98–104
Mulla MS (1990) Activity, field efficacy, and use of Bacillus thurigiensis var. israelensis against mosquitoes. In: De Barjac H, Sutherland DJ (eds) Bacterial control of mosquitoes and blackflies. Rutgers University Press, New Jersey, pp 134–160
Mulla MS, Chaney JD, Rodcharoen J (1993) Elevated dosages of Bacillus thurigiensis var. israelensis fail to extend control of Culex larvae. J Vector Ecol 18:125–132
Nogueira RM, Miagostovich AM, Pereira MA, Schatzmayr HG (2001) Dengue virus type 3 in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 96:925–926
Orduz S, Axtell RC (1991) Compatibility of Bacillus thurigiensis var. israelensis and Bacillus sphaericus with the fungal pathogen Lagenidium giganteum (Oomycetes: Lagenidiales). J Am Mosq Control Assoc 7:188–193
PAHO (1995) Estadísticas de salud de las Américas, Publicación Científica. PAHO, Washington, DC, p 556
Pelizza SA, López Lastra CC, Bisaro V, Becnel JJ, García JJ (2007a) Biotic and abiotic factors affecting Leptolegnia chapmanii infections in Aedes aegypti L. (Diptera: Culicidae). J Am Mosq Control Assoc 23:177–181
Pelizza SA, López Lastra CC, Becnel JJ, Bisaro V, García JJ (2007b) Effects of temperature, pH and salinity on the infection of Leptolegnia chapmanii Seymour (Peronosporomycetes) in mosquito larvae. J Invertebr Pathol 96:133–137
Pelizza SA, López Lastra CC, Becnel JJ, Humber RA, García JJ (2008) Further research on the production, longevity and infectivity of the zoospores of Leptolegnia chapmanii Seymour (Oomycota: Peronosporomycetes). J Invertebr Pathol 98:314–319
Pelizza SA, López Lastra CC, Maciá A, Bisaro V, García JJ (2009) Efecto de la calidad del agua de criaderos de mosquitos (Diptera: Culicidae) sobre la patogenicidad e infectividad de las zoosporas del hongo Leptolegnia chapmanii (Straminipila: Peronosporomycetes). Rev Biol Trop 57:371–380
Pristavko N (1966) Processus pathologiques consécutifs à l’action de Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuill. Associée à de faibles doses de D.D.T., chez Leptinotarsa decemlineata Say. Entomophaga 11:311–324
Rivera MA, Bustillo PA, Marin MP (1994) Compatibilidad de dos aislamientos de Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuill. en mezcla con insecticidas usados en el control de la broca del café, Hypothenemus hampei (Ferrari). Rev Col Entomol 20:209–214
Scholte EJ, Bart G, Knols J, Samson A, Takken W (2004) Entomopathogenic fungi for mosquito control: a review. J Insect Sci 4:19
Seymour RL (1984) Leptolegnia chapmanii, an oomycete pathogen of mosquito larvae. Mycologia 76:113–120
Tabashnik BE (1994) Evolution of resistance to Bacillus thurigiensis. Annu Rev Entomol 39:47–79
Tabashnik BE, Custhing NL, Finson N, Johnson MW (1990) Field development of resistance to Bacillus thurigiensis in the diamondback moth (Plutella xylostella). J Econ Entomol 83:1671–1676
Vazquez C, Saldarriaga Y, Pineda F (2004) Compatibilidad del hongo entomopatógeno Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuill. con triflumuron. Rev Col Entomol 30:23–27
Vazquez C, Saldarriaga Y, Pineda F (2006) Compatibilidad de Beauveria bassiana con fenoxicarb. Manejo Integrado de Plagas y Agroecología 78:80–85
Acknowledgments
This study was partially supported by Agencia National de Promoción Científica y Técnica (PICT No 11118/02), CONICET, and Universidad Nacional de La Plata, La Plata, Argentina. We thank Dr. Joop Van Lenteren for critical reading of the manuscript. The authors also thank to Dr. Donald F. Haggerty, a retired career investigator and native English speaker, for editing the final version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Martin Erlandson.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pelizza, S.A., Scorsetti, A.C., Bisaro, V. et al. Individual and combined effects of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis, temephos and Leptolegnia chapmanii on the larval mortality of Aedes aegypti . BioControl 55, 647–656 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-010-9281-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-010-9281-2