Abstract
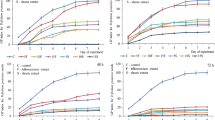
In a damage trial in pots, Lixus aemulus, a stem-boring weevil imported from Brazil, caused 66.6% mortality of the stems and reduced the dry mass of infested Chromolaena odorata stems by 46.6%. There was a 94.4% reduction in the number of achenes produced on the infested branches. These results indicate that L. aemulus has potential to have impact as a biological control agent of C. odorata.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Briese D.T. (1996). Potential impact of the stem-boring weevil Lixus cardui on the growth and reproductive capacity of Onopordum thistles. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 6: 251–261
Julien M.H., Griffiths M.W. (1999). Biological Control of Weeds. A World Catalogue of Agents and their Target Weeds. 4th ed. CABI Publishing, Wallingford
Snedecor G.W., Cochran W.G. (1967). Statistical Methods. The Iowa State University Press, Iowa
Strathie, L.W. and C. Zachariades, 2004. Insects for the biological control of Chromolaena odorata: surveys in the northern Caribbean and efforts undertaken in South Africa. In: Day, M.D. and R.E.C. McFadyen (eds), Proceedings of the Sixth International Workshop on Biological Control and Management of Chromolaena, Cairns, 6–9 May 2003. ACIAR Technical Report 55: 45–52
Zachariades C., Strathie-Korrûbel L.W., Kluge R.L. (1999). The South African programme on the biological control of Chromolaena odorata (L.) King & Robinson (Asteraceae) using insects. African Entomol. Memoir 1: 89–102
Zachariades, C., L.W. Strathie and R.L. Kluge, 2002. Biology, host-specificity and effectiveness of insects for the biocontrol of Chromolaena odorata in South Africa. In: Zachariades, C., R. Muniappan, and L.W. Strathie (eds), Proceedings of the Fifth International Workshop on Biological Control and Management of Chromolaena odorata, Durban, 23–25 October 2000. ARC-PPRI, Pretoria, pp. 160–166
Zachariades C., I. von Senger and N.P. Barker, 2004. Evidence for a northern Caribbean origin for the southern African biotype of Chromolaena odorata. In: Day, M.D. and R.E.C. McFadyen (eds), Proceedings of the Sixth International Workshop on Biological Control and Management of Chromolaena, Cairns, 6–9 May 2003. ACIAR Technical Report 55: 25–27
Acknowledgments
We thank T. Olckers for comments on the manuscript, S. Neser for the collection of L. aemulus, J.M. Goodall for the statistical tests, D.␣Briese for information on L. cardui, D.B. Nkala for data recording, M. Gareeb for dissection of stems and L.D. Khumalo for dry mass determination. Financial support was provided by the ‘Working for Water’ Programme (Department of Water Affairs and Forestry).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kluge, R.L., Zachariades, C. Assessing the damage potential of the stem-boring weevil Lixus aemulus for the biological control of Chromolaena odorata . Biocontrol 51, 547–552 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-006-9004-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-006-9004-x