Abstract
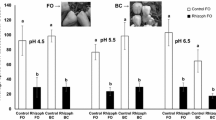
Flowering companion plants and plants producing extrafloral nectar are being proposed to enhance biological control in apple (Malus domestica Borkh.) orchards. This experiment evaluated the impact of floral and extrafloral resources on predation of spirea aphid (Aphis spiraecola Patch) on apple by adult Harmonia axyridis (Pallas) under greenhouse conditions. Predation of spirea aphids was not affected by the presence of flowering buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum) as compared with either buckwheat with flowers removed or an uninfested apple shoot. However, there was a significant reduction in predation of spirea aphids on an apple shoot in the presence of a peach shoot with extrafloral nectar glands compared with either a peach shoot of the same cultivar without nectar glands or an uninfested apple shoot. These findings demonstrate that alternative food resources potentially could interfere with rates of biological control and, therefore, need to be carefully evaluated before incorporating in an orchard design. More studies are needed to adequately gauge the net effects of adding floral or extrafloral resources in orchards for conservation biological control.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bostanian N.J., Goulet H., O’Hara J., Masner L. and Racette G. (2004). Towards insecticide free apple orchards: flowering plants to attract beneficial arthropods. Biocont. Sci and Tech. 14: 25–37
Brown M.W. (2004). Role of aphid predator guild in controlling spirea aphid populations on apple in West Virginia, USA. Biol. Cont. 29: 189–198
Brown M.W. and Glenn D.M. (1999). Ground cover plants and selective insecticides as pest management tools in apple orchards. J. Econ. Entomol. 92: 899–905
Brown M.W. and Miller S.S. (1998). Coccinellidae (Coleoptera) in apple orchards of eastern West Virginia and the impact of invasion by Harmonia axyridis. Entomol. News 109: 136–142
Brown M.W. and Schmitt J.J. (2001). Seasonal and diurnal dynamics of beneficial insect populations in apple orchards under different management intensity. Environ. Entomol. 30: 415–424
Bugg R.L. and Waddington C. (1994). Using cover crops to manage arthropod pests of orchards: a review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 50: 11–28
Caldwell D.L. and Gerhardt K.O. (1986). Chemical analysis of peach extrafloral nectary exudates. Phytochemistry 25: 411–413
Chapin J.B. and Brou V.A. (1991). Harmonia axyridis (Pallas), the third species of the genus to be found in the U.S. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Proc. Entomol. Soc. Wash. 93: 630–635
Colunga-Garcia M. and Gage S.H. (1998). Arrival, establishment and habitat use of the multicolored Asian lady beetle (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in a Michigan landscape. Environ. Entomol. 27: 1574–1580
Hagley E.A.C. and Barber D.R. (1992). Effect of food sources on the longevity and fecundity of Pholetesor ornigis (Weed) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Can. Entomol. 124: 341–346
Hickman J.M. and Wratten S.D. (1996). Use of Phacelia tanacetifolia strips to enhance biological control of aphids by hoverfly larvae in cereal fields. J. Econ. Entomol. 89: 832–840
Landis D.A., Wratten S.D. and Gurr G.M. (2000). Habitat management to conserve natural enemies of arthropod pests in agriculture. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 45: 175–201
LaMana M.L. and Miller J.C. (1996). Field observations on Harmonia axyridis Pallas (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in Oregon. Biol. Cont. 6: 232–237
Leius K. (1967). Influence of wild flowers on parasitism of tent caterpillar and codling moth. Can. Entomol. 99: 444–446
Limburg D.D. and Rosenheim J.A. (2001). Extrafloral nectar consumption and its influence on survival and development of an omnivorous predator, larval Chrysoperla plorabunda (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). Environ. Entomol. 30: 595–604
Lundgren J.G., Razzak A.A. and Wiedenmann R.N. (2004). Population responses and food consumption by predators Coleomegilla maculata and Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) during anthesis in an Illinois cornfield. Environ. Entomol. 33: 958–963
MacLeod A. (1999). Attraction and retention of Episyrphus balteatus DeGeer (Diptera: Syrphidae) at an arable field margin with rich and poor floral resources. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 73: 237–244
Mathews, C.R., 2004. Role of peach Prunus persica (Batsch) extrafloral nectaries in natural enemy–herbivore–host plant interactions. Ph. D. Thesis, Department of Entomology, University of Maryland: College Park, MD, USA
Nicholls C.I., Parrella M. and Altieri M.A. (2001). The effects of a vegetational corridor on the abundance and dispersal of insect biodiversity within a northern California organic vineyard. Landscape Ecol. 16: 133–146
Pemberton R.W. and Vandenberg N.J. (1993). Extrafloral nectar feeding by ladybird beetles (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Proc. Entomol. Soc. Wash. 95: 139–151
(1998). The SAS system for Windows, Release 7.00. SAS Institute, Cary, NC
Shearer P.W. and Atanassov A. (2004). Impact of peach extrafloral nectar on key biological characteristics of Trichogramma minutum (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 97: 789–792
Stapel J.O., Cortesero A.M., Tumlinson J.H. and Lewis W.J. (1997). Extrafloral nectar, honeydew, and sucrose effects on searching behavior and efficiency of Mircoplitis croceipes (Hymonoptera: Braconidae) in cotton. Environ. Entomol. 26: 617–623
Stephens M.J., France C.M., Wratten S.D. and Frampton C. (1998). Enhancing biological control of leafrollers (Lepidopter: Tortricidae) by sowing buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum) in an orchard. Biocont. Sci. Tech. 8: 547–558
Tedders W.L. and Schaefer P.W. (1994). Release and establishment of Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in the southeastern United States. Entomol. News 105: 228–243
Tylianakis J.M., Didham R.K. and Wratten S.D. (2004). Improved fitness of aphid parasitoids receiving resource subsidies. Ecology 85: 658–666
White A.J., Wratten S.D., Berry N.A. and Weigmann U. (1995). Habitat manipulation to enhance biological control of Brassica pests by hover flies (Diptera: Syrphidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 88: 1171–1176
Wyss E. (1995). The effects of weed strips on aphids and aphidophagous predators in an apple orchard. Ent. Exp. et Appl. 75: 43–49
Wyss E. (1996). The effects of artificial weed strips on diversity and abundance of the arthropod fauna in a Swiss experimental apple orchard. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 60: 47–59
Yong T-H. (2003). Nectar-feeding by a predatory ambush bug (Heteroptera: Phymatidae) that hunts on flowers. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 96: 643–651
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spellman, B., Brown, M.W. & Mathews, C.R. Effect of floral and extrafloral resources on predation of Aphis spiraecola by Harmonia axyridis on Apple. BioControl 51, 715–724 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-005-5252-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-005-5252-4