Abstract
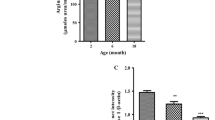
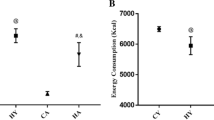
Intracellular orthophosphate and inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi) are by-products of multiple biosynthetic reactions. PPi hydrolysis by soluble inorganic pyrophosphatase (iPPase) has been considered as an important homeostatic mechanism. We investigated the expression and activities (U/mg protein) of iPPase in the liver of young and old mice subjected to short- and long-term dietary restriction. The expression level of iPPase was ascertained by the Western blot analysis using anti-iPPase and differential polymerase chain reaction using iPPase specific primer. Older mice showed a significant increase in the expression and activity of iPPase as compared to younger ones. Short-term fasting of 24 h increased the expression and activity of iPPase in the liver of both young and old mice which were reversed upon 24 h of re-feeding them. However, both young and old mice on long-term dietary restriction showed a cumulative increase in the expression and activity of iPPase when compared with their age-matched controls. This might be due to accumulative adaptation to refill energy deficiency of long-term dietary restricted mice for ATP generation via oxidative phosphorylation, where fatty acid activation could be driven by elevated iPPase.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cavallini G, Donati A, Gori Z, Pollera M, Bergamini E (2001) The protection of rat liver autophagic proteolysis from the age-related decline co-varies with the duration of anti-ageing food restriction. Exp Gerontol 36:497–506
Chen G, Gharib TG, Huang CC, Thomas DG, Shedden KA, Taylor JMG, Kardia SLR, Misek DE, Giordano TJ, Iannettoni MD, Orringer MB, Hanash SM, Beer DG (2002) Proteomic analysis of lung adenocarcinoma: identification of a highly expressed set of proteins in tumors. Clin Cancer Res 8:2298–2305
Clark JM (2006) The epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in adults. J Clin Gastroenterol 40:S5–S10
Dhahbi JM, Mote PL, Wingo J, Rowley BC, Cao SX, Walford RL, Spindler SR (2001) Caloric restriction alters the feeding response of key metabolic enzyme genes. Mech Ageing Dev 122:1033–1048
Donati A, Recchia G, Cavallini G, Bergamini E (2008) Effect of aging and anti-aging calorie restriction on the endocrine regulation of rat liver autophagy. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 63:550–555
Everitt AV, Rattan SIS, Couteur DG, Cabo R (2010) Calorie restriction, aging and longevity. Springer, New York
Goyary D, Sharma R (2008) Late onset of dietary restriction reverses age-related decline of malate-aspartate shuttle enzymes in the liver and kidney of mice. Biogerontology 9:11–18
Hagopian K, Ramsey JJ, Weindruch R (2003) Caloric restriction increases gluconeogenic and transaminase enzyme activities in mouse liver. Exp Gerontol 38:267–278
Heinonen JK (2001) Biological role of inorganic pyrophosphate. Kluwer Academic Publishers, London
Higami Y, Tsuchiya T, Chiba T, Yamaza H, Muraoka I, Hirose M, Komatsu T, Shimokawa I (2006) Hepatic gene expression profile of lipid metabolism in rats: impact of caloric restriction and growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor-1 suppression. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 61:1099–1110
Huang S, Colmer TD, Millar AH (2008) Does anoxia tolerance involves altering the energy currency towards PPi? Trends Plant Sci 13:221–227
Johnson K, Pritzker K, Goding J, Terkeltaub R (2001) The nucleoside triphosphate pyrophosphohydrolase isozyme PC-1 directly promotes cartilage calcification through chondrocyte apoptosis and increased calcium precipitation by mineralizing vesicles. J Rheumatol 28:2681–2691
Kuhla B, Kuhla S, Rudolph PE, Albrecht D, Metges CC (2007) Proteomics analysis of hypothalamic response to energy restriction in dairy cows. Proteomics 7:3602–3617
Lexander H, Palmberg C, Auer G, Hellstrom M, Franzen B, Jornvall H, Egevad L (2005) Proteomic analysis of protein expression in prostate cancer. Anal Quant Cytol Histol 27:263–272
Martin GG, Atshaves BP, McIntosh AL, Mackie JT, Kier AB, Schroeder F (2008) Liver fatty acid-binding protein gene-ablated female mice exhibit increased age-dependent obesity. J Nutr 138:1859–1865
Obled C, Arnal M (1991) Age-related changes in whole-body amino acid kinetics and protein turnover in rats. J Nutr 121:1990–1998
Panda H, Pandey RS, Debata PR, Supakar PC (2007) Age-dependent differential expression and activity of cytosolic inorganic pyrophosphstase gene. Biogerontology 8:517–525
Polewski MD, Johnson KA, Foster M, Millan JL, Terkeltaub R (2010) Inorganic pyrophosphatase induces type I collagen in osteoblasts. Bone 46:81–90
Sang-Ho J, Gyung HK, Young HC (2012) Pyrophosphatase overexpression is associated with cell migration, invasion, and poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Tumor Biol 33:1889–1898
Sharma R (2004) Dietary restriction and its multifaceted effects. Curr Sci 87:1203–1210
Shatton JB, Ward C, Willams A, Weinhouse S (1983) A microcolorimetric assay of inorganic pyrophosphatase. Anal Biochem 130:114–119
Speakman JR, Hambly C (2007) Starving for life: what animal studies can and cannot tell us about the use of caloric restriction to prolong human lifespan. J Nutr 137:1078–1086
Suchiang K, Sharma R (2011) Dietary restriction regulates brain acetylcholinesterase in female mice as a function of age. Biogerontology 12:581–589
Syiem D, Sharma R (1996) Purification and kinetic characterization of chicken liver inorganic pyrophosphatase. Indian J Biochem Biophys 33:363–370
Terkeltaub RA (2001) Inorganic pyrophosphate generation and disposition in pathophysiology. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 281:C1–C11
Tollet-Egnell P, Flores-Morales A, Stahlberg N, Malek RL, Lee N, Norstedt G (2001) Gene expression profile of the aging process in rat liver: normalizing effects of growth hormone replacement. Mol Endocrinol 15:308–318
Weinert BT, Timiras PS (2003) Physiology of aging invited revew: theories of aging. J Appl Physiol 95:1706–1716
Weissen-Plenz, G, Nitschke Y, Rutsch F (2008) Mechanisms of arterial calcification: spotlight on the inhibitors. Adv Clin Chem, p 263–293, Elsevier Ltd., Amsterdam
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to the Department of Biochemistry, North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong for providing research facilities under UGC-UPE, DRS and DST-FIST, New Delhi. WJK thanks CSIR, New Delhi for the Fellowship as JRF and SRF (F.No: 09/347(0185)/2009-EMR-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kharbhih, W.J., Sharma, R. Age-dependent increased expression and activity of inorganic pyrophosphatase in the liver of male mice and its further enhancement with short- and long-term dietary restriction. Biogerontology 15, 81–86 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-013-9481-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-013-9481-0