Abstract
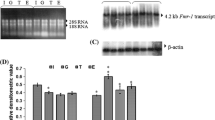
Androgen influences the function of central and peripheral nervous system and plays a crucial role in maintaining reproductive behaviors and neuroendocrine regulation. Such action is mediated by interaction of androgen receptor (AR) promoter with nuclear proteins, which are involved in transcriptional regulation of androgen responsive genes. We have analyzed the binding of AR core promoter to nuclear proteins from the cerebral cortex of adult and old mice of both sexes by electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) and characterized the bound protein by Southwestern blotting. EMSA showed that the binding of nuclear proteins declined in the cerebral cortex of intact old mice as compared to adult. Following gonadectomy, the binding was reduced in old male and adult female but increased in old female. In contrast, estradiol supplementation increased the binding in old male and adult female but decreased in old female. Southwestern blotting analysis revealed that a 40 kDa nuclear protein bound to the promoter and the binding pattern was similar to that observed in EMSA. Further characterization of this protein may help to explore the intricate mechanism that underlies the transcriptional regulation of androgen responsive genes during aging.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian GS, Seto E, Fischbach KS, Rivera EV, Adrian EK, Herbert DC, Walter CA, Weaker FJ, Bowman BH (1996) YY1 and Sp1 transcription factors bind the human transferrin gene in an age-related manner. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 51:B66–B75
Ammendola R, Mesuraca M, Russo T, Cimino F (1992) Sp1 DNA binding efficiency is highly reduced in nuclear extracts from aged rat tissues. J Biol Chem 267:17944–17948
Ammendola R, Mesuraca M, Russo T, Cimino F (1994) The DNA binding efficiency of Sp1 is affected by redox changes. Eur J Biochem 225:483–489
Barrends WM, Themman APN, Blok LJ, Makenbach P, Brinkmann AO, Meijer D, Faber PW, Trapman J, Grootegoed JA (1999) The rat androgen receptor gene promoter. Mol Endocrinol 74:75–84
Blackwood EM, Kadonaga JT (1998) Going the distance: A current view of enhancer action. Science 281:60–63
Brinkmann AO, Jenster G, Ris-Stalpers C, van der Korput JAGM, Brüggenwirth HT, Boehmer ALM, Trapman J (1995) Androgen receptor mutations. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 53:443–448
Courey AJ, Holtzman DA, Jackson SP, Tijan R (1989) Synergistic activation by glutamine-rich domains of human transcription factor Sp1. Cell 59:827–836
Dignam JD, Lebovitz RM, Roeder RG (1983) Accurate transcription by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res 11:1475–1489
Dimri GP, Campisi J (1994) Altered profile of transcription factor-binding activities in senescent human fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res 212:132–140
Faber PW, King A, van Rooij HCJ, Brinkmann OA, de Both NJ, Trapman J (1991) The mouse androgen receptor. Functional analysis of the protein and characterization of the gene. Biochem J 278:269–278
Faber PW, van Rooij JCJ, Schippe HJ, Brinkmann AO, Trapman J (1993) Two different, overlapping pathways of transcription initiation are active on TATA less human androgen receptor promoter, The role of Sp1. J Biol Chem 268:9296–9301
Fukami-Kobayashi J, Mitsui Y (1998) The regulation of cyclin D1 expression in senescent human fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res 241:435–444
Grossmann ME, Lindzey J, Blok LJ, Perry JE, Kumar MV, Tindall DJ (1994) The mouse androgen receptor gene contains second functional promoter which is regulated by dihydrotestosterone. Biochemistry 33:14594–14600
Guccione M, Silbiger S, Lei J, Neugarten J (2002) Estradiol upregulates mesangial cell MMP-2 activity via the transcription factor AP-2. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 282:F164–F169
Heinlein CA, Chang C (2002) The roles of androgen receptors and androgen binding proteins in nongenomic androgen actions. Mol Endocrinol 16:2181–2187
Heydari AR, You S, Takahashi R, Gutsmann-Conrad A, Sarge KD, Richardson A (2000) Age-related alterations in the activation of heat–shock transcription factor 1 in rat hepatocytes. Exp Cell Res 256:83–93
Hubscher (1987) Double replica southwestern. Nucleic Acids Res 15:5846
Issa JP (2000) CpG-island methylation in aging and cancer. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 249:101–118
Kumar MV, Jones EA, Grossmann ME, Blexarud MD, Tindall DJ (1994) Identification and characterization of suppressor element in the 5-flanking region of mouse androgen receptor gene. Nucleic Acids Res 22:3693–3698
Kumar RC, Thakur MK (2004a) Androgen receptor mRNA is inversely regulated by testosterone and estradiol in adult mouse brain. Neurobiol Aging 25:925–933
Kumar RC, Thakur MK (2004b) Sex steroids reduce DNaseI accessibility of androgen receptor promoter in adult male mice brain. Mol Brain Res 134:1–7
Li Y-J, Fu X-H, Liu D-P, Liang C-C (2004) Opening the chromatin for transcription. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:1411–1423
Lovell MA, Xie C, Xiong S, Markesbery WR (2003) Wilms’ tumor suppressor (WT1) is a mediator of neuronal degeneration associated with the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 983:84–96
McAbee MD, DonCarlos LL (1999) Regulation of androgen receptor messenger ribonucleic acid expression in the developing rat forebrain. Endocrinology 140:1807–1814
McGinnis MY, Dreifuss RM (1989) Evidence for a role of testosterone-androgen receptor interactions in mediating masculine sexual behavior in male rats. Endocrinology 124:618–626
Merja H, Maarit HA, Nninen SK, Lehtinen, Salminen A (1996) Changes associated with aging and replicative senescence in the regulation of transcription factor nuclear factor-κB. Biochem J 318:603–608
Mountcastle VB (1997) The columnar organization of neocortex. Brain 120:701–722
O’Malley BW (1990) The steroid receptor superfamily: more excitement predicted for future. Mol Endocrinol 4:363– 369
Patel SA, Graunke DM, Pieper RO (1997) Aberrant silencing of the CpG island-containing O6-methylguanine DNA methtyltransferase gene is associated with the loss nucleosome-like positioning. Mol Cell Biol 17:5813–5822
Prowse DM, Bolgan L, Molnar A, Dotto GP (1997) Involvement of the Sp3 transcription factor in induction of p21Cip1/WAF1 in keratinocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem 272:1308–1314
Richardson B (2003) Impact of aging on DNA methylation. Ageing Res Rev 2:245–261
Romanov GA, Vanyushin BF (1981) Methylation of reiterated sequences in mammalian DNAs. Effects of the tissue type, age, malignancy and hormonal induction. Biochim Biophys Acta 653:204–218
Roy AK, Oh T, Rivera O, Mubiru J, Song CS, Chatterjee B (2002) Impacts of transcriptional regulation on aging and senescence. Ageing Res Rev 1:367–380
Schumacher M, Weill-Engerer S, Liere P, Robert F, Franklin RJM, Garcia-Segura LM et al (2003) Steroid hormones and neurosteroids in normal and pathological aging of the nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 71:3–29
Simon NG (2002) Hormonal systems regulating the development and expression of aggression. In: Pfaff D, Etgen A, Rubin R, Fahrbach B (eds) Hormones, the Brain, and Behavior. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 39–85
Song CS, Her S, Choi JJ, Slomczynska M, Roy AK, Chatterjee B (1993) A distal activation domain is critical in the regulation of rat androgen receptor gene promoter. Biochem J 294:779–784
Supakar PC, Jung MH, Song CS, Chatterjee B, Roy AK (1995) Nuclear factor kappa B functions as a negative regulator for the rat androgen receptor gene and NF-kappa B activity increases during the age-dependent desensitization of the liver. J Biol Chem 270:837–842
Supakar PC, Song CS, Jung MH, Slomczynska MA, Kim JM, Vellanoweth RL, Chatterjee B, Roy AK (1993) A novel regulatory element associated with age-dependent expression of the rat androgen receptor gene. J Biol Chem 268:26400–26408
Supp DM, Witte DP, Branford WW, Smith EP, Potter SS (1996) Sp4, a member of the Sp1-family of zinc finger transcription factors, is required for normal murine growth, viability, and male fertility. Dev Biol 176:284–299
Suske G (1999) The Sp-family of transcription factors. Gene 238:291–300
Thakur MK (2003) Sex steroid signaling during aging. Proc Ind Natn Sci Acad B69:179–190
Thakur MK, Sharma PK, Ghosh S (2005) Estrogen effects in brain: implications for aging, Alzheimer’s disease. In: Thakur MK, Prasad S (eds) Molecular and Cellular Neurobiology. Narosa Publishing House, New Delhi, pp 55–69
Thakur MK, Sharma PK, Ghosh S, Mani ST (2004) Estrogen intervention in aging and longevity: problems and prospectives. Geriat Gerontol Int 4:S259–S261
Tilley WD, Marcelli M, Mc Phaul MJ (1999) Expression of human androgen receptor utilizes a common promoter in diverse human tissues and cell lines. J Biol Chem 265:13776–13781
Truss M, Bartsch J, Schelbert A, Hache RJ, Beato M (1995) Hormone induces binding of receptors and transcription factors to a rearranged nucleosome on the MMTV promoter in vivo. EMBO J 14:1737–1751
Vellanoweth RL, Suprakar PC, Roy AK (1994) Transcription factors in development, growth, and aging. Lab Invest 70:784–799
Wilks AF, Cozens PJ, Mattaj IW, Jost JP (1982) Estrogen induces a demethylation at the 5’ end region of the chicken vitellogenin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:4252–4255
Yamabe Y, Shimamoto A, Goto M, Yokota J, Sugawara M, Furuichi Y (1998) Sp1-mediated transcription of the Werner helicase gene is modulated by Rb and p 53. Mol Cell Biol 18:6191–6200
Acknowledgments
We thank S. Liao (Chicago University, USA) for generous gift of rat AR cDNA and D.J. Tindall (Mayo Foundation, Rochester, USA) for mouse AR 5’ flanking region. R.C.K. acknowledges a research fellowship from the University Grants Commission-sponsored Center of Advanced Study Program. This work was supported by grants from the Department of Science & Technology (SP/SO/B05/99) and Department of Biotechnology (BT/PRO83/HRO/15/87/97), Government of India, to M.K.T.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thakur, M.K., Kumar, R.C. 17β-Estradiol modulates age-dependent binding of 40 kDa nuclear protein to androgen receptor promoter in mouse cerebral cortex. Biogerontology 8, 575–582 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-007-9102-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-007-9102-x