Abstract
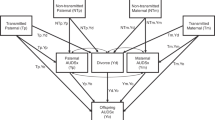
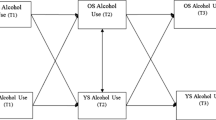
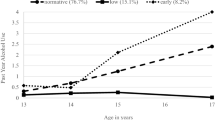
Parent–offspring resemblance for drinking was investigated in a sample of 409 adopted and 208 non-adopted families participating in the Sibling Interaction and Behavior Study. Drinking data was available for 1,229 offspring, assessed longitudinally up to three times in the age range from 10 to 28 years. A single drinking index was computed from four items measuring quantity, frequency and density of drinking. As expected, the mean drinking index increased with age, was greater in males as compared to females (although not at the younger ages), but did not vary significantly by adoption status. Parent–offspring correlation in drinking did not vary significantly by either offspring or parent gender but did differ significantly by adoption status. In adopted families, the parent–offspring correlation was statistically significant at all ages but decreased for the oldest age group (age 22–28). In non-adopted families, the parent–offspring correlation was statistically significant at all ages and increased in the oldest age group. Findings imply that genetic influences on drinking behavior increase with age while shared family environment influences decline, especially during the transition from late-adolescence to early adulthood.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandura A (1999) A sociocognitive analysis of substance abuse: an agentic perspective. Psychol Sci 10(3):214–217. doi:10.1111/1467-9280.00138
Bergen SE, Gardner CO, Kendler KS (2007) Age-related changes in heritability of behavioral phenotypes over adolescence and young adulthood: a meta-analysis. Twin Res Hum Genet 10(3):423–433
Buchanan JP, McGue M, Keyes M, Iacono WG (2009) Are there shared environmental influences on adolescent behavior? Evidence from a study of adoptive siblings. Behav Genet 39(5):532–540. doi:10.1007/s10519-009-9283-y
Burt SA (2009) Rethinking environmental contributions to child and adolescent psychopathology: a meta-analysis of shared environmental influences. Psychol Bull 135(4):608–637. doi:10.1037/a0015702
Dick DM, Prescott C, McGue M (2009) Genetics of substance use and substance use disorders. In: Kim YK (ed) Handbook of behavior genetics. Springer, New York, pp 433–454
Dubois L, Kyvik KO, Girard M, Tatone-Tokuda F, Perusse D, Hjelmborg J, Martin NG (2012) Genetic and environmental contributions to weight, height, and BMI from birth to 19 years of age: an international study of over 12,000 twin pairs. Plos One 7(2):30153. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030153
Grant BF, Dawson DA (1997) Age at onset of alcohol use and its association with DSM-IV alcohol abuse and dependence: results from the National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey. J Subst Abuse 9:103–110
Hussong AM, Curran PJ, Bauer DJ (2013) Integrative Data Analysis in Clinical Psychology Research. Annu Rev Clin Psychol 9(9):61–89. doi:10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-050212-185522
Johnston LD, O’Malley PM, Miech RA, Bachman JG, Schulenberg JE (2014) Monitoring the future national results on drug use: 1975-2013: overview, key findings on adolescent drug use. Institute for Social Research, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor
Kendler KS, Schmitt E, Aggen SH, Prescott CA (2008) Genetic and environmental influences on alcohol, caffeine, cannabis, and nicotine use from early adolescence to middle adulthood. Arch Gen Psychiatry 65(6):674–682
Kendler KS, Gardner CO, Edwards A, Hickman M, Heron J, Macleod J, Dick DM (2013) Dimensions of parental alcohol use/problems and offspring temperament, externalizing behaviors, and alcohol use/problems. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 37(12):2118–2127. doi:10.1111/acer.12196
Keyes MA, Malone SM, Sharma A, Iacono WG, McGue M (2013) Risk of suicide attempt in adopted and nonadopted offspring. Pediatrics 132(4):639–646. doi:10.1542/peds.2012-3251
Koenig LB, McGue M, Iacono WG (2008) Stability and change in religiousness during emerging adulthood. Dev Psychol 44(2):532–543
Latendresse SJ, Rose RJ, Viken RJ, Pulkkinen L, Kaprio J, Dick DM (2008) Parenting mechanisms in links between parents’ and adolescents’ alcohol use behaviors. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 32(2):322–330. doi:10.1111/j.1530-0277.2007.00583.x
Lenroot RK, Giedd JN (2008) The changing impact of genes and environment on brain development during childhood and adolescence: initial findings from a neuroimaging study of pediatric twins. Dev Psychopathol 20(4):1161–1175. doi:10.1017/s0954579408000552
Loehlin JC, Horn JM, Willerman L (1989) Modeling IQ change: evidence from the Texas Adoption Project. Child Dev 60(4):993–1004. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8624.1989.tb03530.x
Loehlin JC, Horn JM, Willerman L (1990) Heredity, environment and personality change: evidence from the Texas Adoption Project. J Pers 58(1):221–243. doi:10.1111/j.1467-6494.1990.tb00914.x
Loehlin JC, Horn JM, Ernst JL (2007) Genetic and environmental influences on adult life outcomes: evidence from the Texas Adoption Project. Behav Genet 37(3):463–476. doi:10.1007/s10519-007-9144-5
Ludeke S, Johnson W, McGue M, Iacono WG (2013) Genetic amplification and the individualization of the parent-child relationship across adolescence. Psychol Med 43(2):413–422. doi:10.1017/s0033291712001201
Marlatt GA (1996) Taxonomy of high-risk situations for alcohol relapse: evolution and development of a cognitive-behavioral model. Addiction 91:S37–S49. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.1996.tb02326.x
Masten AS, Faden VB, Zucker RA, Spear LP (2008) Underage drinking: a developmental framework. Pediatrics 121:S235–S251. doi:10.1542/peds.2007-2243A
McGue M, Iacono WG (2005) The association of early adolescent problem behavior with adult psychopathology. Am J Psychiatry 162(6):1118–1124
McGue M, Irons DE (2013) Etiology. In: McCrady BS, Epstein ES (eds) Addictions: a comprehensive guidebook. Oxford, New York, pp 36–72
McGue M, Iacono WG, Legrand LN, Elkins I (2001) The origins and consequences of age at first drink. I. Associations with substance-use disorders, disinhibitory behavior and psychopathology, and P3 amplitude. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:1156–1165
McGue M, Keyes M, Sharma A, Elkins I, Legrand L, Johnson W, Iacono WG (2007) The environments of adopted and non-adopted youth: evidence on range restriction from the Sibling Interaction and Behavior Study (SIBS). Behav Genet 37(3):449–462
Muthén BO, Muthén LK (2000) The development of heavy drinking and alcohol-related problems from ages 18 to 37 in a U.S. national sample. J Stud Alcohol 61:290–300
Neale MC, Boker SM, Xie G, Maes HH (2003) Mx: statistical modeling, 6th edn. Department of Psychiatry, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA
Plomin R, Daniels D (1987) Why are children in the same family so different from one another? Behavior and Brain Sciences 10:1–60
Robins LM, Baber T, Cottler LB (1987) Composite International Diagnostic Interview: Expanded Substance Abuse Module. Authors, St. Louis
Rose RJ, Dick DM, Viken RJ, Kaprio J (2001) Gene-environment interaction in patterns of adolescent drinking: regional residency moderates longitudinal influences on alcohol use. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25(5):637–643
Scarr S, McCartney K (1983) How people make their own environments: a theory of genotype greater than environment effects. Child Dev 54:424–435
Schulenberg JE, Maggs JL (2002). A developmental perspective on alcohol use and heavy drinking during adolescence and the transition to young adulthood. J Stud Alcohols Drugs Supplement 14:54–70
Stoolmiller M (1999) Implications of restricted range of family environments for estimates of heritability and nonshared environment in behavior-genetic adoption studies. Psychol Bull 125:392–409
Tucker JS, Ellickson PL, Orlando M, Martino SC, Klein DJ (2005) Substance use trajectories from early adolescence to emerging adulthood: a comparison of smoking, binge drinking, and marijuana use. J Drug Issues 35(2):307–331
White HR, Johnson V, Buyske S (2000) Parental modeling and parenting behavior effects on offspring alcohol and cigarette use. A growth curve analysis. J Subst Abuse 12(3):287–310. doi:10.1016/s0899-3289(00)00056-0
Windle M, Spear LP, Fuligni AJ, Angold A, Brown JD, Pine D, Dahl RE (2008) Transitions into underage and problem drinking: developmental processes and mechanisms between 10 and 15 years of age. Pediatrics 121:S273–S289. doi:10.1542/peds.2007-2243C
Acknowledgments
Supported in part by Grants from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (AA11886) and the National Institute of Mental Health (MH066140).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
The SIBS protocol was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board at the University of Minnesota. Written informed assent or consent was obtained from all participants, with parents providing written consent for their minor children.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McGue, M., Malone, S., Keyes, M. et al. Parent–Offspring Similarity for Drinking: A Longitudinal Adoption Study. Behav Genet 44, 620–628 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-014-9672-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-014-9672-8