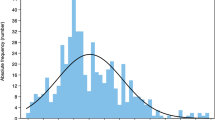
Neurofibromatosis type-1 (NF1) is a common genetic disorder associated with a variety of medical complications, cognitive impairments, and behavioral problems. One hundred and sixteen patients with NF1 (62 males, 54 females; mean age 12.4 years) and 80 typically developing children of the same ages (46 males, 34 females; mean age 11.5 years) were studied in terms of complications and learning impairment (one or more grade repetitions or school exclusion). Seventy of 116 patients had significant learning impairment. Classical complications were present in 53 patients including the three.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clementi M., Barbujani G., Turolla L. and Tenconi R. (1990). Neurofibromatosis-1: a maximum likelihood estimation of mutation rate. Hum. Genet. 84:116–118
Cnossen M. H., Moons K. G. M., Garssen M. P. J., Pasmans N. M. T., de Goede-Bolder A., Niermeijer M. F. and Grobbee D. E. (1998). Neurofibromatosis team of Sophia Children’s Hospital: minor disease features in neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) and their possible value in diagnosis of NF1 in children less than 6 years and clinically suspected of having NF1. J. Med. Genet. 35:624–627
Costa R. M., Federov N. B., Kogan J. H., Murphy G. G., Stern J., Ohno M., Kucherlapati R., Jacks T. and Silva A. J. (2002). Mechanism for the learning deficits in a mouse model of neurofibromatosis type 1. Nature 415:526–530
Costa R. M.,Yang T., Huynh D. P., Pulst S. M.,Viskochil D. H., Silva A. J. and Brannan C. I. (2001). Learning deficits, but normal development and tumor predisposition, in mice lacking exon 23a of Nf1. Nat. Genet. 27:399–405
Costa R. M.and Silva A. J.(2002). Molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the cognitive deficits associated with neurofibromatosis 1. J. Child Neurol. 17(8):622–626
Daston M. M., Scrable H., Nordlund M., Sturbaum A. K., Nissen L. M. and Ratner N. (1992). The protein product of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene is expressed at highest abundance in neurons, Schwann cells, and oligodendrocytes. Neuron 8:41–47
Descheemaeker M. J., Ghesquiere P., Symons H. and Legius E. (2005). Behavioural, academic and neuropsychological profile of normally gifted Neurofibromatosis type 1 children. J. Intellect. Disability Res. 49(Pt1):33–46
Duru-Bellat M., Mons N. and Suchaut B. (2004). Caractéristiques des système éducatifs et compétences des jeunes de 15 ans : L’éclairage des comparaisons entre pays. Cahier de l’IREDU 66: 1–158
Friedman J. M. and Birch P. H. (1997).Type 1 neurofibromatosis: a descriptive analysis of the disorder in 1,728 patients. Am. J. Med. Genet. 70:138–143
Geschwind N. and Galaburda A. M. (1985). Cerebral lateralization: biological mechanisms, associations, and pathology: I. A hypothesis and a program for research. Arch. Neurol. 42:428–459
Hofman K. J., Harris E. L., Bryan R. N. and Denckla M. B. (1994). Neurofibromatosis type 1: the cognitive phenotype. J. Pediatr. 124: S1-S8
Lazaro C., Ravella A., Gaona A., Volpini V. and Estivill X. (1994). Neurofibromatosis type 1 due to germ-line mosaicism in a clinically normal father. N. Engl. J. Med. 331:1403–1407
Müller, W., and Karle, W. (1997). Social selection in Educationnal Systems in Europe, Eur. Sociolo.l Rev. 9(May): 123–156
Müller W. and Shavit Y. (1998). The institutional embedness of the stratification process a comparative study of qualifications and occupations in thirteen countries. In: ShavitY., Müller W. (eds). From School to Work. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Nass R. D. (1993). Sex differences in learning abilities and disabilities. Ann. Dyslexia 43:61—77
Obringer A. C., Meadows A. T. and Zackai E. H. (1989).The diagnosis of neurofibromatosis-1 in the child under the age of 6 years. Am. J. Dis. Child. 143:717–719
Pennington B. F. (1991).Genetics of learning disabilities. Semin Neurol. 11(1):28–34
Rosser T. L. and Packer R. J. (2003). Neurocognitive dysfunction in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 3(2):129–136
Sebold C. D., Lovell A., Hopkin R., Noll R. and Schorry E.(2004). Perception of disease severity in adolescents diagnosed with neurofibromatosis type 1. J. Adolesc. Health. 35(4):297–302
Schrimsher G. W., Billingsley R. L., Slopis J. M. and Moore B. D., III (2003). Visual-spatial performance deficits in children with neurofibromatosis type-1. Am. J. Med. Genet. 120A:326–330
Silva A. J., Frankland P. W., Marowitz Z., Friedman E., Lazlo G., Cioffi D., Jacks T. and Bourtchuladze R.(1997) A mouse model for the learning and memory deficits associated with neurofibromatosis typeI. Nat. Genet. 15:281–284
Stumpf D. A., Alksne J. F., Annegers J. F., Brown S. S., Conneally P. M., Housman D., Leppert M. F., Miller J. P., Moss M. L., Pileggi A. J., Rapin I., Strohman R. C., Swanson L. W. and Zimmerman A. (1988). Neurofibromatosis: conference statement. Arch. Neurol. 45:575–578
Wadsby M., Lindehammar H. and Eeg-Olofsson O. (1989). Neurofibromatosis in childhood: neuropsychological aspects. Neurofibromatosis 2 (5–6):251–260
Wadsworth S. J., Olson R. K., Pennington B. F. and Defries J. C. (2000). Differential genetic etiology of reading disability as a function of IQ. J. Learn. Disab. 33:192–9
Acknowledgments
The study was funded by the association “Neurofibromatoses et Recklinghausen”, 34 Vieux Chemin de Grenade, 31700 Blagnac, France
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coudé, F.X., Mignot, C., Lyonnet, S. et al. Academic Impairment is the Most Frequent Complication of Neurofibromatosis Type-1 (NF1) in Children. Behav Genet 36, 660–664 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-005-9040-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-005-9040-9