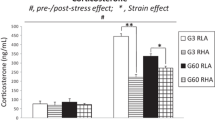
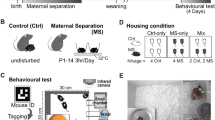
Reciprocal embryo transfers were conducted to examine genetic and maternal effects on the behavior of inbred C3H/HeN and DBA/2J mice, and outbred NMRI mice using a motility-box. The behavioral variables measured were (i) horizontal locomotor activity assessed as the path and time spent during traveling; (ii) vertical activity assessed as the time spent with and numbers of rearings/leanings; (iii) and the time spent in the more anxiogenic central field. The transfer procedure per se resulted in a minor increase in vertical activity of inbred C3H/HeN mice, but had no effect in inbred DBA/2J mice. In contrast, outbred NMRI mice displayed a lower central field activity following embryo transfer indicating a higher anxiety level. Moreover, genetic differences between the mouse strains studied remained stable following embryo transfer for locomotor and vertical activity, but not central field activity depending on the recipient mother strain. Maternal effects were found for (i) vertical activity in the two inbred mouse strains, (ii) all behavioral variables studied in outbred NMRI mice, and (iii) an interaction with gender for the time spent in the anxiogenic central field. An additional fostering procedure revealed that the vertical activity of NMRI mice was modified towards the behavior of the recipient C3H/HeN strain by uterine factors, whereas the postnatal maternal effect of C3H/HeN mothers was the opposite. In summary, the effects of the embryo transfer procedure per se, stability of genetic characteristics following embryo transfer and maternal effects were related to the mouse strains used as donators and recipients, and the behavioral variables studied.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadiyeh N., Churchill G. A., Shimomura K., Solberg L. C., Takahashi J. S., and Redei E. E. (2003). X-linked and lineage-dependent inheritance of coping responses to stress. Mamm. Genome 14:748–757
Akman C., Zhao Q., Liu X., and Holmes G. L. (2004). Effect of food deprivation during early development on cognition and neurogenesis in the rat. Epilepsy Behav. 5:446–454
Alonso S. J., Damas C., and Navarro E. (2000). Behavioral despair in mice after prenatal stress. J. Physiol. Biochem. 56:77–82
Archer J. (1973). Tests for emotionality in rats and mice: a review. Anim. Behav. 21:205–235
Auerbach A. B., Norinsky R., Ho W., Losos K., Guo Q., Chatterjee S., and Joyner A. L. (2003). Strain-dependent differences in the efficiency of transgenic mouse production. Transgenic Res. 12:59–69
Beermann F., Ruppert S., Hummler E., Bosch F. X., Muller G., Ruther U., and Schutz G. (1990). Rescue of the albino phenotype by introduction of a functional tyrosinase gene into mice. EMBO J. 9:2819–2826
Bovet-Nitti F., Oliverio A., and Bovet D. (1968) Effects of cross-fostering on avoidance learning and freezing behavior of DBA2J and C3H/He inbred mice. Life Sci. 7:791–797
Brown R. E., Mathieson W. B., Stapleton J., and Neumann P. E. (1999). Maternal behavior in female C57BL/6J and DBA/2J inbred mice. Physiol. Behav. 67:599–605
Brush F. R., Gendron C. M., and Isaacson M. D. (1999). A selective genetic analysis of the Syracuse high- and low-avoidance (SHA/Bru and SLA/Bru) strains of rats (Rattus norvegicus). Behav. Brain Res. 106:1–11
Calatayud F., and Belzung C. (2001). Emotional reactivity in mice, a case of nongenetic heredity? Physiol. Behav. 74:355–362
Caldji C., Tannenbaum B., Sharma S., Francis D., Plotsky P. M., and Meaney M. J. (1998). Maternal care during infancy regulates the development of neural systems mediating the expression of fearfulness in the rat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:5335–5340
Caldji C., Francis D., and Sharma S. (2000). The effects of early rearing environment on the development of GABAA and central benzodiazepine receptor levels and novelty-induced fearfulness in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 22:219–229
Caldji C., Diorio J., Anisman H. and Meaney M. J. (2004). Maternal behavior regulates benzodiazepine/GABAA receptor subunit expression in brain regions associated with fear in BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1344–1352
Carlier M., Nosten-Bertrand M., and Michard-Vanhée C. (1992). Separating genetic effects from maternal environmental effects. In: Goldowitz D., Wahlsten D., and Wimer R. E. (eds). Techniques for the Genetic Analysis of Brain and Behavior. Elsevier Science Publishers BV, Amsterdam, pp. 111–122
Carlier M., Roubertoux P., and Cohen-Salmon C. (1982). Differences in patterns of pup care in Mus musculus domesticus. I. Comparisons between eleven inbred strains. Behav. Neurol. Biol. 35:205–210
Carrié I., Clément M., DeJavel D., Francès H., and Bourre J. M. (2000). Phospholipid supplementation reverses behavioural and biochemical alterations induced by n-3 polyunsatured fatty acid deficiency in mice. J. Lipid Res. 41:473–480
Champagne F. A., Francis D. D., Mar A., and Meaney M. J. (2003). Variations in maternal care in the rat as a mediating influence for the effects of environment on development. Physiol. Behav. 79:359–371
Commissaris R. L., Harrington G. M., Baginski T. J., and Altman H. J. (1988). MR/Har and MNRA/Har Maudsley rat strains: differences in acoustic startle habituation. Behav. Genet. 18:663–669
Cook M. N., and Bolivar V. J. (2002). Behavioral differences among 129 substrains: implications for knockout and transgenic mice. Behav. Neurosci. 116:600–611
Crabbe J. C., and Phillips T. J. (2003). Mother nature meets mother nurture. Nature Neurosci. 6:440–442
Crawley J. N., Belknap J. K., Collins A., Crabbe J. C., Frankel W., Henderson N., Hitzemann R. J., Maxson S. C., Miner L. L., Silva A. J., Wehner J. M., Wynshaw-Boris A., and Paylor R. (1997). Behavioral phenotypes of inbred mouse strains: implications and recommendations for molecular studies. Psychopharmacology 132:107–124
D’Amato F. R., Cabib S., Ventura R., and Orsini C. (1998). Long-term effects of postnatal manipulation on emotionality are prevented by maternal anxiolytic treatment in mice. Dev. Psychobiol. 32:225–234
Denenberg V. H. (1999). Commentary: Is maternal stimulation the mediator of the handling effect in infancy? Dev. Psychobiol. 34:1–3
Denenberg V. H., Hoplight B. J., and Mobraaten L. E. (1998). The uterine environment enhances cognitive competence. Neuroreport 9:1667–1671
Dulioust E., Toyama K., Busnel M. C., Moutier R., Carlier M., Marchaland C., Ducot B., Roubertoux P., and Auroux M. (1995). Long-term effects of embryo freezing in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92:589–593
Erkadius E., Morgan T. O., and Nicolantonio R. (1996). Full expression of the exaggerated salt appetite of the spontaneously hypertensive rat requires a prenatal factor. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 23:619–620
Falls W. A., Carlson S., Turner J. G., and Willott J. F. (1997). Fear-potentiated startle response in two strains of inbred mice. Behav. Neurosci. 111:855–861
Fernandez-Gonzalez R., Moreira P., Bilbao A., Jimenez A., Perez-Crespo M., Ramirez M. A., Rodriguez De Fonseca F., Pintado B., and Gutierrez-Adan A. (2004). Long-term effect of in vitro culture of mouse embryos with serum on mRNA expression of imprinting genes, development, and behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101:5880–5885
Fernandez-Teruel A., Escorihuela R. M., Gray J. A., Aguilar R., Gil L., Gimenez-Llort L., Tobena A., Bhomra A., Nicod A., Mott R., Driscoll P., Dawson G. R., and Flint J. (2002). A quantitative trait locus influencing anxiety in the laboratory rat. Genome Res. 12:618–626
File S. E. (2001). Factors controlling measures of anxiety and responses to novelty in the mouse. Behav. Brain Res. 125:151–157
Fleming A. S., O’Day D. H., and Kraemer G. W. (1999). Neurobiology of mother-infant interactions: experience and central nervous system plasticity across development and generations. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 23:673–685
Flint J. (2003). Analysis of quantitative trait loci that influence animal behavior. J. Neurobiol. 54:46–77
Fonseca E. S., Massoco C. O., and Palermo-Neto J. (2002). Effects of prenatal stress on stress-induced changes in behavior and macrophage activity of mice. Physiol. Behav. 77:205–215
Foster R. G., Provencio I., Hudson D., Fiske S., De Grip W. and Menaker M. (1991). Circadian photoreception in the retinally degenerate mouse (rd/rd). J. Comp. Physiol. 169: 39–50
Francis D. D., Szegda K., Campbell G., Martin W. D., and Insel T. R. (2003). Epigenetic sources of behavioral differences in mice. Nat. Neurosci. 6:445–446
Fujita O., Annen Y., and Kitaoka A. (1994). Tsukuba highand low-emotional strains of rats (Rattus norvegicus): an overview. Behav. Genet. 24:389–415
Gershenfeld H. K., Neumann P. E., Mathis C., Crawley J. N., Li X., and Paul S. M. (1997). Mapping quantitative trait loci for open-field behavior in mice. Behav. Genet. 27:201–210
Gill K. J., and Boyle A. E. (2005) Quantitative trait loci for novelty/stress-induced locomotor activation in recombinant inbred (RI) and recombinant congenic (RC) strains of mice. Behav. Brain Res. 161:113–124
Goma M., and Tobena A. (1978). Reliability of various measures obtained in open-field test. Psychol. Rep. 43:1123–1128
Gomez-Serrano M., Tonelli L., Listwak S., Sternberg E., and Riley A. L. (2001) Effects of cross fostering on open-field behavior, acoustic startle, lipopolysaccharide-induced corticosterone release, and body weight in Lewis and Fischer rats. Behav. Genet. 31:427–436
Henderson N. D., Turri M. G., DeFries J. C., and Flint J. (2004). QTL analysis of multiple behavioral measures of anxiety in mice. Behav. Genet. 34:267–93
Huot R. L., Thrivikraman K. V., Meaney M. J., and Plotsky P. M. (2001). Development of adult ethanol preference and anxiety as a consequence of neonatal maternal separation in Long Evans rats and reversal with antidepressant treatment. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 158:366–373
Kafkafi N., Benjamini Y., Sakov A., Elmer G. I., and Golani I. (2005). Genotype-environment interactions in mouse behavior: a way out of the problem. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102:4619–4624
Landgraf R., and Wigger A. (2003). Born to be anxious: neuroendocrine and genetic correlates of trait anxiety in HAB rats. Stress 6:111–119
Latham K. E. (1999). Mechanisms and control of embryonic genome activation in mammalian embryos. Int. Rev. Cytol. 193:71–124
LaVail M. M., Matthes M. T., Yasumura D., and Steinberg R. H. (1997). Variability in rate of cone degeneration in the retinal degeneration (rd/rd) mouse. Exp. Eye Res. 65: 45–50
Leppanen P. K., and Ewalds-Kvist S. B. (2005). Crossfostering in mice selectively bred for high and low levels of open-field thigmotaxis. Scand. J. Psychol. 46:21–29
Liu D., Dioro J., Day J. C., Francis D. D., and Meaney M. J. (2000). Maternal care, hippocampal synaptogenesis and cognitive development in rats. Nat. Neurosci. 3:799–806
Liu D., Diorio J., Tannembaum B., Caldji C., Darlene F., Freedman A., Sharma S., Pearson D., Plotsky A., and Meaney M. J. (1997). Maternal care, hippocampal glucocorticoid receptors, and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal responses to stress. Science 277:1659–1662
Luhmann H. J., Huston J. P., and Hasenohrl R. U. (2005). Contralateral increase in thigmotactic scanning following unilateral barrel-cortex lesion in mice. Behav. Brain Res. 157:39–43
Manning C. J., Wakeland E. K., and Potts W. K. (1992). Communal nesting patterns in mice implicate MHC genes in kin recognition. Nature 360:581–583
Markel A. L., Galaktionov Y. K., and Efimov V. M. (1989). Factor analysis of rat behavior in an open field test. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 19:279–286
McCaughran J. A. Jr., Bell J. 3rd, and Hitzemann R. J. (2000). Fear-potentiated startle response in mice: genetic analysis of the C57BL/6J and DBA/2J intercross. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 65:301–312
Mc Laren A., and Michie D. (1956). Studies on the transfer of fertilized mouse eggs to uterine foster mothers. I. Factors affecting the implantation and survival of native and transferred eggs. J. Exp. Biol. 33:394–416
Meier H., Hoag W. G., and McBurney J. J. (1965). Chemical characterization of inbred strain mouse milk. I. Cross composition and amino analysis. J. Nutr. 85:305–309
Meerlo P., Horvath K. M., Nagy G. M., Bohus B., and Koolhaas J. M. (1999). The influence of postnatal handling on adult neuroendocrine and behavioural stress reactivity. J. Neuroendocrinol. 11:925–933
Meyer M. E., and Meyer M. E. (1992) The effects of bilateral and unilateral vibrissotomy on behavior within aquatic and terrestrial environments. Physiol. Behav. 151:877–880
Nagy A., Gerstenstein M., Vintersten K., and Behringer R. (2003). Manipulating the mouse embryo. In: Inglis J. (eds). A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Nagy Z. M., and Misanin J. R. (1970). Visual perception in the retinal degenerate C3H mouse. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 72: 306–310
Nagy Z. M., and McKay C. S. (1972) Development of adult-like open-field behaviors in young retinal-degenerate C3H mice. Dev. Psychobiol. 5:249–258
Paterson A., Whiting P. J., Gray J. A., Flint J., and Dawson G. R. (2001). Lack of consistent behavioural effects of Maudsley reactive and non-reactive rats in a number of animal tests of anxiety and activity. Psychopharmacology 154:336–342
Paylor R., Tracy R., Wehner J., and Rudy J. W. (1994). DBA/2 and C57BL/6J mice differ in contextual fear conditioning but not auditory fear conditioning. Behav. Neurosci. 108:810–817
Pittler S. J., and Baehr W. (1991) Identification of a nonsense mutation in the rod photoreceptor cGMP phosphodiesterase beta-subunit gene of the rd mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:8322–8326
Poley W., and Royce J. R. (1970). Genotype, maternal stimulation, and factors of mouse emotionality. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 71:264–250
Poltyrev T., Keshet G. I., Kay G., and Weinstock M. (1996). Role of experimental conditions in determining differences in exploratory behavior of prenatally stressed rats. Dev. Psychobiol. 29:453–462
Ramos A., Moisan M. P., Chaouloff F., Mormede C., and Mormede P. (1999). Identification of female-specific QTLs affecting an emotionality-related behavior in rats. Mol. Psychiatry 4:453–462
Reading A. J. (1966). Effects of maternal environment on the behavior of inbred mice. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 71:264–250
Ressler R. H. (1962). Parental handling in two strains of mice reared by foster parents. Science 137:129–130
Robinson G. E. (2004). Beyond nature and nuture. Science 304:397–399
Rodgers R.J. (1997). Animal models of “anxiety”: where next? Behav. Pharmacol. 8:477–496
Romeo R. D., Mueller A., Sisti H. M., Ogawa S., McEwen B. S., and Brake W. G. (2003). Anxiety and fear behaviors in adult male and female C57BL/6 mice are modulated by maternal separation. Horm. Behav. 43:561–567
Roubertoux P. L., Nosten-Bertrand M., and Carlier M. (1990). Additive and interactive effects of genotype and maternal environment. Adv. Study Behav. 19:205–247
Schwegler H., Boldyreva M., Linke R., Wu J., Zilles K., and Crusio W. E. (1996). Genetic variation in the morphology of the septo-hippocampal cholinergic and GABAergic systems in mice: II. Morpho-behavioral correlations. Hippocampus 6:535–545
Singer J. B., Hill A. E., Nadeau J. H., and Lander E. S. (2005). Mapping quantitative trait loci for anxiety in chromosome substitution strains of mice. Genetics 169:855–862
Treit D., and Fundytus M. (1988). Thigmotaxis as a test for anxiolytic activity in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 31:959–962
Trullas R., and Skolnick P. (1993). Differences in fear motivated behaviors among inbred mouse strains. Psychopharmacology 111:323–331
Umewaza M., Kogishi K., Tajo H., Yoshimura S., Serin N., Takeda T., and Hosokawa M. (1999). High-linoleate and high-alpha-linoleate diets affect learning ability and natural behaviour in SMAR1 mice. J. Nutr. 129:431–437
Vallée M., Mayo W., Dellu F., Le Moal M., Simon H., and Maccari S. (1997). Prenatal stress induces high anxiety and postnatal handling induces low anxiety in adult offspring: correlation with stress induced corticosterone secretion. J. Neurosci. 17:2626–2636
Wainwright P. E. (2001). The role of nutritional factors in behavioural development in laboratory mice. Behav. Brain Res. 125:75–80
Ward R. (1980). Some effects of strain differences in the maternal behavior of inbred mice. Dev. Psychobiol. 13:181–190
Weaver I. C. G., Cervoni N., Champagne F. A., D’Alessio A. C., Sharma S., Seckl J. R., Dymov S., Szyf M., and Meaney M. J. (2004). Epigenetic programming by maternal behavior. Nat. Neurosci. 7:847–854
Weinstock M. (1997). Does prenatal stress impair coping and regulation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 21:1–13
Wigger A., Loerscher P., Weissenbacher P., Holsboer F., and Landgraf R. (2001). Cross-fostering and cross-breeding of HAB and LAB rats: a genetic rat model of anxiety. Behav. Genet. 31:371–382
Yamazaki K., Beauchamp G. K., Imai Y., and Boyse E. A. (1992). Expression of urinary H-2 odortypes by infant mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:2756–2758
Yamazaki K., Beauchamp G. K., Curran M., Bard J., and Boyse E. A. (2000). Parent-progeny recognition as a function of MHC odortype identity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:10500–10502
Yilmazer-Hanke D. M., Hantsch M., Hanke J., Schulz C., Faber-Zuschratter H., and Schwegler H. (2004). Neonatal thyroxine treatment: changes in the number of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) and neuropeptide Y (NPY) containing neurons and density of tyrosine hydroxylase positive fibers (TH) in the amygdala correlate with anxiety-related behavior of Wistar rats. Neuroscience 124:283–297
Yilmazer-Hanke D. M., Roskoden T., Zilles K., and Schwegler H. (2003). Anxiety-related behavior and densities of glutamate, GABAA, acetylcholine and serotonin receptors in the amygdala of seven inbred mouse strains. Behav. Brain Res. 145:145–159
Yilmazer-Hanke D. M., Faber-Zuschratter H., Linke R., and Schwegler H. (2002). Contribution of amygdala neurons containing peptides and calcium-binding proteins to fear-potentiated startle and exploration-related anxiety in inbred Roman highand low-avoidance rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 15:1206–1218
Young L. J., Winslow J. T., Wang Z., Gingrich B., Guo Q., Matzuk M. M., and Insel T. R. (1997). Gene targeting approaches to neuroendocrinology: oxytocin, maternal behavior, and affiliation. Horm. Behav. 31:221–231
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank Mrs I. Zipress and Mrs. S. Röhl for expert technical assistance. We thank Professor B. Sabel (Institute of Medical Psychology) for using the motility test.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rose, C., Röhl, FW., Schwegler, H. et al. Maternal and Genetic Effects on Anxiety-Related Behavior of C3H/HeN, DBA/2J and NMRI Mice in a Motility-Box Following Blastocyst Transfer. Behav Genet 36, 745–762 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-005-9037-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-005-9037-4