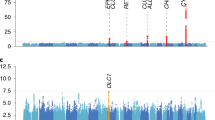
Many twin studies have identified sex differences in the influence of genetic and environmental factors on smoking behaviors. We explore the evidence for sex differences for smoking initiation and cigarette consumption in a sample of Australian twin families, and extend these models to incorporate sex differences in linkage analyses for these traits. We further examine the impact of including or excluding non-smokers in genetic analyses of tobacco consumption. Accounting for sex differences improved linkage results in some instances. We identified one region suggestive of linkage on chromosome 11p12. This locus, as well as another region identified on chromosome 6p12, replicates regions identified in previous studies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abecasis G. R., Cherny S. S., Cookson W. O. and Cardon L. R. (2001). GRR: graphical representation of relationship errors. Bioinformatics 17(8):742–743
Abecasis G. R., Cherny S. S., Cookson W. O. and Cardon L. R. (2002). Merlin – rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat. Genet. 30:97–101
Bierut L. J., Rice J. P., Goate A., Hinrichs A. L., Saccone N. L., Foroud T., Edenberg H. J., Cloninger C. R., Begleiter H., Conneally P. M., Crowe R. R., Hesselbrock V., Li T.-K., Nurngerger J. I., Porjesz B., Schuckit M. A., Reich T. (2004). A genomic scan for habitual smoking in families of alcoholics: common and specific genetic factors in substance dependence. Am. J. Med. Genet. 124A:19–27
Cornes B. K., Medland S. E., Ferreira M. A. R., Morley K. I., Duffy D. L., Heijmans B. T., Montgomery G. W. and Martin N. G. (2005). Sex-limited genome-wide linkage scan for body mass index in an unselected sample of 933 Australian twin families. Twin Res.Hum.Genet. 8(6):616–632
Corrao M. A., Guindon G. E., Cokkinides V. and Sharma N. (2000). Building the evidence base for global tobacco control. Bull. World Health Organ. 78(7):884–890
Cryan J. F., Gasparini F., van Heeke G. and Markou A. (2003). Non-nicotinic neuropharmacological strategies for nicotine dependence: beyond bupropion. Drug Discov. Today 8(22):1025–1034
Duffy D. L. (2002). Sib-pair version 0.99.9 [Computer program]. Queensland Institute of Medical Research, Brisbane, Australia
Duggirala R., Almasy L. and Blangero J. (1999). Smoking behavior is under the influence of a major quantitative trait locus on human chromosome 5q. Genet. Epidemiol. 17(Suppl 1):S139–S144
Duren, W. L., Epstein, M. P., Li, M., and Boehnke, M. (2003). RELPAIR: A Program that Infers the Relationships of Pairs of Individuals Based on Marker Data. Version 2.0.
Eaves L. J., Last K. A., Young P. A. and Martin N. G. (1978). Model-fitting approaches to the analysis of human behaviour. Heredity 41(3):249–320
Epstein M. P., Duren W. L. and Boehnke M. (2000). Improved inference of relationship for pairs of individuals. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 67(5):1219–1213
Ezzati M. and Lopez A. D. (2003). Estimates of global mortality attributable to smoking in 2000. Lancet 362:847–852
Ezzati M. and Lopez A. D. (2004). Regional, disease specific patterns of smoking-attributable mortality in 2000. Tob. Control 13:388–395
Ezzati M., Lopez A. D., Rodgers A., Vander Hoorn S., Murray C. J. L., Comparative Risk Assessment Collaborating Group. (2002). Selected major risk factors and global and regional burden of disease. Lancet 360:1347–1360
Falconer D. S., Mackay T. F. C. (1996). Introduction to Quantitative Genetics. Longman, Essex
Gelernter J., Liu X., Hesselbrock V., Page G.P., Goddard A., and Zhang H. (2004). Results of a genomewide linkage scan: support for chromosomes 9 and 11 loci increasing risk for cigarette smoking. Am. J. Med. Genet. 128B:94–101
George T. P. and O’Malley S. S. (2004). Current pharmacological treatments for nicotine dependence. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 25(1):42–48
Goode E.L., Badzioch M.D., Kim H., Gagnon F., Rozek L.S., Edwards K.L., Jarvik G.P. (2003). Multiple genome-wide analyses of smoking behavior in the Framingham Heart Study. BMC Genet. 4(Suppl 1): S102
Grayson D. A. (1989). Twins reares together: minimizing shared environmental effects. Behav. Genet. 19(4):593–604
Heath A. C., Madden P. A., and Martin N. G. (1998). Statistical methods in genetic research on smoking. Stat. Methods. Med. Res. 7(2):165–186
Heath A. C., and Martin N. G. (1993). Genetic models for the natural history of smoking: evidence for a genetic influence on smoking persistence. Addict. Behav. 18(1):19–34
Heath A. C., and Martin N. G. (1994). Genetic influences on alcohol consumption patterns and problem drinking: results from the Australian NH & MRC twin panel follow-up survey. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 780:72–85
Hettema J. M., Corey L. A., Kendler K. S. (1999). A multivariate genetic analysis of the use of tobacco, alcohol, and caffeine in a population based sample of male and female twins. Drug Alcohol Depend. 57(1):69–78
Hewitt J. K. (1989). Of biases and more in the study of twins reared together: a reply to Grayson. Behav. Genet. 19(4):593–604
Kendler K. S. and Gardner C. O. Jr. (1998). Twin studies of adult psychiatric and substance dependence disorders: are they biased by differences in the environmental experiences of monozygotic and dizygotic twins in childhood and adolescence? Psychol. Med. 28(3):625–633
Kendler K.S., Neale M.C., Sullivan P., Corey L.A., Gardner C.O. and Prescott C.A. (1999). A population-based twin study in women of smoking initiation and nicotine dependence. Psychol. Med. 29(2):299–308
Kendler K. S., Thornton L. M., and Pedersen N. L. (2000). Tobacco consumption in Swedish twins reared apart and reared together. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 57(9):886–892
Kirk K. M., Birley A. J., Statham D. J., Haddon B., Lake R. I. E., Andrews J. G. and Martin N. G. (2000). Anxiety and depression in twin and sib pairs extremely discordant and concordant for neuroticism: prodromus to a linkage study. Twin Res. 3:299–309
Koeppen-Schomerus G., Spinath F. M. and Plomin R. (2003). Twins and non-twin siblings: different estimates of shared environmental influence in early childhood. Twin Res. 6(2):97–105
Kong X., Murphy K., Raj T., He C., White P. S. and Matise T. C. (2004). A combined linkage-physical map of the human genome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 75(6):1143–1148
Koopmans J. R., Slutske W. S., Heath A. C., Neale M. C. and Boomsma D. I. (1999). The genetics of smoking initiation and quantity smoked in Dutch adolescent and young adult twins. Behav. Genet. 29(6):383–393
Kruglyak L., Daly M. J., Reeve-Daly M. P., Lander E. S. (1996). Parametric and nonparametric linkage analysis: a unified multipoint approach. Am. J. Hum. Genet 58(6): 1347–1363
Lake R. I., Eaves L. J., Maes H. H., Heath A. C. and Martin N. G. (2000). Further evidence against the environmental transmission of individual differences in neuroticism from a collaborative study of 45,850 twins and relatives on two continents. Behav. Genet. 30(3): 223–233
Lander E. and Kruglyak L. (1995). Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nat. Genet. 11: 241–247
Lange K., Weeks D. and Boehnke M. (1988). Programs for pedigree analysis: MENDEL, FISHER, and dGENE. Genet. Epidemiol. 5(6): 471–472
Li M. D., Cheng R., Ma J. Z., Swan G. E. (2003a). A meta-analysis of estimated genetic and environmental effects on smoking behavior in male and female adult twins. Addiction 98(1): 23–31
Li M. D., Ma J. Z., Cheng R., Dupont R. T., Williams N. J., Crews K. M., Payne T. J., and Elston R. C. (2003b). A genome-wide scan to identify loci for smoking rate in the Framingham Heart Study population. BMC Genet. 4(Suppl 1): S103
Madden P. A., Heath A. C., Pedersen N. L., Kaprio J., Koskenvuo M. J., and Martin N. G. (1999). The genetics of smoking persistence in men and women: a multicultural study. Behav. Genet. 29(6):423–431
Madden P. A., Pedersen N. L., Kaprio J., Koskenvuo M. J. and Martin N. G. (2004). The epidemiology and genetics of smoking initiation and persistence: crosscultural comparisons of twin study results. Twin Res. 7(1):82–97
Maes H. H., Sullivan P. F., Bulik C. M., Neale M. C., Prescott C. A., Eaves L. J. and Kendler K. S. (2004). A twin study of genetic and environmental influences on tobacco initiation, regular tobacco use and nicotine dependence. Psychol. Med. 34:1–11
Medland S. E. (2004). Alternate parameterization for scalar and non-scalar sex-limitation models in Mx. Twin Res. 7(3):299–305
Medland S.E. (2005). Parameterization of sex-limited autosomal linkage analysis for Mx. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 8(6): 569–573
Munafo M. R., Clark T. G., Johnstone E. C., Murphy M. F. G., and Walton R. T. (2004). The genetic basis for smoking behavior: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nicotine Tob. Res. 6(4): 583–597
Neale M. C. (1998). Twin analysis. In: Armitage P., Colton T. (eds) Encyclopedia of Biostatistics. Wiley, Chinchester, New York, pp. 4613–4626
Neale, M. C., Boker, S. M., Xie, G., and Maes, H. H. (2003). Mx: Statistical Modeling. VCU Box 900126, (6th Ed.), Richmond, VA 23298: Department of Psychiatry
Neale M. C., Cardon L. R. (1992). Methodology for Genetic Studies of Twins and Families. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Boston, London
Neale M. C., Walters E. E., Eaves L. J., Maes H. H., and Kendler K. S. (1994). Multivariate genetic analysis of twin-family data on fears: Mx models. Behav. Genet. 24(2): 119–139
Posthuma D., Beem A. L., de Geus E. J. C., van Baal G. C. M., von Hjelmborg J. B., Iachine I. and Boomsma D. I. (2003). Theory and practice in quantitative genetics. Twin Res. 6(5): 361–376
Posthuma D. and Boomsma D. I. (2000). A note on the statistical power in extended twin designs. Behav. Genet. 30: 147–158
Saccone N. L., Neuman R. J., Saccone S. F., and Rice J. P. (2003). Genetic analysis of maximum cigarette-use phenotypes. BMC Genet. 4(Suppl 1): S105
Sham P. (1998). Statistics in Human Genetics. Arnold, London
Straub R. E., Sullivan P. F., Ma Y., Myakishev M. V., Harris-Kerr C., Wormley B., Kadambi B., Sadek H., Silverman M. A., Webb B. T., Neale M. C., Bulik C. M., Joyce P. R. and Kendler K. S. (1999). Susceptibility genes for nicotine dependence: a genome scan and followup in an independent sample suggest that regions on chromosomes 2, 4, 10, 16, 17 and 18 merit further study. Mol. Psychiatry 4(2): 129–144
Sullivan, P. F., and Kendler, K. S. (1999). The genetic epidemiology of smoking. Nicotine Tob. Res. 1 Suppl 2: S51–S57; discussion S69–70
Sullivan P. F., Neale B. M., van den Oord E., Miles M. F., Neale M. C., Bulik C. M., Joyce P. R., Straub R. E., and Kendler K. S. (2004). Candidate genes for nicotine dependence via linkage, epistasis, and bioinformatics. Am. J. Med. Genet. 126(1): 23–36
Vink J. M., Beem A. L., Posthuma D., Neale M. C., Willemsen G., Kendler K. S., Slagboom P. E. and Boomsma D. I. (2004). Linkage analysis of smoking initiation and quantity in Dutch sibling pairs. Pharmacogenomics J. 4(4): 274–282
Acknowledgments
We thank the twins and their families for their participation in the various studies. We acknowledge the funding sources that supported this project, and earlier studies that collected the genotype and phenotype data used: NIH grants (DA00272, DA12854, DA12540, CA75581, AA07535, and AA07728), Australian NH & NRC grants (971232 and 941177), Gemini Genomics, the former Sequana Therapeutics, the Mammalian Genotyping Service at the Center for Medical Genetics, and Leiden University Medical School. K.I.M. is supported by an Ian Scott Fellowship from the Australian Rotary Health Research Fund.
We also acknowledge the help and support provided by the many individuals at the Queensland Institute of Medical Research who worked on developing the combined dataset analyzed here: Anjali Henders and the blood processing team; Megan Campbell and the DNA processing team; Dixie Statham and the phenotype collection team; and Scott Gordon, Harry Beeby, David Smyth and Olivia Zheng for data integrity work. We would also thank Wayne D. Hall and Susan A. Treloar for helpful advice and comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morley, K.I., Medland, S.E., Ferreira, M.A. et al. A Possible Smoking Susceptibility Locus on Chromosome 11p12: Evidence from Sex-limitation Linkage Analyses in a Sample of Australian Twin Families. Behav Genet 36, 87–99 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-005-9004-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-005-9004-0