Abstract
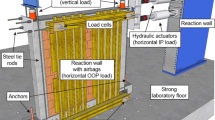
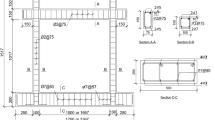
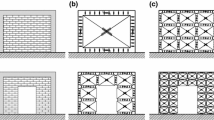
It is generally known that reinforced concrete frame structures with unreinforced masonry infills frequently suffer severe damage when subjected to earthquake loading. Recent earthquakes show that the damage occurs to both older buildings and new seismically designed buildings. This is somehow surprising as this construction type has been the subject of intensive research projects for decades and simplified verification concepts are available in standards. However, these concepts are based on the separate verification of in-plane and out-of-plane loading although the importance of the design for combined loading conditions is already known. This situation was the reason to perform comprehensive investigations of the seismic behaviour of this traditional construction type for separate and combined in-plane and out-of-plane loading within the framework of the collaborative European research project INSYSME (Innovative systems for earthquake resistant masonry buildings in reinforced concrete buildings). These investigations are helpful to develop innovative approaches to improve the seismic behaviour of infilled frames. This article presents the fundamental project results of experimental investigations on reinforced concrete frames filled with high thermal insulating clay bricks under separate, sequential and combined in- and out-of-plane loading. The test results clearly illustrate that the load-bearing capacity severely depends on the boundary conditions in the connection area between the infill and the frame.































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhoundi F, Vasconcelos G, Lourenco P, Silva L (2016) Out-of-plane response of masonry infilled RC frames: effect of workmanship and opening. In: 16th international brick and block masonry conference, Pádua, Italy
Al-Chaar G, Issa M, Sweeney S (2002) Behavior of masonry-infilled nonductile reinforced concrete frames. J Struct Eng 128(8):1055–1063
Angel R, Abrams D, Shapiro D, Uzarski J, Webster M (1994) Behavior of reinforced concrete frames with masonry infills. Civil Engineering Studies, Structural Research Series No. 589, UILU-ENG-94-2005, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign
Anil Ö, Altin S (2007) An experimental study on reinforced concrete partially infilled frames. Eng Struct 29(3):449–460
ASCE/SEI 41-06 (2007) Seismic rehabilitation of existing buildings
Asteris PG, Cavaleri L, Di Trapani F, Tsaris AK (2017) Numerical modelling of out-of-plane response of infilled frames: state of the art and future challenges for the equivalent strut macromodels. Eng Struct 132:110–122
Blasi G, De Luca F, Aiello MA (2018) Brittle failure in RC masonry infilled frames: the role of infill overstrength. Eng Struct 177:506–518
Brodsky A, Rabinovitch O, Yankelevsky DZ (2018) Determination of the interaction between a masonry wall and a confining frame. Eng Struct 167:214–226
Calvi GM, Bolognini D (2001) Seismic response of reinforced concrete frames infilled with weakly reinforced masonry panels. J Earthq Eng 5:153–185
Calvi GM, Bolognini D, Penna A (2004) Seismic performance of masonry-infilled RC frames: benefits of slight reinforcements, Sísmica 2004 - 6o Congresso Nacional de Sismologia e Engenharia Sísmica, Lisboa
Crisafulli FJ (1997). Seismic behaviour of reinforced concrete structures with masonry infills. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand
CSA S304.1-04 (2004) Design of masonry Structures S304.1-04. Canadian Standards Association, 5060 Spectrum Way, Suite 100, Ontario, Canada
da Porto F, Guidi G, Dalla Benetta M, Verlato N (2013) Combined in-plane/out-of-plane experimental behaviour of reinforced and strengthened infill masonry walls. In: Proceedings of the 12th Canadian masonry symposium, Vancouver, British Columbia
Dafnis A, Kolsch H, Reimerdes H (2002) Arching in masonry walls subjected to earthquake motions. J Struct Eng ASCE 128(2):153–159
Dawe JL, Seah CK (1989) Out-of-plane resistance of concrete masonry infilled panels. Can J Civ Eng 16(6):854–864
Dazio A, Beyer K, Braune F, Fritsche S, Mittaz X (2009) Das Mw = 6.3 Erdbeben von L’Aquila am 6. April 2009. Report of SGEB-Erkundungsmissionvom, 15-18
De Luca F, Verderame GM, Gómez-Martínez F, Pérez-García A (2014) The structural role played by masonry infills on RC building performances after the 2011 Lorca, Spain, earthquake. Bull Earthq Eng 12(5):1999–2026
DIN EN 1015, Teile 3, 7, 11, Prüfverfahren für Mörtel für Mauerwerk, Deutsche Fassungen EN 772, Teil 3 – Mai 2007
DIN EN 1052, Teile 1, 2, 3, 5: Prüfverfahren für Mauerwerk, Deutsche Fassung EN 1052-2, Teil 1 – Dezember 1998
DIN EN 1992-1-1 (2011) Eurocode 2: Bemessung und Konstruktion von Stahlbeton- und Spann-betontragwerken – Teil 1-1: Allgemeine Bemessungsregeln und Regeln für den Hochbau; Deutsche Fassung EN 1992-1-1:2004 + AC:2010
DIN EN 1998-1 (2010) Eurocode 8: Auslegung von Bauwerken gegen Erdbeben – Teil 1: Grundlagen, Erdbebeneinwirkungen und Regeln für Hochbauten; Deutsche Fassung EN 1998-1:2004 + AC:2009
DIN EN 772, Teile 1-21: Prüfverfahren für Mauersteine, Deutsche Fassungen EN 772, Teil 1 – Mai 2016
El-Dakhakhni WW, Elgaaly M, Hamid AA (2003) Three-strut model for concrete masonry-infilled steel frames. J Struct Eng 129(2):177–185
Fardis MN, Panagiotakos TB (1997) Seismic design and response of bare and masonry-infilled reinforced concrete buildings part II: infilled structures. J Earthq Eng 1(03):475–503
Fehling E, Ismail M, Samaan S, Meyer U (2015) Flexural tensile tests with vertically perforated clay unit masonry with thin layer mortar/Biegezugversuche an Planziegelmauerwerk. Mauerwerk 19(5):355–362
Fehling E, Ismail M, Meyer U, Samaan S (2016) Flexural strength of vertically perforated thermal insulating clay unit masonry. In: Proceedings of the 16th international brick and block masonry conference, Padova, Italy, 26–30 June 2016
Flanagan RD, Bennett RM (1999) Bidirectional behavior of structural clay tile infilled frames. J Struct Eng 125(3):236–244
Furtado A, Rodrigues H, Arêde A (2015) Modelling of masonry infill walls participation in the seismic behaviour of RC buildings using OpenSees. Int J Adv Struct Eng (IJASE) 7(2):117–127
Furtado A, Rodrigues H, Arêde A, Varum H (2016) Experimental evaluation of out-of-plane capacity of masonry infill walls. Eng Struct 111:48–63
Hak S, Morandi P, Magenes G (2017) Prediction of inter-storey drifts for regular RC structures with masonry infills based on bare frame modelling. Bull Earthq Eng 16(1):397–425
Hashemi A, Mosalam KM (2007) Seismic evaluation of reinforced concrete buildings including effects of masonry infill walls, Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center, University of California, Berkeley, PEER, Report 2007/100
Hendry A (1981) Structural brickwork. Macmillan, London
INSYSME (2017) Internal report D5.3. Technical report with the experimental results on masonry enclosures
Kadysiewski S, Mosalam KM (2009). Modeling of unreinforced masonry infill walls considering in-plane and out-of-plane interaction, Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center, PEER Report 2008/102, University of California, Berkley
Komaraneni S, Rai DC, Singhal V (2011) Seismic behavior of framed masonry panels with prior damage when subjected to out-of-plane loading. Earthq Spectra 27(4):1077–1103
Kubalski T, Butenweg C, Marinković M, Klinkel S (2017) Investigation of the seismic behaviour of infill masonry using numerical modelling approaches. In: 16th world conference on earthquake engineering, Santiago, Chile
Manfredi V, Masi A (2014) Combining in-plane and out-of-plane behaviour of masonry infills in the seismic analysis of RC buildings. Earthq Struct 6(5):515–537
Manfredi G, Prota A, Verderame GM, De Luca F, Ricci P (2014) 2012 Emilia earthquake, Italy: reinforced concrete buildings response. Bull Earthq Eng 12(5):2275–2298
Marinković M, Butenweg C (2018) Innovative system for earthquake resistant masonry infill walls. In: 16th European conference on earthquake engineering, Thessaloniki, Greece
Masi A (2003) Seismic vulnerability assessment of gravity load designed R/C frames. Bull Earthq Eng 1(3):371–395
McDowell EL, McKee KE, Sevin E (1956) Arching action theory of masonry walls. J Struct Div 82(ST2):9151–91518
Mehrabi AB, Benson Shing P, Schuller MP, Noland JL (1996) Experimental evaluation of masonry-infilled RC frames. J Struct Eng 122(3):228–237
Milanesi RR, Morandi P, Magenes G (2018) Local effects on RC frames induced by AAC masonry infills through FEM simulation of in-plane tests. Bull Earthq Eng 16:4053–4080
Morandi P, Hak S, Magenes G (2018a) Performance-based interpretation of in-plane cyclic tests on RC frames with strong masonry infills. Eng Struct 156:503–521
Morandi P, Milanesi RR, Magenes G (2018b) Innovative solution for seismic-resistant masonry infills with sliding joints: in-plane experimental performance. Eng Struct 176:719–733
Paulay T, Priestley MJN (1992) Seismic design of reinforced concrete and masonry buildings. Wiley, New York
Pereira MP, Pereira MN, Ferreira JD, Lourenço P (2012) Behavior of damaged masonry infill panels in RC frames subjected to out of plane loads. Archit Civ Eng Environ 5(3):83–98
Rai DC, Komaraneni S, Singhal V (2009) Out-of-plane seismic behaviour of brick masonry infilled panels with prior in-plane damage. In: Proceedings of 11th Canadian Masonry symposium, Toronto, Ontario, May 31–June 3, 2009, Paper No. 239
Ricci P, Di Domenico M, Verderame GM (2018) Experimental assessment of the in-plane/out-of-plane interaction in unreinforced masonry infill walls. Eng Struct 173:960–978
Stafford Smith B, Carter C (1969) A method of analysis for infilled frames. Proc Inst Civ Eng 44(1):31–48
Stylianidis KC (2012) Experimental investigation of masonry infilled RC frames. Open Constr Build Technol J 6(1):194–212
Verderame GM, De Luca F, Ricci P, Manfredi G (2011) Preliminary analysis of a soft-storey mechanism after the 2009 L’Aquila earthquake. Earthq Eng Struct Dyn 40:925–944
Vougioukas E (2012) Out-of-plane response of infill masonry walls. Open Constr Build Technol J 6(Suppl 1-M20):325–333
Walsh KQ, Dizhur DY, Giongo I, Derakhshan H, Ingham JM (2017) Effect of boundary conditions and other factors on URM wall out-of-plane behaviour: design demands, predicted capacity, and in situ proof test results. SESOC J 30(1):57
Yuen TY, Kuang JS, Ali BSM (2016) Assessing the effect of bi-directional loading on nonlinear static and dynamic behaviour of masonry-infilled frames with openings. Bull Earthq Eng 14(6):1721–1755
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the “Arbeitsgemeinschaft Mauerziegel im Bundesverband der Deutschen Ziegelindustrie e.V” and express their special thanks to Dr. Udo Meyer for his valuable suggestions and support during the execution of the European project INSYSME. Furthermore we would like to thank Prof. Ekkehard Fehling, Dr. Thomas Hahn and M.Sc. Thomas Pfetzing from Kassel University for the execution of the experimental tests, discussions and excellent cooperation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butenweg, C., Marinković, M. & Salatić, R. Experimental results of reinforced concrete frames with masonry infills under combined quasi-static in-plane and out-of-plane seismic loading. Bull Earthquake Eng 17, 3397–3422 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-019-00602-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-019-00602-7