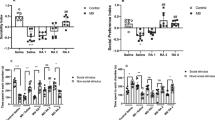
We studied the effect of inducible NO synthase (iNOS) inhibitor aminoguanidine on the behavioral effects of chronic perinatal caffeine exposure. Administration of caffeine in the prenatal and early postnatal periods led to the development of anxiolytic, stimulating, and analgesic effects. Administration of aminoguanidine attenuated the anxiolytic and stimulating effects and potentiated the analgesic effect of perinatal administration of caffeine. Chronic perinatal administration of caffeine leads to significant changes in the level of anxiety, motor activity, and pain sensitivity, and inhibition of iNOS has a pronounced multidirectional effect on these effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang Y, Hong F, Yang S. Roles of nitric oxide in brain ischemia and reperfusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022;23(8):4243. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084243
Banach M, Piskorska B, Czuczwar SJ, Borowicz KK. Nitric oxide, epileptic seizures, and action of antiepileptic drugs. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets. 2011;10(7):808-819. doi: https://doi.org/10.2174/187152711798072347
Bashkatova V. Metabotropic glutamate receptors and nitric oxide in dopaminergic neurotoxicity. World J. Psychiatry. 2021;11(10):830-840. doi: https://doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v11.i10.830
Medeiros KAAL, Almeida-Souza TH, Silva RS, Santos HF, Santos EV, Gois AM, Leal PC, Santos JR. Involvement of nitric oxide in the neurobiology of fear-like behavior. Nitric Oxide. 2022;124:24-31. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2022.04.003
Pałasz A, Menezes IC, Worthington JJ. The role of brain gaseous neurotransmitters in anxiety. Pharmacol. Rep. 2021;73(2):357-371. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-021-00242-2
Omar NM, Hussein AM, Malek HA, Saad MA, Saleh DM. Influence of age on pain sensitivity in response to paw pressure and formalin injection in rats: a role of nitric oxide. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2012;31(2):185-194. doi: https://doi.org/10.4149/gpb_2012_023
Kraus MM, Bashkatova V, Vanin A, Philippu A, Prast H. Dizocilpine inhibits amphetamine-induced formation of nitric oxide and amphetamine-induced release of amino acids and acetylcholine in the rat brain. Neurochem. Res. 2002;27(3):229-235. doi: https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1014836621717
Schiavone S, Neri M, Maffione AB, Frisoni P, Morgese MG, Trabace L, Turillazzi E. Increased iNOS and nitrosative stress in dopaminergic neurons of MDMA-exposed rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20(5):1242. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051242
Bashkatova VG, Alekseeva EV, Nazarova GA, Sudakov SK. Effect of nitric oxide synthase inhibitor on the learning and spatial memory in rats subjected to long-term perinatal administration of caffeine. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2022;173(1):21-23. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-022-05484-5
Kayir H, Uzbay IT. Evidence for the role of nitric oxide in caffeine-induced locomotor activity in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2004;172(1):11-15. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1625-5
Kimura M, Ushijima I, Hiraki M, Kimura M, Ono N. Enhancement of caffeine-induced locomotor hyperactivity produced by the combination with L-arginine or taurine in mice: Possible involvement of nitric oxide. Methods Find Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009;31(9):585-589. doi: https://doi.org/10.1358/mf.2009.31.9.1435462
Li Q, Song W, Tian Z, Wang P. Aminoguanidine alleviated MMA-induced impairment of cognitive ability in rats by downregulating oxidative stress and inflammatory reaction. Neurotoxicology. 2017;59:121-130. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2017.02.005
Bondarenko DA, D’yachenko IA, Skobtsov DI, Murashev AN. In vivo models for studying the analgesic activity. Biomeditsina. 2011;(2):84-94. Russian.
Ramos AC, de Mattos Hungria F, Camerini BA, Suiama MA, Calzavara MB. Potential beneficial effects of caffeine administration in the neonatal period of an animal model of schizophrenia. Behav. Brain Res. 2020; 391:112674. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2020.112674
Björklund O, Kahlström J, Salmi P, Fredholm BB. Perinatal caffeine, acting on maternal adenosine A(1) receptors, causes long-lasting behavioral changes in mouse offspring. PLoS One. 2008;3(12):e3977. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0003977
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 175, No. 6, pp. 730-733, June, 2023
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bashkatova, V.G., Bogdanova, N.G., Nazarova, G.A. et al. Influence of a Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor on the Anxiolytic, Stimulating, and Analgesic Effects of Long-Term Perinatal Caffeine Exposure in Rats. Bull Exp Biol Med 175, 774–776 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-023-05944-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-023-05944-6