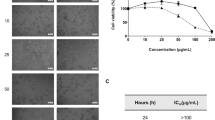
We studied the effect of dehydrocostus lactone (DHL) on the biological characteristics of HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. The inhibition of cell viability by different concentrations of DHL (10, 20, 40, 80, and 160 μmol/liter) was measured using MTT test. As the determined half-maximum inhibitory concentration (IC50) was 20.33 μmol/liter, DHL in a concentration of 20 μmol/liter was used in further experiments. Cell proliferation, migration, invasion ability, and apoptosis were assessed by Ki-67 immunofluorescence, Transwell assay, and TUNEL analysis. The level of p-AKT protein was determined by Western blotting. DHL significantly inhibited the viability, proliferation, migration, and invasion of HepG2 cells in comparison with the control group, and induced cells apoptosis. DHL down-regulated the expression of p-AKT protein in the HepG2 cells in comparison with the control group. PI3K/AKT signaling pathway activator 740Y-P could block the above-mentioned effects of DHL. Thus, DHL inhibits the malignancy of HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells via down-regulation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fan Y, Guan W, Huang R, Lin SY, Song Y, Lu S, Kang L, Yang Q, Lang J, Zhang P. Clinical characteristics and survival outcomes of ascending, descending and mixed types of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in the non-endemic areas of China: A propensity score matching analysis. Cancer Med. 2020;9(24):9315-9325. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.3537
Fernández-Barrena MG, Arechederra M, Colyn L, Berasain C, Avila MA. Epigenetics in hepatocellular carcinoma development and therapy: The tip of the iceberg. JHEP Rep. 2020;2(6):100167. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhepr.2020.100167
Yang JD, Heimbach JK. New advances in the diagnosis and management of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMJ. 2020;371:m3544. doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m3544
Trevisan França de Lima L, Broszczak D, Zhang X, Bridle K, Crawford D, Punyadeera C. The use of minimally invasive biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer. 2020;1874(2):188451. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188451
Bodzin AS, Lunsford KE, Markovic D, Harlander-Locke MP, Busuttil RW, Agopian VG. Predicting Mortality in Patients Developing Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Liver Transplantation: Impact of Treatment Modality and Recurrence Characteristics. Ann Surg. 2017;266(1):118-125. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000001894
Lin X, Peng Z, Su C. Potential anti-cancer activities and mechanisms of costunolide and dehydrocostuslactone. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015;16(5):10888-10906. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160510888
Zheng H, Chen Y, Zhang J, Wang L, Jin Z, Huang H, Man S, Gao W. Evaluation of protective effects of costunolide and dehydrocostuslactone on ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in mice based on multi-pathway regulation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016;250:68-77. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2016.03.003
Lee HK, Song HE, Lee HB, Kim CS, Koketsu M, Ngan LT, Ahn YJ. Growth inhibitory, bactericidal, and morphostructural effects of dehydrocostus lactone from Magnolia sieboldii Leaves on antibiotic-susceptible and -resistant strains of Helicobacter pylori. PLoS One. 2014;9(4):e95530. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0095530
Park EJ, Park SW, Kim HJ, Kwak JH, Lee DU, Chang KC. Dehydrocostuslactone inhibits LPS-induced inflammation by p38MAPK-dependent induction of hemeoxygenase-1 in vitro and improves survival of mice in CLP-induced sepsis in vivo. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014;22(2):332-340. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2014.07.012
Zhao Q, Chen A, Wang X, Zhang Z, Zhao Y, Huang Y, Ren S, Zhu Y. Protective effects of dehydrocostuslactone on rat hippocampal slice injury induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018;42(2):1190-1198. doi: https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3691
Hung JY, Hsu YL, Ni WC, Tsai YM, Yang CJ, Kuo PL, Huang MS. Oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling are involved in dehydrocostuslactone-mediated apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer. 2010;68(3):355-365. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2009.07.017
Zhang R, Hao J, Wu Q, Guo K, Wang C, Zhang WK, Liu W, Wang Q, Yang X. Dehydrocostus lactone inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by PI3K/Akt/Bad and ERS signalling pathway in human laryngeal carcinoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020;24(11):6028-6042. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15131
Hoxhaj G, Manning BD. The PI3K-AKT network at the interface of oncogenic signalling and cancer metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2020;20(2):74-88. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-019-0216-7
Wang J, Wang W, Cai H, Du B, Zhang L, Ma W, Hu Y, Feng S, Miao G. MACC1 facilitates chemoresistance and cancer stem cell-like properties of colon cancer cells through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017;16(6):8747-8754. doi: https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.7721
Noorolyai S, Shajari N, Baghbani E, Sadreddini S, Baradaran B. The relation between PI3K/AKT signalling pathway and cancer. Gene. 2019;698:120-128. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2019.02.076
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 174, No. 9, pp. 350-355, September, 2022
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, W., Zhao, H., Yuan, H. et al. Dehydrocostus Lactone Reduced Malignancy of HepG2 Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells via Down-Regulation of the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Bull Exp Biol Med 174, 360–364 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-023-05708-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-023-05708-2