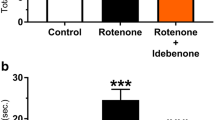
A comprehensive study of the functioning of antioxidant system in rats with rotenone-induced parkinsonism was conducted. The development of pathology led to inhibition of the majority of the studied antioxidant enzymes in the brain and blood serum of animals, which can be associated with decompensation of oxidative stress under conditions of prolonged mitochondrial dysfunction. These changes apparently make an important contribution into neuronal degeneration in the cerebral cortex and striatum and motor disorders in experimental animals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
19 November 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-021-05342-w
References
Ablat N, Lv D, Ren R, Xiaokaiti Y, Ma X, Zhao X, Sun Y, Lei H, Xu J, Ma Y, Qi X, Ye M, Xu F, Han H, Pu X. Neuroprotective effects of a standardized flavonoid extract from safflower against a rotenone-induced rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Molecules. 2016;21(9):1107. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21091107
Ball N, Teo WP, Chandra S, Chapman J. Parkinson’s disease and the environment. Front. Neurol. 2019;10:218. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.00218
Blauwendraat C, Nalls MA, Singleton AB. The genetic architecture of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19(2):170-178. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30287-X
Gökçe Çokal B, Yurtdaş M, Keskin Güler S, Güneş HN, Ataç Uçar C, Aytaç B, Durak ZE, Yoldaş TK, Durak İ, Çubukçu HC. Serum glutathione peroxidase, xanthine oxidase, and superoxide dismutase activities and malondialdehyde levels in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurol. Sci. 2017;38(3):425-431. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-016-2782-8
Góth L. A simple method for determination of serum catalase activity and revision of reference range. Clin. Chim. Acta. 1991;196(2-3):143-151. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-8981(91)90067-m
Greenamyre JT, Cannon JR, Drolet R, Mastroberardino PG. Lessons from the rotenone model of Parkinson’s disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2010;31(4):141-142; author reply 142-3. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2009.12.006
Guo JD, Zhao X, Li Y, Li GR, Liu XL. Damage to dopaminergic neurons by oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018;41(4):1817-1825. doi: https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3406
Kryl’skii ED, Popova TN, Safonova OA, Stolyarova AO, Razuvaev GA, de Carvalho MAP. Transcriptional regulation of antioxidant enzymes activity and modulation of oxidative stress by melatonin in rats under cerebral ischemia/reperfusion conditions. Neuroscience. 2019;406:653-666. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.01.046
Kujawska M, Jourdes M, Kurpik M, Szulc M, Szaefer H, Chmielarz P, Kreiner G, Krajka-Kuźniak V, Mikołajczak PŁ, Teissedre PL, Jodynis-Liebert J. Neuroprotective effects of pomegranate juice against Parkinson’s disease and presence of ellagitannins-derived metabolite-urolithin A-in the brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;21(1):202. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010202
Piskarev IM, Trofimova SV, Burkhina OE, Ivanova IP. Investigation of free radical processes in substrates and biological samples by means of induced chemiluminescence. Biofizika. 2015;60(3):496-505.
Sarbishegi M, Charkhat Gorgich EA, Khajavi O, Komeili G, Salimi S. The neuroprotective effects of hydro-alcoholic extract of olive (Olea europaea L.) leaf on rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease in rat. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018;33(1):79-88. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-0131-0.
Sharma A, Kaur P, Kumar B, Prabhakar S, Gill KD. Plasma lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status of Parkinson’s disease patients in the Indian population. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2008;14(1):52-57. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2007.06.009
Wei Z, Li X, Li X, Liu Q, Cheng Y. Oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018;11:236. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2018.00236
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 171, No. 6, pp. 701-707, June, 2021
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kryl’skii, E.D., Razuvaev, G.A., Potapova, T.N. et al. Functioning of the Antioxidant Defense System in Rotenone-Induced Parkinson’s Disease. Bull Exp Biol Med 171, 716–721 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-021-05302-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-021-05302-4